Description
This project plans to create an MCP Trace Suite, a system that consolidates commonly used Linux debugging tools such as bpftrace, perf, and ftrace.
The suite is implemented as an MCP Server. This architecture allows an AI agent to leverage the server to diagnose Linux issues and perform targeted system debugging by remotely executing and retrieving tracing data from these powerful tools.
- Repo: https://github.com/r1chard-lyu/systracesuite
- Demo: Slides
Goals
Build an MCP Server that can integrate various Linux debugging and tracing tools, including bpftrace, perf, ftrace, strace, and others, with support for future expansion of additional tools.
Perform testing by intentionally creating bugs or issues that impact system performance, allowing an AI agent to analyze the root cause and identify the underlying problem.
Resources
- Gemini CLI: https://geminicli.com/
- eBPF: https://ebpf.io/
- bpftrace: https://github.com/bpftrace/bpftrace/
- perf: https://perfwiki.github.io/main/
- ftrace: https://github.com/r1chard-lyu/tracium/
This project is part of:
Hack Week 25
Activity
Comments
-

about 2 months ago by r1chard-lyu | Reply
Hack Week 25 - Status
Day 1
- Systracesuite Development:
- Feature Development (Server & Tracing Integration):
- Secured non-interactive
sudoforbpftrace_list. - Integrated Bpftrace utilities (
versionandhelpcommands). - Added
.geminisettings for Gemini CLI MCP connection. - Added
fastmcptorequirements.txt. - Implemented initial FastMCP server (with
status,echo,stop,top,perftools).
- Secured non-interactive
- Documentation:
- Refined JSON examples in README to a single-line format.
- Updated
README.mdwith FastMCP server installation, JSON-RPC 2.0, and usage instructions.
- Initial Setup: Added
README.mdfile.
- Feature Development (Server & Tracing Integration):
Day 2
- Systracesuite Development:
- Feature Development (Tracing Tools):
- Added
read_bpftrace_toolfor Bpftrace tool information. - Integrated new Bpftrace tools (e.g.,
tcpconnect.bt,tcpdrop.bt, etc.). - Added
bpftrace_helptool. - Added
ftrace_helpandftrace_versiontools. - Added
strace_helpandstrace_versiontools.
- Added
- Refactoring & Setup:
- Refactored interactive root handling, removing password
prompts; now uses
bpftrace_list_all(assumes passwordless sudo). - Implemented
setup.shfor passwordlesssudoon specific tools.
- Refactored interactive root handling, removing password
prompts; now uses
- Documentation:
READMEupdated to reflect these changes.
- Feature Development (Tracing Tools):
Day 3
- Systracesuite Development:
- Project Refactoring: Rename project to "Systracesuite"; update README, MCP server name, and arguments.
- Maintenance: Remove local Gemini settings; add to
.gitignore. - Documentation: Update the README; add
LICENSEfile.
- Testing the execution result of Systracesuite.
- Testing bpftrace tools from upstream and SUSE sources.
Day 4
- Systracesuite Development:
- Documentation Updates: Clarify Bpftrace tool sources in README; include a system architecture diagram.
- Testing different Systracesuite use cases, such as network latency and program crashes.
- Prepare demo experiments and slides.
Day 5
- Demo. Slides
- Collect Q&A and feedback.
- Plan and outline optimization directions.
- Systracesuite Development:
Similar Projects
Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition by mackenzie.techdocs

Description
Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition is an AI-powered documentation navigator that makes finding information across SUSE, Rancher, K3s, and RKE2 documentation effortless. Built as a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, it enables semantic search, intelligent Q&A, and documentation summarization using 100% open-source AI models (no API keys required!). The project also allows you to bring your own keys from Anthropic and Open AI for parallel processing.
Goals
- [ X ] Build functional MCP server with documentation tools
- [ X ] Implement semantic search with vector embeddings
- [ X ] Create user-friendly web interface
- [ X ] Optimize indexing performance (parallel processing)
- [ X ] Add SUSE branding and polish UX
- [ X ] Stretch Goal: Add more documentation sources
- [ X ] Stretch Goal: Implement document change detection for auto-updates
Coming Soon!
- Community Feedback: Test with real users and gather improvement suggestions
Resources
- Repository: Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition GitHub
- UI Demo: Live UI Demo of Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition
Update M2Crypto by mcepl
There are couple of projects I work on, which need my attention and putting them to shape:
Goal for this Hackweek
- Put M2Crypto into better shape (most issues closed, all pull requests processed)
- More fun to learn jujutsu
- Play more with Gemini, how much it help (or not).
