Description
Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining (CLAP) is an open-source library that enables the training of a neural network on both Audio and Text descriptions, making it possible to search for Audio using a Text input. Several pre-trained models for song search are already available on huggingface

Goals
Evaluate how CLAP can be used for song searching and determine which types of queries yield the best results by developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in Python. Based on the results of this MVP, future steps could include:
- Music Tagging;
- Free text search;
- Integration with an LLM (for example, with MCP or the OpenAI API) for music suggestions based on your own library.
The code for this project will be entirely written using AI to better explore and demonstrate AI capabilities.
Result
In this MVP we implemented:
- Async Song Analysis with Clap model
- Free Text Search of the songs
- Similar song search based on vector representation
- Containerised version with web interface
We also documented what went well and what can be improved in the use of AI.
You can have a look at the result here:
Future implementation can be related to performance improvement and stability of the analysis.
References
- CLAP: The main model being researched;
- huggingface: Pre-trained models for CLAP;
- Free Music Archive: Creative Commons songs that can be used for testing;
Looking for hackers with the skills:
This project is part of:
Hack Week 25
Activity
Comments
-

-

about 2 months ago by gcolangiuli | Reply
Project finished! (for what an MVP can be finished) have a look at the result on the github repo. You can also look the presentation slide.
Similar Projects
Liz - Prompt autocomplete by ftorchia
Description
Liz is the Rancher AI assistant for cluster operations.
Goals
We want to help users when sending new messages to Liz, by adding an autocomplete feature to complete their requests based on the context.
Example:
- User prompt: "Can you show me the list of p"
- Autocomplete suggestion: "Can you show me the list of p...od in local cluster?"
Example:
- User prompt: "Show me the logs of #rancher-"
- Chat console: It shows a drop-down widget, next to the # character, with the list of available pod names starting with "rancher-".
Technical Overview
- The AI agent should expose a new ws/autocomplete endpoint to proxy autocomplete messages to the LLM.
- The UI extension should be able to display prompt suggestions and allow users to apply the autocomplete to the Prompt via keyboard shortcuts.
Resources
Improvements to osc (especially with regards to the Git workflow) by mcepl
Description
There is plenty of hacking on osc, where we could spent some fun time. I would like to see a solution for https://github.com/openSUSE/osc/issues/2006 (which is sufficiently non-serious, that it could be part of HackWeek project).
Improve/rework household chore tracker `chorazon` by gniebler
Description
I wrote a household chore tracker named chorazon, which is meant to be deployed as a web application in the household's local network.
It features the ability to set up different (so far only weekly) schedules per task and per person, where tasks may span several days.
There are "tokens", which can be collected by users. Tasks can (and usually will) have rewards configured where they yield a certain amount of tokens. The idea is that they can later be redeemed for (surprise) gifts, but this is not implemented yet. (So right now one needs to edit the DB manually to subtract tokens when they're redeemed.)
Days are not rolled over automatically, to allow for task completion control.
We used it in my household for several months, with mixed success. There are many limitations in the system that would warrant a revisit.
It's written using the Pyramid Python framework with URL traversal, ZODB as the data store and Web Components for the frontend.
Goals
- Add admin screens for users, tasks and schedules
- Add models, pages etc. to allow redeeming tokens for gifts/surprises
- …?
Resources
tbd (Gitlab repo)
Testing and adding GNU/Linux distributions on Uyuni by juliogonzalezgil
Join the Gitter channel! https://gitter.im/uyuni-project/hackweek
Uyuni is a configuration and infrastructure management tool that saves you time and headaches when you have to manage and update tens, hundreds or even thousands of machines. It also manages configuration, can run audits, build image containers, monitor and much more!
Currently there are a few distributions that are completely untested on Uyuni or SUSE Manager (AFAIK) or just not tested since a long time, and could be interesting knowing how hard would be working with them and, if possible, fix whatever is broken.
For newcomers, the easiest distributions are those based on DEB or RPM packages. Distributions with other package formats are doable, but will require adapting the Python and Java code to be able to sync and analyze such packages (and if salt does not support those packages, it will need changes as well). So if you want a distribution with other packages, make sure you are comfortable handling such changes.
