Description
The idea is to implement the SUSE Observability Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server as a specialized, middle-tier API designed to translate the complex, high-cardinality observability data from StackState (topology, metrics, and events) into highly structured, contextually rich, and LLM-ready snippets.
This MCP Server abstract the StackState APIs. Its primary function is to serve as a Tool/Function Calling target for AI agents. When an AI receives an alert or a user query (e.g., "What caused the outage?"), the AI calls an MCP Server endpoint. The server then fetches the relevant operational facts, summarizes them, normalizes technical identifiers (like URNs and raw metric names) into natural language concepts, and returns a concise JSON or YAML payload. This payload is then injected directly into the LLM's prompt, ensuring the final diagnosis or action is grounded in real-time, accurate SUSE Observability data, effectively minimizing hallucinations.
Goals
- Grounding AI Responses: Ensure that all AI diagnoses, root cause analyses, and action recommendations are strictly based on verifiable, real-time data retrieved from the SUSE Observability StackState platform.
- Simplifying Data Access: Abstract the complexity of StackState's native APIs (e.g., Time Travel, 4T Data Model) into simple, semantic functions that can be easily invoked by LLM tool-calling mechanisms.
- Data Normalization: Convert complex, technical identifiers (like component URNs, raw metric names, and proprietary health states) into standardized, natural language terms that an LLM can easily reason over.
- Enabling Automated Remediation: Define clear, action-oriented MCP endpoints (e.g., execute_runbook) that allow the AI agent to initiate automated operational workflows (e.g., restarts, scaling) after a diagnosis, closing the loop on observability.
Hackweek STEP
- Create a functional MCP endpoint exposing one (or more) tool(s) to answer queries like "What is the health of service X?") by fetching, normalizing, and returning live StackState data in an LLM-ready format.
Scope
- Implement read-only MCP server that can:
- Connect to a live SUSE Observability instance and authenticate (with API token)
- Use tools to fetch data for a specific component URN (e.g., current health state, metrics, possibly topology neighbors, ...).
- Normalize response fields (e.g., URN to "Service Name," health state DEVIATING to "Unhealthy", raw metrics).
- Return the data as a structured JSON payload compliant with the MCP specification.
Deliverables
- MCP Server v0.1 A running Golang MCP server with at least one tool.
- A README.md and a test script (e.g., curl commands or a simple notebook) showing how an AI agent would call the endpoint and the resulting JSON payload.
Outcome A functional and testable API endpoint that proves the core concept: translating complex StackState data into a simple, LLM-ready format. This provides the foundation for developing AI-driven diagnostics and automated remediation.
Resources
- https://www.honeycomb.io/blog/its-the-end-of-observability-as-we-know-it-and-i-feel-fine
- https://www.datadoghq.com/blog/datadog-remote-mcp-server
- https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/2025-06-18/index
- https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/develop/build-server
Basic implementation
- https://github.com/drutigliano19/suse-observability-mcp-server
Results
Successfully developed and delivered a fully functional SUSE Observability MCP Server that bridges language models with SUSE Observability's operational data. This project demonstrates how AI agents can perform intelligent troubleshooting and root cause analysis using structured access to real-time infrastructure data.
Example execution
Prompt: The application in sock-shop namespace is very slow and seems to have a problem
Answer:
Based on the investigation, I have concluded the following:
catalogue Service is the Root Cause: The
catalogueservice is in aCRITICALstate, experiencing a severe performance degradation that started around 17:15:00. This is evidenced by a sharp increase in both response times (exceeding 3.5 seconds) and 5xx error rates (peaking over 9%).front-end Service is a Victim: The
front-endservice is in aDEVIATINGstate solely due to an increase in 5xx errors it is receiving. Its own performance monitors are clear, indicating that it is being affected by a downstream dependency.Inferred Dependency: Although I was unable to confirm the direct dependency via the topology query, the correlated timing and the nature of the errors strongly suggest that the
front-endservice relies on thecatalogueservice. Whencataloguefails,front-endreports errors.
Conclusion and Recommendation
The root cause of the performance issue in the sock-shop namespace is the failure of the catalogue service.
I recommend that the engineering team immediately investigate the catalogue service to diagnose the cause of its high latency and error rates. The front-end service is expected to recover once the catalogue service is restored to a healthy state.