- Perhaps, also (just slightly related), help to fix vis to work with LuaJIT, particularly to make vis-lspc working.
MCP Server for SCC by digitaltomm
Description
Provide an MCP Server implementation for customers to access data on scc.suse.com via MCP protocol. The core benefit of this MCP interface is that it has direct (read) access to customer data in SCC, so the AI agent gets enhanced knowledge about individual customer data, like subscriptions, orders and registered systems.
Architecture
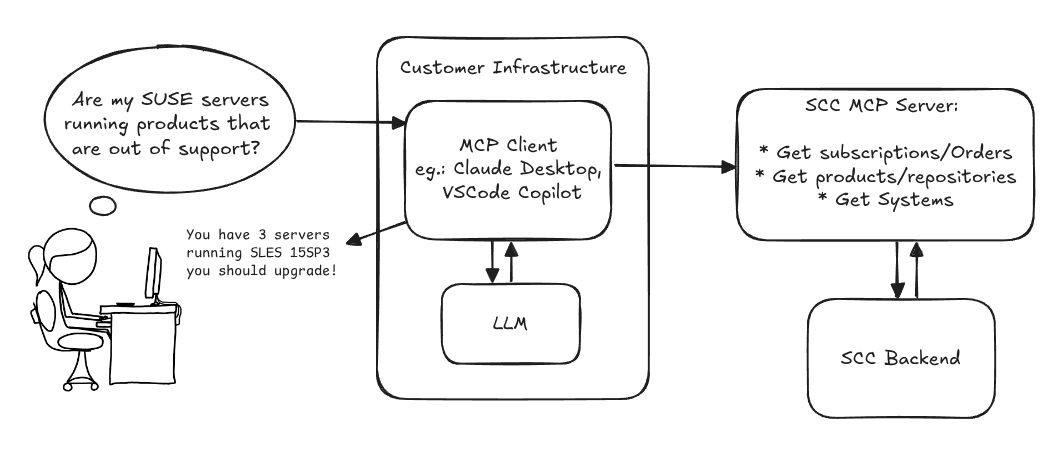
Goals
We want to demonstrate a proof of concept to connect to the SCC MCP server with any AI agent, for example gemini-cli or codex. Enabling the user to ask questions regarding their SCC inventory.
For this Hackweek, we target that users get proper responses to these example questions:
- Which of my currently active systems are running products that are out of support?
- Do I have ready to use registration codes for SLES?
- What are the latest 5 released patches for SLES 15 SP6? Output as a list with release date, patch name, affected package names and fixed CVEs.
- Which versions of kernel-default are available on SLES 15 SP6?
Technical Notes
Similar to the organization APIs, this can expose to customers data about their subscriptions, orders, systems and products. Authentication should be done by organization credentials, similar to what needs to be provided to RMT/MLM. Customers can connect to the SCC MCP server from their own MCP-compatible client and Large Language Model (LLM), so no third party is involved.
Milestones
[x] Basic MCP API setup MCP endpoints [x] Products / Repositories [x] Subscriptions / Orders [x] Systems [x] Packages [x] Document usage with Gemini CLI, Codex
Resources
Gemini CLI setup:
~/.gemini/settings.json:
Local AI assistant with optional integrations and mobile companion by livdywan
Description
Setup a local AI assistant for research, brainstorming and proof reading. Look into SurfSense, Open WebUI and possibly alternatives. Explore integration with services like openQA. There should be no cloud dependencies. Mobile phone support or an additional companion app would be a bonus. The goal is not to develop everything from scratch.
User Story
- Allison Average wants a one-click local AI assistent on their openSUSE laptop.
- Ash Awesome wants AI on their phone without an expensive subscription.
Goals
- Evaluate a local SurfSense setup for day to day productivity
- Test opencode for vibe coding and tool calling
Timeline
Day 1
- Took a look at SurfSense and started setting up a local instance.
- Unfortunately the container setup did not work well. Tho this was a great opportunity to learn some new podman commands and refresh my memory on how to recover a corrupted btrfs filesystem.
Day 2
- Due to its sheer size and complexity SurfSense seems to have triggered btrfs fragmentation. Naturally this was not visible in any podman-related errors or in the journal. So this took up much of my second day.