No developer experience? No worries! We had non-developers contributors in the past, and we are ready to help as long as you are willing to learn. If you don't want to code at all, you can also help us preparing the documentation after someone else has the initial code ready, or you could also help with testing :-)
The idea is testing Salt (including bootstrapping with bootstrap script) and Salt-ssh clients
To consider that a distribution has basic support, we should cover at least (points 3-6 are to be tested for both salt minions and salt ssh minions):
- Reposync (this will require using spacewalk-common-channels and adding channels to the .ini file)
- Onboarding (salt minion from UI, salt minion from bootstrap scritp, and salt-ssh minion) (this will probably require adding OS to the bootstrap repository creator)
- Package management (install, remove, update...)
- Patching
- Applying any basic salt state (including a formula)
- Salt remote commands
- Bonus point: Java part for product identification, and monitoring enablement
- Bonus point: sumaform enablement (https://github.com/uyuni-project/sumaform)
- Bonus point: Documentation (https://github.com/uyuni-project/uyuni-docs)
- Bonus point: testsuite enablement (https://github.com/uyuni-project/uyuni/tree/master/testsuite)
If something is breaking: we can try to fix it, but the main idea is research how supported it is right now. Beyond that it's up to each project member how much to hack :-)
- If you don't have knowledge about some of the steps: ask the team
- If you still don't know what to do: switch to another distribution and keep testing.
This card is for EVERYONE, not just developers. Seriously! We had people from other teams helping that were not developers, and added support for Debian and new SUSE Linux Enterprise and openSUSE Leap versions :-)
In progress/done for Hack Week 25
Guide
We started writin a Guide: Adding a new client GNU Linux distribution to Uyuni at https://github.com/uyuni-project/uyuni/wiki/Guide:-Adding-a-new-client-GNU-Linux-distribution-to-Uyuni, to make things easier for everyone, specially those not too familiar wht Uyuni or not technical.
openSUSE Leap 16.0
The distribution will all love!
https://en.opensuse.org/openSUSE:Roadmap#DRAFTScheduleforLeap16.0
Curent Status We started last year, it's complete now for Hack Week 25! :-D
[W]Reposync (this will require using spacewalk-common-channels and adding channels to the .ini file) NOTE: Done, client tools for SLMicro6 are using as those for SLE16.0/openSUSE Leap 16.0 are not available yet[W]Onboarding (salt minion from UI, salt minion from bootstrap scritp, and salt-ssh minion) (this will probably require adding OS to the bootstrap repository creator)[W]Package management (install, remove, update...). Works, even reboot requirement detection
Update M2Crypto by mcepl
There are couple of projects I work on, which need my attention and putting them to shape:
Goal for this Hackweek
- Put M2Crypto into better shape (most issues closed, all pull requests processed)
- More fun to learn jujutsu
- Play more with Gemini, how much it help (or not).
- Perhaps, also (just slightly related), help to fix vis to work with LuaJIT, particularly to make vis-lspc working.
MCP Server for SCC by digitaltomm
Description
Provide an MCP Server implementation for customers to access data on scc.suse.com via MCP protocol. The core benefit of this MCP interface is that it has direct (read) access to customer data in SCC, so the AI agent gets enhanced knowledge about individual customer data, like subscriptions, orders and registered systems.
Architecture
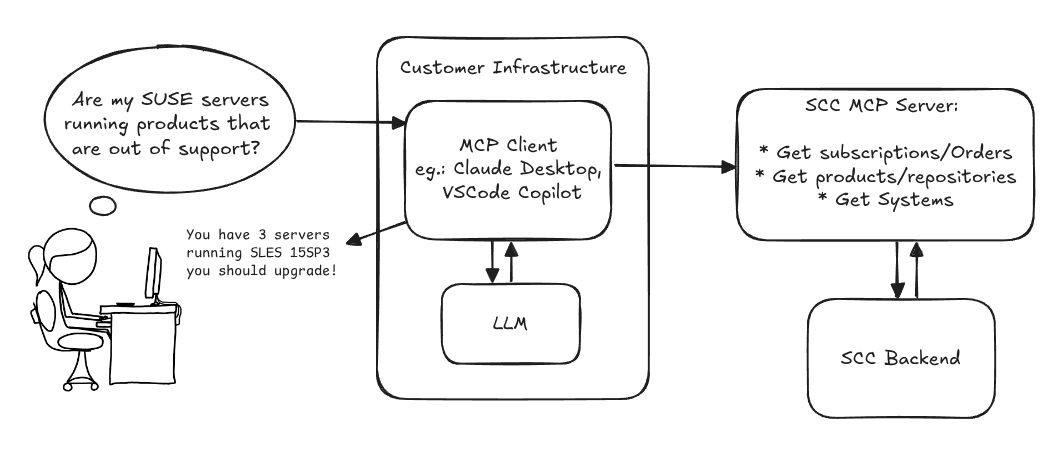
Goals
We want to demonstrate a proof of concept to connect to the SCC MCP server with any AI agent, for example gemini-cli or codex. Enabling the user to ask questions regarding their SCC inventory.