Looking for hackers with the skills:
mcp suseobservability ai agents agenticai mcpserver observability artificial-intelligence llm stackstate generativeai sre itoperations aioperations aiops
This project is part of:
Hack Week 25
Activity
Comments
Similar Projects
Try to use AI and MCP for ACPI table analysis by joeyli
Description
Try to use AI and MCP if they can help with ACPI table analysis.
Goals
It's not easy for looking at ACPI tables even it be disassemble to ASL. I want to learn AI and MCP in Hackweek 25 to see if they can help ACPI table analysis.
Resources
Any resources about AI and MCP.
MCP Trace Suite by r1chard-lyu
Description
This project plans to create an MCP Trace Suite, a system that consolidates commonly used Linux debugging tools such as bpftrace, perf, and ftrace.
The suite is implemented as an MCP Server. This architecture allows an AI agent to leverage the server to diagnose Linux issues and perform targeted system debugging by remotely executing and retrieving tracing data from these powerful tools.
- Repo: https://github.com/r1chard-lyu/systracesuite
- Demo: Slides
Goals
Build an MCP Server that can integrate various Linux debugging and tracing tools, including bpftrace, perf, ftrace, strace, and others, with support for future expansion of additional tools.
Perform testing by intentionally creating bugs or issues that impact system performance, allowing an AI agent to analyze the root cause and identify the underlying problem.
Resources
- Gemini CLI: https://geminicli.com/
- eBPF: https://ebpf.io/
- bpftrace: https://github.com/bpftrace/bpftrace/
- perf: https://perfwiki.github.io/main/
- ftrace: https://github.com/r1chard-lyu/tracium/
MCP Perl SDK by kraih
Description
We've been using the MCP Perl SDK to connect openQA with AI. And while the basics are working pretty well, the SDK is not fully spec compliant yet. So let's change that!
Goals
- Support for Resources
- All response types (Audio, Resource Links, Embedded Resources...)
- Tool/Prompt/Resource update notifications
- Dynamic Tool/Prompt/Resource lists
- New authentication mechanisms
Resources
Enable more features in mcp-server-uyuni by j_renner
Description
I would like to contribute to mcp-server-uyuni, the MCP server for Uyuni / Multi-Linux Manager) exposing additional features as tools. There is lots of relevant features to be found throughout the API, for example:
- System operations and infos
- System groups
- Maintenance windows
- Ansible
- Reporting
- ...
At the end of the week I managed to enable basic system group operations:
- List all system groups visible to the user
- Create new system groups
- List systems assigned to a group
- Add and remove systems from groups
Goals
- Set up test environment locally with the MCP server and client + a recent MLM server [DONE]
- Identify features and use cases offering a benefit with limited effort required for enablement [DONE]
- Create a PR to the repo [DONE]
Resources
Song Search with CLAP by gcolangiuli
Description
Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining (CLAP) is an open-source library that enables the training of a neural network on both Audio and Text descriptions, making it possible to search for Audio using a Text input. Several pre-trained models for song search are already available on huggingface

Goals
Evaluate how CLAP can be used for song searching and determine which types of queries yield the best results by developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in Python. Based on the results of this MVP, future steps could include:
- Music Tagging;
- Free text search;
- Integration with an LLM (for example, with MCP or the OpenAI API) for music suggestions based on your own library.
The code for this project will be entirely written using AI to better explore and demonstrate AI capabilities.
Result
In this MVP we implemented:
- Async Song Analysis with Clap model
- Free Text Search of the songs
- Similar song search based on vector representation
- Containerised version with web interface
We also documented what went well and what can be improved in the use of AI.
You can have a look at the result here:
Future implementation can be related to performance improvement and stability of the analysis.
References
- CLAP: The main model being researched;
- huggingface: Pre-trained models for CLAP;
- Free Music Archive: Creative Commons songs that can be used for testing;
MCP Server for SCC by digitaltomm
Description
Provide an MCP Server implementation for customers to access data on scc.suse.com via MCP protocol. The core benefit of this MCP interface is that it has direct (read) access to customer data in SCC, so the AI agent gets enhanced knowledge about individual customer data, like subscriptions, orders and registered systems.