Day 3
- Trying out opencode with Qwen3-Coder and Qwen2.5-Coder.
Day 4
- Context size is a thing, and models are not equally usable for vibe coding.
- Through arduous browsing for ollama models I did find some like
myaniu/qwen2.5-1m:7bwith 1m but even then it is not obvious if they are meant for tool calls.
Day 5
- Whilst trying to make opencode usable I discovered ramalama which worked instantly and very well.
Outcomes
surfsense
I could not easily set this up completely. Maybe in part due to my filesystem issues. Was expecting this to be less of an effort.
opencode
Installing opencode and ollama in my distrobox container along with the following configs worked for me.
When preparing a new project from scratch it is a good idea to start out with a template.
opencode.json
``` {
Flaky Tests AI Finder for Uyuni and MLM Test Suites by oscar-barrios
Description
Our current Grafana dashboards provide a great overview of test suite health, including a panel for "Top failed tests." However, identifying which of these failures are due to legitimate bugs versus intermittent "flaky tests" is a manual, time-consuming process. These flaky tests erode trust in our test suites and slow down development.
This project aims to build a simple but powerful Python script that automates flaky test detection. The script will directly query our Prometheus instance for the historical data of each failed test, using the jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age metric. It will then format this data and send it to the Gemini API with a carefully crafted prompt, asking it to identify which tests show a flaky pattern.
The final output will be a clean JSON list of the most probable flaky tests, which can then be used to populate a new "Top Flaky Tests" panel in our existing Grafana test suite dashboard.
Goals
By the end of Hack Week, we aim to have a single, working Python script that:
- Connects to Prometheus and executes a query to fetch detailed test failure history.
- Processes the raw data into a format suitable for the Gemini API.
- Successfully calls the Gemini API with the data and a clear prompt.
- Parses the AI's response to extract a simple list of flaky tests.
- Saves the list to a JSON file that can be displayed in Grafana.
- New panel in our Dashboard listing the Flaky tests
Resources
- Jenkins Prometheus Exporter: https://github.com/uyuni-project/jenkins-exporter/
- Data Source: Our internal Prometheus server.
- Key Metric:
jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age{jobname, buildid, suite, case, status, failedsince}. - Existing Query for Reference:
count by (suite) (max_over_time(jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age{status=~"FAILED|REGRESSION", jobname="$jobname"}[$__range])). - AI Model: The Google Gemini API.
- Example about how to interact with Gemini API: https://github.com/srbarrios/FailTale/
- Visualization: Our internal Grafana Dashboard.
- Internal IaC: https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/tree/master/srv/salt/monitoring
Outcome
- Jenkins Flaky Test Detector: https://github.com/srbarrios/jenkins-flaky-tests-detector and its container
- IaC on MLM Team: https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/tree/master/srv/salt/monitoring/jenkinsflakytestsdetector?reftype=heads, https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/blob/master/srv/salt/monitoring/grafana/dashboards/flaky-tests.json?ref_type=heads, and others.
- Grafana Dashboard: https://grafana.mgr.suse.de/d/flaky-tests/flaky-tests-detection @ @ text
Uyuni Health-check Grafana AI Troubleshooter by ygutierrez
Description
This project explores the feasibility of using the open-source Grafana LLM plugin to enhance the Uyuni Health-check tool with LLM capabilities. The idea is to integrate a chat-based "AI Troubleshooter" directly into existing dashboards, allowing users to ask natural-language questions about errors, anomalies, or performance issues.
Goals
- Investigate if and how the
grafana-llm-appplug-in can be used within the Uyuni Health-check tool. - Investigate if this plug-in can be used to query LLMs for troubleshooting scenarios.
- Evaluate support for local LLMs and external APIs through the plugin.
- Evaluate if and how the Uyuni MCP server could be integrated as another source of information.
Resources
Multi-agent AI assistant for Linux troubleshooting by doreilly
Description
Explore multi-agent architecture as a way to avoid MCP context rot.
Having one agent with many tools bloats the context with low-level details about tool descriptions, parameter schemas etc which hurts LLM performance. Instead have many specialised agents, each with just the tools it needs for its role. A top level supervisor agent takes the user prompt and delegates to appropriate sub-agents.
Goals
Create an AI assistant with some sub-agents that are specialists at troubleshooting Linux subsystems, e.g. systemd, selinux, firewalld etc. The agents can get information from the system by implementing their own tools with simple function calls, or use tools from MCP servers, e.g. a systemd-agent can use tools from systemd-mcp.