For this Hackweek, we target that users get proper responses to these example questions:
- Which of my currently active systems are running products that are out of support?
- Do I have ready to use registration codes for SLES?
- What are the latest 5 released patches for SLES 15 SP6? Output as a list with release date, patch name, affected package names and fixed CVEs.
- Which versions of kernel-default are available on SLES 15 SP6?
Technical Notes
Similar to the organization APIs, this can expose to customers data about their subscriptions, orders, systems and products. Authentication should be done by organization credentials, similar to what needs to be provided to RMT/MLM. Customers can connect to the SCC MCP server from their own MCP-compatible client and Large Language Model (LLM), so no third party is involved.
Milestones
[x] Basic MCP API setup MCP endpoints [x] Products / Repositories [x] Subscriptions / Orders [x] Systems [x] Packages [x] Document usage with Gemini CLI, Codex
Resources
Gemini CLI setup:
~/.gemini/settings.json:
Is SUSE Trending? Popularity and Developer Sentiment Insight Using Native AI Capabilities by terezacerna
Description
This project aims to explore the popularity and developer sentiment around SUSE and its technologies compared to Red Hat and their technologies. Using publicly available data sources, I will analyze search trends, developer preferences, repository activity, and media presence. The final outcome will be an interactive Power BI dashboard that provides insights into how SUSE is perceived and discussed across the web and among developers.
Goals
- Assess the popularity of SUSE products and brand compared to Red Hat using Google Trends.
- Analyze developer satisfaction and usage trends from the Stack Overflow Developer Survey.
- Use the GitHub API to compare SUSE and Red Hat repositories in terms of stars, forks, contributors, and issue activity.
- Perform sentiment analysis on GitHub issue comments to measure community tone and engagement using built-in Copilot capabilities.
- Perform sentiment analysis on Reddit comments related to SUSE technologies using built-in Copilot capabilities.
- Use Gnews.io to track and compare the volume of news articles mentioning SUSE and Red Hat technologies.
- Test the integration of Copilot (AI) within Power BI for enhanced data analysis and visualization.
- Deliver a comprehensive Power BI report summarizing findings and insights.
- Test the full potential of Power BI, including its AI features and native language Q&A.
Resources
- Google Trends: Web scraping for search popularity data
- Stack Overflow Developer Survey: For technology popularity and satisfaction comparison
- GitHub API: For repository data (stars, forks, contributors, issues, comments).
- Gnews.io API: For article volume and mentions analysis.
- Reddit: SUSE related topics with comments.
Try out Neovim Plugins supporting AI Providers by enavarro_suse
Description
Experiment with several Neovim plugins that integrate AI model providers such as Gemini and Ollama.
Goals
Evaluate how these plugins enhance the development workflow, how they differ in capabilities, and how smoothly they integrate into Neovim for day-to-day coding tasks.
Resources
- Neovim 0.11.5
- AI-enabled Neovim plugins:
- avante.nvim: https://github.com/yetone/avante.nvim
- Gp.nvim: https://github.com/Robitx/gp.nvim
- parrot.nvim: https://github.com/frankroeder/parrot.nvim
- gemini.nvim: https://dotfyle.com/plugins/kiddos/gemini.nvim
- ...
- Accounts or API keys for AI model providers.
- Local model serving setup (e.g., Ollama)
- Test projects or codebases for practical evaluation:
- OBS: https://build.opensuse.org/
- OBS blog and landing page: https://openbuildservice.org/
- ...