Architecture
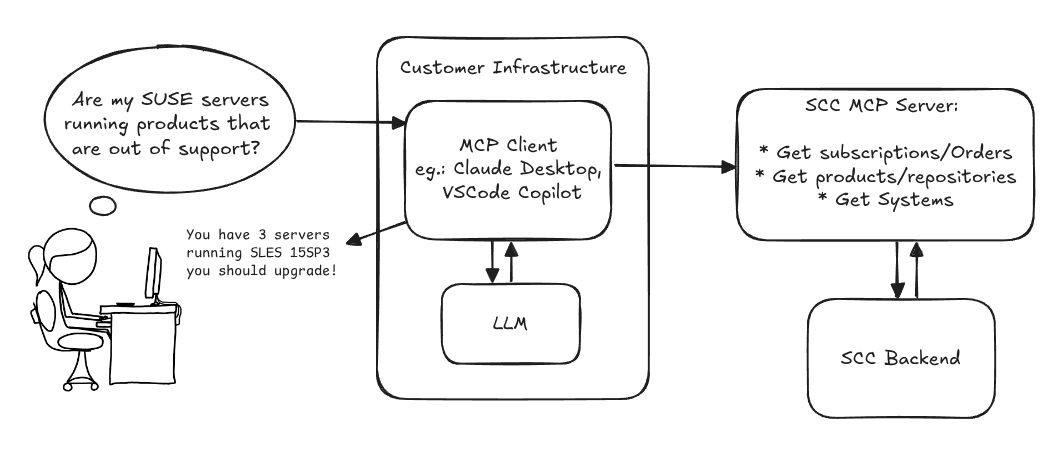
Goals
We want to demonstrate a proof of concept to connect to the SCC MCP server with any AI agent, for example gemini-cli or codex. Enabling the user to ask questions regarding their SCC inventory.
For this Hackweek, we target that users get proper responses to these example questions:
- Which of my currently active systems are running products that are out of support?
- Do I have ready to use registration codes for SLES?
- What are the latest 5 released patches for SLES 15 SP6? Output as a list with release date, patch name, affected package names and fixed CVEs.
- Which versions of kernel-default are available on SLES 15 SP6?
Technical Notes
Similar to the organization APIs, this can expose to customers data about their subscriptions, orders, systems and products. Authentication should be done by organization credentials, similar to what needs to be provided to RMT/MLM. Customers can connect to the SCC MCP server from their own MCP-compatible client and Large Language Model (LLM), so no third party is involved.
Milestones
[x] Basic MCP API setup MCP endpoints [x] Products / Repositories [x] Subscriptions / Orders [x] Systems [x] Packages [x] Document usage with Gemini CLI, Codex
Resources
Gemini CLI setup:
~/.gemini/settings.json:
Uyuni Health-check Grafana AI Troubleshooter by ygutierrez
Description
This project explores the feasibility of using the open-source Grafana LLM plugin to enhance the Uyuni Health-check tool with LLM capabilities. The idea is to integrate a chat-based "AI Troubleshooter" directly into existing dashboards, allowing users to ask natural-language questions about errors, anomalies, or performance issues.
Goals
- Investigate if and how the
grafana-llm-appplug-in can be used within the Uyuni Health-check tool. - Investigate if this plug-in can be used to query LLMs for troubleshooting scenarios.
- Evaluate support for local LLMs and external APIs through the plugin.
- Evaluate if and how the Uyuni MCP server could be integrated as another source of information.
Resources
Explore LLM evaluation metrics by thbertoldi
Description
Learn the best practices for evaluating LLM performance with an open-source framework such as DeepEval.
Goals
Curate the knowledge learned during practice and present it to colleagues.
-> Maybe publish a blog post on SUSE's blog?
Resources
https://deepeval.com
https://docs.pactflow.io/docs/bi-directional-contract-testing
Bugzilla goes AI - Phase 1 by nwalter
Description
This project, Bugzilla goes AI, aims to boost developer productivity by creating an autonomous AI bug agent during Hackweek. The primary goal is to reduce the time employees spend triaging bugs by integrating Ollama to summarize issues, recommend next steps, and push focused daily reports to a Web Interface.
Goals
To reduce employee time spent on Bugzilla by implementing an AI tool that triages and summarizes bug reports, providing actionable recommendations to the team via Web Interface.
Project Charter
Description
Project Achievements during Hackweek
In this file you can read about what we achieved during Hackweek.
Liz - Prompt autocomplete by ftorchia
Description
Liz is the Rancher AI assistant for cluster operations.