Example prompts/responses:
user$ the system seems slow
assistant$ process foo with pid 12345 is using 1000% cpu ...
user$ I can't connect to the apache webserver
assistant$ the firewall is blocking http ... you can open the port with firewall-cmd --add-port ...
Resources
Language Python. The Python ADK is more mature than Golang.
https://google.github.io/adk-docs/
https://github.com/djoreilly/linux-helper
Enable more features in mcp-server-uyuni by j_renner
Description
I would like to contribute to mcp-server-uyuni, the MCP server for Uyuni / Multi-Linux Manager) exposing additional features as tools. There is lots of relevant features to be found throughout the API, for example:
- System operations and infos
- System groups
- Maintenance windows
- Ansible
- Reporting
- ...
At the end of the week I managed to enable basic system group operations:
- List all system groups visible to the user
- Create new system groups
- List systems assigned to a group
- Add and remove systems from groups
Goals
- Set up test environment locally with the MCP server and client + a recent MLM server [DONE]
- Identify features and use cases offering a benefit with limited effort required for enablement [DONE]
- Create a PR to the repo [DONE]
Resources
SUSE Edge Image Builder MCP by eminguez
Description
Based on my other hackweek project, SUSE Edge Image Builder's Json Schema I would like to build also a MCP to be able to generate EIB config files the AI way.
Realistically I don't think I'll be able to have something consumable at the end of this hackweek but at least I would like to start exploring MCPs, the difference between an API and MCP, etc.
Goals
- Familiarize myself with MCPs
- Unrealistic: Have an MCP that can generate an EIB config file
Resources
Result
https://github.com/e-minguez/eib-mcp
I've extensively used antigravity and its agent mode to code this. This heavily uses https://hackweek.opensuse.org/25/projects/suse-edge-image-builder-json-schema for the MCP to be built.
I've ended up learning a lot of things about "prompting", json schemas in general, some golang, MCPs and AI in general :)
Example:
Generate an Edge Image Builder configuration for an ISO image based on slmicro-6.2.iso, targeting x86_64 architecture. The output name should be 'my-edge-image' and it should install to /dev/sda. It should deploy
a 3 nodes kubernetes cluster with nodes names "node1", "node2" and "node3" as:
* hostname: node1, IP: 1.1.1.1, role: initializer
* hostname: node2, IP: 1.1.1.2, role: agent
* hostname: node3, IP: 1.1.1.3, role: agent
The kubernetes version should be k3s 1.33.4-k3s1 and it should deploy a cert-manager helm chart (the latest one available according to https://cert-manager.io/docs/installation/helm/). It should create a user
called "suse" with password "suse" and set ntp to "foo.ntp.org". The VIP address for the API should be 1.2.3.4
Generates:
``` apiVersion: "1.0" image: arch: x86_64 baseImage: slmicro-6.2.iso imageType: iso outputImageName: my-edge-image kubernetes: helm: charts: - name: cert-manager repositoryName: jetstack
Try to use AI and MCP for ACPI table analysis by joeyli
Description
Try to use AI and MCP if they can help with ACPI table analysis.
Goals
It's not easy for looking at ACPI tables even it be disassemble to ASL. I want to learn AI and MCP in Hackweek 25 to see if they can help ACPI table analysis.
Resources
Any resources about AI and MCP.
dynticks-testing: analyse perf / trace-cmd output and aggregate data by m.crivellari
Description
dynticks-testing is a project started years ago by Frederic Weisbecker. One of the feature is to check the actual configuration (isolcpus, irqaffinity etc etc) and give feedback on it.
An important goal of this tool is to parse the output of trace-cmd / perf and provide more readable data, showing the duration of every events grouped by PID (showing also the CPU number, if the tasks has been migrated etc).
An example of data captured on my laptop (incomplete!!):
-0 [005] dN.2. 20310.270699: sched_wakeup: WaylandProxy:46380 [120] CPU:005
-0 [005] d..2. 20310.270702: sched_switch: swapper/5:0 [120] R ==> WaylandProxy:46380 [120]
...