Enable more features in mcp-server-uyuni by j_renner
Description
I would like to contribute to mcp-server-uyuni, the MCP server for Uyuni / Multi-Linux Manager) exposing additional features as tools. There is lots of relevant features to be found throughout the API, for example:
- System operations and infos
- System groups
- Maintenance windows
- Ansible
- Reporting
- ...
At the end of the week I managed to enable basic system group operations:
- List all system groups visible to the user
- Create new system groups
- List systems assigned to a group
- Add and remove systems from groups
Goals
- Set up test environment locally with the MCP server and client + a recent MLM server [DONE]
- Identify features and use cases offering a benefit with limited effort required for enablement [DONE]
- Create a PR to the repo [DONE]
Resources
The Agentic Rancher Experiment: Do Androids Dream of Electric Cattle? by moio
Rancher is a beast of a codebase. Let's investigate if the new 2025 generation of GitHub Autonomous Coding Agents and Copilot Workspaces can actually tame it. 
The Plan
Create a sandbox GitHub Organization, clone in key Rancher repositories, and let the AI loose to see if it can handle real-world enterprise OSS maintenance - or if it just hallucinates new breeds of Kubernetes resources!
Specifically, throw "Agentic Coders" some typical tasks in a complex, long-lived open-source project, such as:
❥ The Grunt Work: generate missing GoDocs, unit tests, and refactorings. Rebase PRs.
❥ The Complex Stuff: fix actual (historical) bugs and feature requests to see if they can traverse the complexity without (too much) human hand-holding.
❥ Hunting Down Gaps: find areas lacking in docs, areas of improvement in code, dependency bumps, and so on.
If time allows, also experiment with Model Context Protocol (MCP) to give agents context on our specific build pipelines and CI/CD logs.
Why?
We know AI can write "Hello World." and also moderately complex programs from a green field. But can it rebase a 3-month-old PR with conflicts in rancher/rancher? I want to find the breaking point of current AI agents to determine if and how they can help us to reduce our technical debt, work faster and better. At the same time, find out about pitfalls and shortcomings.
The CONCLUSION!!!
A ![]() State of the Union
State of the Union ![]() document was compiled to summarize lessons learned this week. For more gory details, just read on the diary below!
document was compiled to summarize lessons learned this week. For more gory details, just read on the diary below! ![]()
"what is it" file and directory analysis via MCP and local LLM, for console and KDE by rsimai
Description
Users sometimes wonder what files or directories they find on their local PC are good for. If they can't determine from the filename or metadata, there should an easy way to quickly analyze the content and at least guess the meaning. An LLM could help with that, through the use of a filesystem MCP and to-text-converters for typical file types. Ideally this is integrated into the desktop environment but works as well from a console. All data is processed locally or "on premise", no artifacts remain or leave the system.
Goals
- The user can run a command from the console, to check on a file or directory
- The filemanager contains the "analyze" feature within the context menu
- The local LLM could serve for other use cases where privacy matters
TBD
- Find or write capable one-shot and interactive MCP client
- Find or write simple+secure file access MCP server
- Create local LLM service with appropriate footprint, containerized
- Shell command with options
- KDE integration (Dolphin)
- Package
- Document
Resources
Bugzilla goes AI - Phase 1 by nwalter
Description
This project, Bugzilla goes AI, aims to boost developer productivity by creating an autonomous AI bug agent during Hackweek. The primary goal is to reduce the time employees spend triaging bugs by integrating Ollama to summarize issues, recommend next steps, and push focused daily reports to a Web Interface.
Goals
To reduce employee time spent on Bugzilla by implementing an AI tool that triages and summarizes bug reports, providing actionable recommendations to the team via Web Interface.
Project Charter
Description
Project Achievements during Hackweek
In this file you can read about what we achieved during Hackweek.
SUSE Observability MCP server by drutigliano
Description
The idea is to implement the SUSE Observability Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server as a specialized, middle-tier API designed to translate the complex, high-cardinality observability data from StackState (topology, metrics, and events) into highly structured, contextually rich, and LLM-ready snippets.