Goals
We want to help users when sending new messages to Liz, by adding an autocomplete feature to complete their requests based on the context.
Example:
- User prompt: "Can you show me the list of p"
- Autocomplete suggestion: "Can you show me the list of p...od in local cluster?"
Example:
- User prompt: "Show me the logs of #rancher-"
- Chat console: It shows a drop-down widget, next to the # character, with the list of available pod names starting with "rancher-".
Technical Overview
- The AI agent should expose a new ws/autocomplete endpoint to proxy autocomplete messages to the LLM.
- The UI extension should be able to display prompt suggestions and allow users to apply the autocomplete to the Prompt via keyboard shortcuts.
Resources
Background Coding Agent by mmanno
Description
I had only bad experiences with AI one-shots. However, monitoring agent work closely and interfering often did result in productivity gains.
Now, other companies are using agents in pipelines. That makes sense to me, just like CI, we want to offload work to pipelines: Our engineering teams are consistently slowed down by "toil": low-impact, repetitive maintenance tasks. A simple linter rule change, a dependency bump, rebasing patch-sets on top of newer releases or API deprecation requires dozens of manual PRs, draining time from feature development.
So far we have been writing deterministic, script-based automation for these tasks. And it turns out to be a common trap. These scripts are brittle, complex, and become a massive maintenance burden themselves.
Can we make prompts and workflows smart enough to succeed at background coding?
Goals
We will build a platform that allows engineers to execute complex code transformations using prompts.
By automating this toil, we accelerate large-scale migrations and allow teams to focus on high-value work.
Our platform will consist of three main components:
- "Change" Definition: Engineers will define a transformation as a simple, declarative manifest:
- The target repositories.
- A wrapper to run a "coding agent", e.g., "gemini-cli".
- The task as a natural language prompt.
- The target repositories.
- "Change" Management Service: A central service that orchestrates the jobs. It will receive Change definitions and be responsible for the job lifecycle.
- Execution Runners: We could use existing sandboxed CI runners (like GitHub/GitLab runners) to execute each job or spawn a container.
MVP
- Define the Change manifest format.
- Build the core Management Service that can accept and queue a Change.
- Connect management service and runners, dynamically dispatch jobs to runners.
- Create a basic runner script that can run a hard-coded prompt against a test repo and open a PR.
Stretch Goals:
- Multi-layered approach, Workflow Agents trigger Coding Agents:
- Workflow Agent: Gather information about the task interactively from the user.
- Coding Agent: Once the interactive agent has refined the task into a clear prompt, it hands this prompt off to the "coding agent." This background agent is responsible for executing the task and producing the actual pull request.
- Workflow Agent: Gather information about the task interactively from the user.
- Use MCP:
- Workflow Agent gathers context information from Slack, Github, etc.
- Workflow Agent triggers a Coding Agent.
- Workflow Agent gathers context information from Slack, Github, etc.
- Create a "Standard Task" library with reliable prompts.
- Rebasing rancher-monitoring to a new version of kube-prom-stack
- Update charts to use new images
- Apply changes to comply with a new linter
- Bump complex Go dependencies, like k8s modules
- Backport pull requests to other branches
- Rebasing rancher-monitoring to a new version of kube-prom-stack
- Add “review agents” that review the generated PR.
See also
Enable more features in mcp-server-uyuni by j_renner
Description
I would like to contribute to mcp-server-uyuni, the MCP server for Uyuni / Multi-Linux Manager) exposing additional features as tools. There is lots of relevant features to be found throughout the API, for example:
- System operations and infos
- System groups
- Maintenance windows
- Ansible
- Reporting
- ...
At the end of the week I managed to enable basic system group operations:
- List all system groups visible to the user
- Create new system groups
- List systems assigned to a group
- Add and remove systems from groups
Goals
- Set up test environment locally with the MCP server and client + a recent MLM server [DONE]
- Identify features and use cases offering a benefit with limited effort required for enablement [DONE]
- Create a PR to the repo [DONE]
Resources
The Agentic Rancher Experiment: Do Androids Dream of Electric Cattle? by moio
Rancher is a beast of a codebase. Let's investigate if the new 2025 generation of GitHub Autonomous Coding Agents and Copilot Workspaces can actually tame it. 