WaylandProxy-46380 [004] d..2. 20310.295397: sched_switch: WaylandProxy:46380 [120] S ==> swapper/4:0 [120]
-0 [006] d..2. 20310.295397: sched_switch: swapper/6:0 [120] R ==> firefox:46373 [120]
firefox-46373 [006] d..2. 20310.295408: sched_switch: firefox:46373 [120] S ==> swapper/6:0 [120]
-0 [004] dN.2. 20310.295466: sched_wakeup: WaylandProxy:46380 [120] CPU:004
Output of noise_parse.py:
Task: WaylandProxy Pid: 46380 cpus: {4, 5} (Migrated!!!)
Wakeup Latency Nr: 24 Duration: 89
Sched switch: kworker/12:2 Nr: 1 Duration: 6
My first contribution is around Nov. 2024!
Goals
- add more features (eg cpuset)
- test / bugfix
Resources
- Frederic's public repository: https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/frederic/dynticks-testing.git/
- https://docs.kernel.org/timers/no_hz.html#testing
Progresses
isolcpus and cpusets implemented and merged in master: dynticks-testing.git commit
bpftrace contribution by mkoutny
Description
bpftrace is a great tool, no need to sing odes to it here. It can access any kernel data and process them in real time. It provides helpers for some common Linux kernel structures but not all.
Goals
- set up bpftrace toolchain
- learn about bpftrace implementation and internals
- implement support for
percpu_counters - look into some of the first issues
- send a refined PR (on Thu)
Resources
SUSE Observability MCP server by drutigliano
Description
The idea is to implement the SUSE Observability Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server as a specialized, middle-tier API designed to translate the complex, high-cardinality observability data from StackState (topology, metrics, and events) into highly structured, contextually rich, and LLM-ready snippets.
This MCP Server abstract the StackState APIs. Its primary function is to serve as a Tool/Function Calling target for AI agents. When an AI receives an alert or a user query (e.g., "What caused the outage?"), the AI calls an MCP Server endpoint. The server then fetches the relevant operational facts, summarizes them, normalizes technical identifiers (like URNs and raw metric names) into natural language concepts, and returns a concise JSON or YAML payload. This payload is then injected directly into the LLM's prompt, ensuring the final diagnosis or action is grounded in real-time, accurate SUSE Observability data, effectively minimizing hallucinations.
Goals
- Grounding AI Responses: Ensure that all AI diagnoses, root cause analyses, and action recommendations are strictly based on verifiable, real-time data retrieved from the SUSE Observability StackState platform.
- Simplifying Data Access: Abstract the complexity of StackState's native APIs (e.g., Time Travel, 4T Data Model) into simple, semantic functions that can be easily invoked by LLM tool-calling mechanisms.
- Data Normalization: Convert complex, technical identifiers (like component URNs, raw metric names, and proprietary health states) into standardized, natural language terms that an LLM can easily reason over.
- Enabling Automated Remediation: Define clear, action-oriented MCP endpoints (e.g., execute_runbook) that allow the AI agent to initiate automated operational workflows (e.g., restarts, scaling) after a diagnosis, closing the loop on observability.
Hackweek STEP
- Create a functional MCP endpoint exposing one (or more) tool(s) to answer queries like "What is the health of service X?") by fetching, normalizing, and returning live StackState data in an LLM-ready format.
Scope
- Implement read-only MCP server that can:
- Connect to a live SUSE Observability instance and authenticate (with API token)
- Use tools to fetch data for a specific component URN (e.g., current health state, metrics, possibly topology neighbors, ...).
- Normalize response fields (e.g., URN to "Service Name," health state DEVIATING to "Unhealthy", raw metrics).
- Return the data as a structured JSON payload compliant with the MCP specification.
Deliverables
- MCP Server v0.1 A running Golang MCP server with at least one tool.
- A README.md and a test script (e.g., curl commands or a simple notebook) showing how an AI agent would call the endpoint and the resulting JSON payload.
Outcome A functional and testable API endpoint that proves the core concept: translating complex StackState data into a simple, LLM-ready format. This provides the foundation for developing AI-driven diagnostics and automated remediation.
Resources
- https://www.honeycomb.io/blog/its-the-end-of-observability-as-we-know-it-and-i-feel-fine
- https://www.datadoghq.com/blog/datadog-remote-mcp-server
- https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/2025-06-18/index
- https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/develop/build-server
Basic implementation
- https://github.com/drutigliano19/suse-observability-mcp-server
Results
Successfully developed and delivered a fully functional SUSE Observability MCP Server that bridges language models with SUSE Observability's operational data. This project demonstrates how AI agents can perform intelligent troubleshooting and root cause analysis using structured access to real-time infrastructure data.
Example execution