This MCP Server abstract the StackState APIs. Its primary function is to serve as a Tool/Function Calling target for AI agents. When an AI receives an alert or a user query (e.g., "What caused the outage?"), the AI calls an MCP Server endpoint. The server then fetches the relevant operational facts, summarizes them, normalizes technical identifiers (like URNs and raw metric names) into natural language concepts, and returns a concise JSON or YAML payload. This payload is then injected directly into the LLM's prompt, ensuring the final diagnosis or action is grounded in real-time, accurate SUSE Observability data, effectively minimizing hallucinations.
Goals
- Grounding AI Responses: Ensure that all AI diagnoses, root cause analyses, and action recommendations are strictly based on verifiable, real-time data retrieved from the SUSE Observability StackState platform.
- Simplifying Data Access: Abstract the complexity of StackState's native APIs (e.g., Time Travel, 4T Data Model) into simple, semantic functions that can be easily invoked by LLM tool-calling mechanisms.
- Data Normalization: Convert complex, technical identifiers (like component URNs, raw metric names, and proprietary health states) into standardized, natural language terms that an LLM can easily reason over.
- Enabling Automated Remediation: Define clear, action-oriented MCP endpoints (e.g., execute_runbook) that allow the AI agent to initiate automated operational workflows (e.g., restarts, scaling) after a diagnosis, closing the loop on observability.
Hackweek STEP
- Create a functional MCP endpoint exposing one (or more) tool(s) to answer queries like "What is the health of service X?") by fetching, normalizing, and returning live StackState data in an LLM-ready format.
Scope
- Implement read-only MCP server that can:
- Connect to a live SUSE Observability instance and authenticate (with API token)
- Use tools to fetch data for a specific component URN (e.g., current health state, metrics, possibly topology neighbors, ...).
- Normalize response fields (e.g., URN to "Service Name," health state DEVIATING to "Unhealthy", raw metrics).
- Return the data as a structured JSON payload compliant with the MCP specification.
Deliverables
- MCP Server v0.1 A running Golang MCP server with at least one tool.
- A README.md and a test script (e.g., curl commands or a simple notebook) showing how an AI agent would call the endpoint and the resulting JSON payload.
Outcome A functional and testable API endpoint that proves the core concept: translating complex StackState data into a simple, LLM-ready format. This provides the foundation for developing AI-driven diagnostics and automated remediation.
Resources
- https://www.honeycomb.io/blog/its-the-end-of-observability-as-we-know-it-and-i-feel-fine
- https://www.datadoghq.com/blog/datadog-remote-mcp-server
- https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/2025-06-18/index
- https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/develop/build-server
Basic implementation
- https://github.com/drutigliano19/suse-observability-mcp-server
Results
Successfully developed and delivered a fully functional SUSE Observability MCP Server that bridges language models with SUSE Observability's operational data. This project demonstrates how AI agents can perform intelligent troubleshooting and root cause analysis using structured access to real-time infrastructure data.
Example execution
Explore LLM evaluation metrics by thbertoldi
Description
Learn the best practices for evaluating LLM performance with an open-source framework such as DeepEval.
Goals
Curate the knowledge learned during practice and present it to colleagues.
-> Maybe publish a blog post on SUSE's blog?
Resources
https://deepeval.com
https://docs.pactflow.io/docs/bi-directional-contract-testing
Extended private brain - RAG my own scripts and data into offline LLM AI by tjyrinki_suse
Description
For purely studying purposes, I'd like to find out if I could teach an LLM some of my own accumulated knowledge, to use it as a sort of extended brain.
I might use qwen3-coder or something similar as a starting point.
Everything would be done 100% offline without network available to the container, since I prefer to see when network is needed, and make it so it's never needed (other than initial downloads).
Goals
- Learn something about RAG, LLM, AI.
- Find out if everything works offline as intended.
- As an end result have a new way to access my own existing know-how, but so that I can query the wisdom in them.
- Be flexible to pivot in any direction, as long as there are new things learned.
Resources
To be found on the fly.
Timeline
Day 1 (of 4)
- Tried out a RAG demo, expanded on feeding it my own data
- Experimented with qwen3-coder to add a persistent chat functionality, and keeping vectors in a pickle file
- Optimizations to keep everything within context window
- Learn and add a bit of PyTest
Day 2
- More experimenting and more data
- Study ChromaDB
- Add a Web UI that works from another computer even though the container sees network is down
Day 3
- The above RAG is working well enough for demonstration purposes.