The Plan
Create a sandbox GitHub Organization, clone in key Rancher repositories, and let the AI loose to see if it can handle real-world enterprise OSS maintenance - or if it just hallucinates new breeds of Kubernetes resources!
Specifically, throw "Agentic Coders" some typical tasks in a complex, long-lived open-source project, such as:
❥ The Grunt Work: generate missing GoDocs, unit tests, and refactorings. Rebase PRs.
❥ The Complex Stuff: fix actual (historical) bugs and feature requests to see if they can traverse the complexity without (too much) human hand-holding.
❥ Hunting Down Gaps: find areas lacking in docs, areas of improvement in code, dependency bumps, and so on.
If time allows, also experiment with Model Context Protocol (MCP) to give agents context on our specific build pipelines and CI/CD logs.
Why?
We know AI can write "Hello World." and also moderately complex programs from a green field. But can it rebase a 3-month-old PR with conflicts in rancher/rancher? I want to find the breaking point of current AI agents to determine if and how they can help us to reduce our technical debt, work faster and better. At the same time, find out about pitfalls and shortcomings.
The CONCLUSION!!!
A ![]() State of the Union
State of the Union ![]() document was compiled to summarize lessons learned this week. For more gory details, just read on the diary below!
document was compiled to summarize lessons learned this week. For more gory details, just read on the diary below! ![]()
SUSE Edge Image Builder MCP by eminguez
Description
Based on my other hackweek project, SUSE Edge Image Builder's Json Schema I would like to build also a MCP to be able to generate EIB config files the AI way.
Realistically I don't think I'll be able to have something consumable at the end of this hackweek but at least I would like to start exploring MCPs, the difference between an API and MCP, etc.
Goals
- Familiarize myself with MCPs
- Unrealistic: Have an MCP that can generate an EIB config file
Resources
Result
https://github.com/e-minguez/eib-mcp
I've extensively used antigravity and its agent mode to code this. This heavily uses https://hackweek.opensuse.org/25/projects/suse-edge-image-builder-json-schema for the MCP to be built.
I've ended up learning a lot of things about "prompting", json schemas in general, some golang, MCPs and AI in general :)
Example:
Generate an Edge Image Builder configuration for an ISO image based on slmicro-6.2.iso, targeting x86_64 architecture. The output name should be 'my-edge-image' and it should install to /dev/sda. It should deploy
a 3 nodes kubernetes cluster with nodes names "node1", "node2" and "node3" as:
* hostname: node1, IP: 1.1.1.1, role: initializer
* hostname: node2, IP: 1.1.1.2, role: agent
* hostname: node3, IP: 1.1.1.3, role: agent
The kubernetes version should be k3s 1.33.4-k3s1 and it should deploy a cert-manager helm chart (the latest one available according to https://cert-manager.io/docs/installation/helm/). It should create a user
called "suse" with password "suse" and set ntp to "foo.ntp.org". The VIP address for the API should be 1.2.3.4
Generates:
``` apiVersion: "1.0" image: arch: x86_64 baseImage: slmicro-6.2.iso imageType: iso outputImageName: my-edge-image kubernetes: helm: charts: - name: cert-manager repositoryName: jetstack
Intelligent Vulnerability Detection for Private Registries by ibone.gonzalez
Description:
This project wants to build an MCP server that connects your LLM to your private registry. It fetches vulnerability reports, probably generated by Trivy, with all the CVEs, and uses the LLM to develop the exact terminal commands or containers updates needed to resolve them.
Goals:
Our goal is to build an MCP for private registries that:
Detects Vulnerabilities: Proactively finds risks in your packages.
Automates Security: Keeps software secure with automated checks and updates.
Fits Your Workflow: Integrates seamlessly so you never leave your tools.
Protects Privacy: Delivers actionable insights without compromising private data.
To provide automated, privacy-first security for private packages that deliver actionable risk alerts directly within the developer’s existing workflow.
Resources:
Code:
MCP Server for SCC by digitaltomm
Description
Provide an MCP Server implementation for customers to access data on scc.suse.com via MCP protocol. The core benefit of this MCP interface is that it has direct (read) access to customer data in SCC, so the AI agent gets enhanced knowledge about individual customer data, like subscriptions, orders and registered systems.
Architecture

Goals
We want to demonstrate a proof of concept to connect to the SCC MCP server with any AI agent, for example gemini-cli or codex. Enabling the user to ask questions regarding their SCC inventory.
For this Hackweek, we target that users get proper responses to these example questions:
- Which of my currently active systems are running products that are out of support?
- Do I have ready to use registration codes for SLES?
- What are the latest 5 released patches for SLES 15 SP6? Output as a list with release date, patch name, affected package names and fixed CVEs.
- Which versions of kernel-default are available on SLES 15 SP6?
Technical Notes
Similar to the organization APIs, this can expose to customers data about their subscriptions, orders, systems and products. Authentication should be done by organization credentials, similar to what needs to be provided to RMT/MLM. Customers can connect to the SCC MCP server from their own MCP-compatible client and Large Language Model (LLM), so no third party is involved.
Milestones
[x] Basic MCP API setup MCP endpoints [x] Products / Repositories [x] Subscriptions / Orders [x] Systems [x] Packages [x] Document usage with Gemini CLI, Codex
Resources
Gemini CLI setup:
~/.gemini/settings.json:
Enable more features in mcp-server-uyuni by j_renner
Description
I would like to contribute to mcp-server-uyuni, the MCP server for Uyuni / Multi-Linux Manager) exposing additional features as tools. There is lots of relevant features to be found throughout the API, for example:
- System operations and infos
- System groups
- Maintenance windows
- Ansible
- Reporting
- ...
At the end of the week I managed to enable basic system group operations:
- List all system groups visible to the user
- Create new system groups
- List systems assigned to a group
- Add and remove systems from groups
Goals
- Set up test environment locally with the MCP server and client + a recent MLM server [DONE]
- Identify features and use cases offering a benefit with limited effort required for enablement [DONE]
- Create a PR to the repo [DONE]
Resources
Bugzilla goes AI - Phase 1 by nwalter
Description
This project, Bugzilla goes AI, aims to boost developer productivity by creating an autonomous AI bug agent during Hackweek. The primary goal is to reduce the time employees spend triaging bugs by integrating Ollama to summarize issues, recommend next steps, and push focused daily reports to a Web Interface.
Goals
To reduce employee time spent on Bugzilla by implementing an AI tool that triages and summarizes bug reports, providing actionable recommendations to the team via Web Interface.
Project Charter
Description
Project Achievements during Hackweek
In this file you can read about what we achieved during Hackweek.
MCP Trace Suite by r1chard-lyu
Description
This project plans to create an MCP Trace Suite, a system that consolidates commonly used Linux debugging tools such as bpftrace, perf, and ftrace.
The suite is implemented as an MCP Server. This architecture allows an AI agent to leverage the server to diagnose Linux issues and perform targeted system debugging by remotely executing and retrieving tracing data from these powerful tools.
- Repo: https://github.com/r1chard-lyu/systracesuite
- Demo: Slides
Goals
Build an MCP Server that can integrate various Linux debugging and tracing tools, including bpftrace, perf, ftrace, strace, and others, with support for future expansion of additional tools.
Perform testing by intentionally creating bugs or issues that impact system performance, allowing an AI agent to analyze the root cause and identify the underlying problem.
Resources
- Gemini CLI: https://geminicli.com/
- eBPF: https://ebpf.io/
- bpftrace: https://github.com/bpftrace/bpftrace/
- perf: https://perfwiki.github.io/main/
- ftrace: https://github.com/r1chard-lyu/tracium/
bpftrace contribution by mkoutny
Description
bpftrace is a great tool, no need to sing odes to it here. It can access any kernel data and process them in real time. It provides helpers for some common Linux kernel structures but not all.
Goals
- set up bpftrace toolchain
- learn about bpftrace implementation and internals
- implement support for
percpu_counters - look into some of the first issues
- send a refined PR (on Thu)
Resources
Explore LLM evaluation metrics by thbertoldi
Description
Learn the best practices for evaluating LLM performance with an open-source framework such as DeepEval.
Goals
Curate the knowledge learned during practice and present it to colleagues.
-> Maybe publish a blog post on SUSE's blog?
Resources
https://deepeval.com
https://docs.pactflow.io/docs/bi-directional-contract-testing
issuefs: FUSE filesystem representing issues (e.g. JIRA) for the use with AI agents code-assistants by llansky3
Description
Creating a FUSE filesystem (issuefs) that mounts issues from various ticketing systems (Github, Jira, Bugzilla, Redmine) as files to your local file system.