- Pivot to trying out OpenCode, configuring local Ollama qwen3-coder there, to analyze the RAG demo.
- Figured out how to configure Ollama template to be usable under OpenCode. OpenCode locally is super slow to just running qwen3-coder alone.
Day 4 (final day)
- Battle with OpenCode that was both slow and kept on piling up broken things.
- Call it success as after all the agentic AI was working locally.
- Clean up the mess left behind a bit.
Blog Post
Summarized the findings at blog post.
Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition by mackenzie.techdocs

Description
Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition is an AI-powered documentation navigator that makes finding information across SUSE, Rancher, K3s, and RKE2 documentation effortless. Built as a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, it enables semantic search, intelligent Q&A, and documentation summarization using 100% open-source AI models (no API keys required!). The project also allows you to bring your own keys from Anthropic and Open AI for parallel processing.
Goals
- [ X ] Build functional MCP server with documentation tools
- [ X ] Implement semantic search with vector embeddings
- [ X ] Create user-friendly web interface
- [ X ] Optimize indexing performance (parallel processing)
- [ X ] Add SUSE branding and polish UX
- [ X ] Stretch Goal: Add more documentation sources
- [ X ] Stretch Goal: Implement document change detection for auto-updates
Coming Soon!
- Community Feedback: Test with real users and gather improvement suggestions
Resources
- Repository: Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition GitHub
- UI Demo: Live UI Demo of Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition
Uyuni Health-check Grafana AI Troubleshooter by ygutierrez
Description
This project explores the feasibility of using the open-source Grafana LLM plugin to enhance the Uyuni Health-check tool with LLM capabilities. The idea is to integrate a chat-based "AI Troubleshooter" directly into existing dashboards, allowing users to ask natural-language questions about errors, anomalies, or performance issues.
Goals
- Investigate if and how the
grafana-llm-appplug-in can be used within the Uyuni Health-check tool. - Investigate if this plug-in can be used to query LLMs for troubleshooting scenarios.
- Evaluate support for local LLMs and external APIs through the plugin.
- Evaluate if and how the Uyuni MCP server could be integrated as another source of information.
Resources
Bugzilla goes AI - Phase 1 by nwalter
Description
This project, Bugzilla goes AI, aims to boost developer productivity by creating an autonomous AI bug agent during Hackweek. The primary goal is to reduce the time employees spend triaging bugs by integrating Ollama to summarize issues, recommend next steps, and push focused daily reports to a Web Interface.
Goals
To reduce employee time spent on Bugzilla by implementing an AI tool that triages and summarizes bug reports, providing actionable recommendations to the team via Web Interface.
Project Charter
Description
Project Achievements during Hackweek
In this file you can read about what we achieved during Hackweek.
"what is it" file and directory analysis via MCP and local LLM, for console and KDE by rsimai
Description
Users sometimes wonder what files or directories they find on their local PC are good for. If they can't determine from the filename or metadata, there should an easy way to quickly analyze the content and at least guess the meaning. An LLM could help with that, through the use of a filesystem MCP and to-text-converters for typical file types. Ideally this is integrated into the desktop environment but works as well from a console. All data is processed locally or "on premise", no artifacts remain or leave the system.
Goals
- The user can run a command from the console, to check on a file or directory
- The filemanager contains the "analyze" feature within the context menu
- The local LLM could serve for other use cases where privacy matters
TBD
- Find or write capable one-shot and interactive MCP client
- Find or write simple+secure file access MCP server
- Create local LLM service with appropriate footprint, containerized
- Shell command with options
- KDE integration (Dolphin)
- Package
- Document
Resources
Enable more features in mcp-server-uyuni by j_renner
Description
I would like to contribute to mcp-server-uyuni, the MCP server for Uyuni / Multi-Linux Manager) exposing additional features as tools. There is lots of relevant features to be found throughout the API, for example:
- System operations and infos
- System groups
- Maintenance windows
- Ansible
- Reporting
- ...
At the end of the week I managed to enable basic system group operations:
- List all system groups visible to the user
- Create new system groups
- List systems assigned to a group
- Add and remove systems from groups
Goals
- Set up test environment locally with the MCP server and client + a recent MLM server [DONE]
- Identify features and use cases offering a benefit with limited effort required for enablement [DONE]
- Create a PR to the repo [DONE]
Resources