And why this is good idea?
- User can use favorite command line tools to view and search the tickets from various sources
- User can use AI agents capabilities from your favorite IDE or cli to ask question about the issues, project or functionality while providing relevant tickets as context without extra work.
- User can use it during development of the new features when you let the AI agent to jump start the solution. The issuefs will give the AI agent the context (AI agents just read few more files) about the bug or requested features. No need for copying and pasting issues to user prompt or by using extra MCP tools to access the issues. These you can still do but this approach is on purpose different.

Goals
- Add Github issue support
- Proof the concept/approach by apply the approach on itself using Github issues for tracking and development of new features
- Add support for Bugzilla and Redmine using this approach in the process of doing it. Record a video of it.
- Clean-up and test the implementation and create some documentation
- Create a blog post about this approach
Resources
There is a prototype implementation here. This currently sort of works with JIRA only.
"what is it" file and directory analysis via MCP and local LLM, for console and KDE by rsimai
Description
Users sometimes wonder what files or directories they find on their local PC are good for. If they can't determine from the filename or metadata, there should an easy way to quickly analyze the content and at least guess the meaning. An LLM could help with that, through the use of a filesystem MCP and to-text-converters for typical file types. Ideally this is integrated into the desktop environment but works as well from a console. All data is processed locally or "on premise", no artifacts remain or leave the system.
Goals
- The user can run a command from the console, to check on a file or directory
- The filemanager contains the "analyze" feature within the context menu
- The local LLM could serve for other use cases where privacy matters
TBD
- Find or write capable one-shot and interactive MCP client
- Find or write simple+secure file access MCP server
- Create local LLM service with appropriate footprint, containerized
- Shell command with options
- KDE integration (Dolphin)
- Package
- Document
Resources
Self-Scaling LLM Infrastructure Powered by Rancher by ademicev0
Self-Scaling LLM Infrastructure Powered by Rancher

Description
The Problem
Running LLMs can get expensive and complex pretty quickly.
Today there are typically two choices:
- Use cloud APIs like OpenAI or Anthropic. Easy to start with, but costs add up at scale.
- Self-host everything - set up Kubernetes, figure out GPU scheduling, handle scaling, manage model serving... it's a lot of work.
What if there was a middle ground?
What if infrastructure scaled itself instead of making you scale it?
Can we use existing Rancher capabilities like CAPI, autoscaling, and GitOps to make this simpler instead of building everything from scratch?
Project Repository: github.com/alexander-demicev/llmserverless
What This Project Does
A key feature is hybrid deployment: requests can be routed based on complexity or privacy needs. Simple or low-sensitivity queries can use public APIs (like OpenAI), while complex or private requests are handled in-house on local infrastructure. This flexibility allows balancing cost, privacy, and performance - using cloud for routine tasks and on-premises resources for sensitive or demanding workloads.
A complete, self-scaling LLM infrastructure that:
- Scales to zero when idle (no idle costs)
- Scales up automatically when requests come in
- Adds more nodes when needed, removes them when demand drops
- Runs on any infrastructure - laptop, bare metal, or cloud
Think of it as "serverless for LLMs" - focus on building, the infrastructure handles itself.
How It Works
A combination of open source tools working together:
Flow:
- Users interact with OpenWebUI (chat interface)
- Requests go to LiteLLM Gateway
- LiteLLM routes requests to:
- Ollama (Knative) for local model inference (auto-scales pods)
- Or cloud APIs for fallback
Extended private brain - RAG my own scripts and data into offline LLM AI by tjyrinki_suse
Description
For purely studying purposes, I'd like to find out if I could teach an LLM some of my own accumulated knowledge, to use it as a sort of extended brain.
I might use qwen3-coder or something similar as a starting point.
Everything would be done 100% offline without network available to the container, since I prefer to see when network is needed, and make it so it's never needed (other than initial downloads).
Goals
- Learn something about RAG, LLM, AI.
- Find out if everything works offline as intended.
- As an end result have a new way to access my own existing know-how, but so that I can query the wisdom in them.
- Be flexible to pivot in any direction, as long as there are new things learned.
Resources
To be found on the fly.
Timeline
Day 1 (of 4)
- Tried out a RAG demo, expanded on feeding it my own data
- Experimented with qwen3-coder to add a persistent chat functionality, and keeping vectors in a pickle file
- Optimizations to keep everything within context window
- Learn and add a bit of PyTest
Day 2
- More experimenting and more data
- Study ChromaDB
- Add a Web UI that works from another computer even though the container sees network is down
Day 3
- The above RAG is working well enough for demonstration purposes.
- Pivot to trying out OpenCode, configuring local Ollama qwen3-coder there, to analyze the RAG demo.
- Figured out how to configure Ollama template to be usable under OpenCode. OpenCode locally is super slow to just running qwen3-coder alone.
Day 4 (final day)
- Battle with OpenCode that was both slow and kept on piling up broken things.
- Call it success as after all the agentic AI was working locally.
- Clean up the mess left behind a bit.
Blog Post
Summarized the findings at blog post.
DNS management with DNSControl by itorres
Description
We use several systems to manage DNS at SUSE and openSUSE: BIND, external providers, PowerDNS... each of them is managed in a different way either with raw zones (BIND) or Terraform (external providers).
DNSControl is an opinionated tool to manage DNS as code while being provider agnostic. It's developed and used by StackExchange, was spearheaded by Tom Limoncelly and is already being used to manage DNS for openSUSE.
Implementing DNSControl should allow us to have a single DNS operations interface that end users can leverage.
This would reduce complexity for end users as they can use a single simplified ECMAScript based DSL instead of BIND zones for internal and HCL config for external.
Operations for our IT organization would be greatly reduced. DNSControl itself has several internal checks that reduce our need to do linting and we can concentrate on implementing logical checks based on ownership.
This simplifies reviews a lot and the integration with BIND and providers allows our IT organization to implement an apply on merge.
At an organizational level it will separate our DNS tasks from other IT operations, speeding up DNS changes and allowing us to delegate DNS reviews to service desk or even customer teams through CODEOWNERS.
Goals
- Create a test subdomain in one of our internal BIND servers to be managed with DNSControl.
- Create an internal DNSControl repository to implement gitops for DNS.
- Deploy DNS changes strictly through gitops.
Extended goals
- Implement CODEOWNERS.
- Replicate main goals for external DNS.
Resources
- DNSControl documentation and introduction
- Opinions guiding DNSControl
- Package in OBS
- openSUSE repo to manage DNS with DNS Control
Bugzilla goes AI - Phase 1 by nwalter
Description
This project, Bugzilla goes AI, aims to boost developer productivity by creating an autonomous AI bug agent during Hackweek. The primary goal is to reduce the time employees spend triaging bugs by integrating Ollama to summarize issues, recommend next steps, and push focused daily reports to a Web Interface.
Goals
To reduce employee time spent on Bugzilla by implementing an AI tool that triages and summarizes bug reports, providing actionable recommendations to the team via Web Interface.
Project Charter
Description
Project Achievements during Hackweek
In this file you can read about what we achieved during Hackweek.
Exploring Modern AI Trends and Kubernetes-Based AI Infrastructure by jluo
Description
Build a solid understanding of the current landscape of Artificial Intelligence and how modern cloud-native technologies—especially Kubernetes—support AI workloads.
Goals
Use Gemini Learning Mode to guide the exploration, surface relevant concepts, and structure the learning journey:
- Gain insight into the latest AI trends, tools, and architectural concepts.
- Understand how Kubernetes and related cloud-native technologies are used in the AI ecosystem (model training, deployment, orchestration, MLOps).
Resources
Red Hat AI Topic Articles
- https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/ai
Kubeflow Documentation
- https://www.kubeflow.org/docs/
Q4 2025 CNCF Technology Landscape Radar report:
- https://www.cncf.io/announcements/2025/11/11/cncf-and-slashdata-report-finds-leading-ai-tools-gaining-adoption-in-cloud-native-ecosystems/
- https://www.cncf.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/cncfreporttechradar_111025a.pdf
Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol
- https://developers.googleblog.com/en/a2a-a-new-era-of-agent-interoperability/
Explore LLM evaluation metrics by thbertoldi
Description
Learn the best practices for evaluating LLM performance with an open-source framework such as DeepEval.
Goals
Curate the knowledge learned during practice and present it to colleagues.
-> Maybe publish a blog post on SUSE's blog?
Resources
https://deepeval.com
https://docs.pactflow.io/docs/bi-directional-contract-testing