The Agama project is a multi-language Linux installer that leverages the distinct strengths of several key technologies:
- Rust: Used for the back-end services and the core HTTP API, providing performance and safety.
- TypeScript (React/PatternFly): Powers the modern web user interface (UI), ensuring a consistent and responsive user experience.
- Ruby: Integrates existing, robust YaST libraries (e.g.,
yast-storage-ng) to reuse established functionality.
The Problem: Testing Overhead
Developing and maintaining code across these three languages requires a significant, tedious effort in writing, reviewing, and updating unit tests for each component. This high cost of testing is a drain on developer resources and can slow down the project's evolution.
The Solution: AI-Driven Automation
This project aims to eliminate the manual overhead of unit testing by exploring and integrating AI-driven code generation tools. We will investigate how AI can:
- Automatically generate new unit tests as code is developed.
- Intelligently correct and update existing unit tests when the application code changes.
By automating this crucial but monotonous task, we can free developers to focus on feature implementation and significantly improve the speed and maintainability of the Agama codebase.
Goals
- Proof of Concept: Successfully integrate and demonstrate an authorized AI tool (e.g.,
gemini-cli) to automatically generate unit tests. - Workflow Integration: Define and document a new unit test automation workflow that seamlessly integrates the selected AI tool into the existing Agama development pipeline.
- Knowledge Sharing: Establish a set of best practices for using AI in code generation, sharing the learned expertise with the broader team.
Contribution & Resources
We are seeking contributors interested in AI-powered development and improving developer efficiency. Whether you have previous experience with code generation tools or are eager to learn, your participation is highly valuable.
If you want to dive deep into AI for software quality, please reach out and join the effort!
- Authorized AI Tools: Tools supported by SUSE (e.g.,
gemini-cli) - Focus Areas: Rust, TypeScript, and Ruby components within the Agama project.
Interesting Links
Looking for hackers with the skills:
This project is part of:
Hack Week 25
Activity
Comments
-

2 months ago by ancorgs | Reply
Time for some reporting.
Both @joseivanlopez and me have been doing experiments with AI and the unit tests of Agama's web interface (Javascript + React).
Probably @joseivanlopez will write in more detail about his experience. But this report is about some common experiments we both did using different AI solutions. Let's start with some context.
There is a branch
api-v2in the Agama repository that dramatically changes how the web UI interacts with the backend. The code already works but the javascript unit tests are not adapted accordingly yet. The main idea was to simplify the process of adapting those unit tests with the help of AI.@joseivanlopez did it using the company-provided Gemini, this pull request shows some partial results. Gemini was able to adapt several tests. Although it would be more accurate to say that it rewrote the tests. It feels like it ignored the current unit tests and wrote another ones from scratch. Those generated unit tests are indeed useful, they cover many scenarios and look quite sane, although some of them are not very semantic.
Gemini was not blazing fast (it took 10+ minutes to adapt a single test) and sometimes it struggled to find its way (felt like a pure trial and error process). But the outcome is certainly useful. The experiment can be labeled as a relative success.
But all that applies only to the
gemini-promodel. Sadly it looks like the SUSE-provided license provides a very limited number of tokens to be spend ongemini-pro. After spending those in adapting 4 or 5 unit tests, everything fall backs to the uselessgemini-flashmodel. That means only a few tests per developer can be adapted every day.In parallel I ran a very similar experiment but using Claude.ai, an AI solution that is not endorsed by SUSE, so we cannot use it for production code. I used the completely free version that only provides access to a web console so I had to upload many source-code files manually) and that only allows a few queries to their intermediate model (using it for longer or accessing the advanced model would have implied a fee).
Even with all those limitations, I feel the experiment was clearly more successful than the Gemini one. You can see some partial results in this pull request.
When asked to adapt existing unit tests, Claude really did all the necessary changes to get them running again, but without rewriting everything. Sometimes it added a missing scenario, but it respected the approach of the existing tests and scenarios. When asked to write a new test from scratch, it apparently produced a quite comprehensive and semantic unit test. Claude really felt like a tool that could potentially save a lot of manual work in a reliable way.
Compared to Gemini, Claude was way faster and straight to the point. It was able to produce good results in seconds without really having access to my development environment. Gemini seemed to work a bit more by trial and error, with several iterations of adjusting things to then run the tests and adjust things again.
-

2 months ago by joseivanlopez | Reply
AI Experiment Report: Gemini-CLI for Agama Unit Test Automation
This report summarizes the results of an experiment using the
gemini-clitool (powered by the Gemini Pro model) to automatically update outdated React unit tests in the Agama UI codebase.Scenario & Goal
The Agama UI code was adapted to use a new HTTP API, leaving existing unit tests broken and outdated. The goal was to use
gemini-clito automatically fix and adapt these broken React unit tests.- Tool:
gemini-cli - Model: Gemini Pro
- Example Prompt:
"Fix tests from [@src](/users/src)/components/storage/PartitionPage.test.tsx"
Key Results and Observations
Success and Capability
- High Adaptation Rate: The AI demonstrated its capability to adapt a significant number of existing React tests to the new API structure and component logic. (See results: https://github.com/agama-project/agama/pull/2927)
- Actionable Output: The output was often directly usable, requiring minimal manual cleanup or correction.
Performance and Efficiency Challenges
- Speed/Time: The process was very slow. Adapting a single test suite typically took around 15 minutes. This time investment sometimes approaches or exceeds the time a developer might take to fix the tests manually, impacting developer workflow adoption.
- Reliability: The process was unstable and sometimes stalled completely. This requires developer intervention (canceling the request and resubmitting) to complete the task.
- Strategy: The model appeared to operate in a "try/error" mode (iterative guessing based on error messages) rather than demonstrating a deep comprehension of the code. This trial-and-error approach contributes directly to the poor performance and high latency observed.
Conclusion
Based on the experiment's results, while the Gemini Pro model currently exhibits significant performance issues (slowness and stalling) that make large-scale, automated fixes impractical, it demonstrates core capabilities that point to its potential value in specific scenarios within the Agama project.
Creating Tests From Scratch
Gemini is highly useful for generating the initial boilerplate and structure for new unit tests. A developer shouldn't spend time setting up mocks, imports, and basic assertion structures for a new component. The AI can quickly create a functional test file based solely on the component's public interface. This dramatically lowers the barrier to writing new tests and speeds up the initial development phase, turning test creation from a chore into a rapid scaffolding process.
Progressive and Incremental Adaptation
The AI is valuable for progressive adaptations as code evolves. Instead of waiting for a massive refactor that breaks hundreds of tests (creating a daunting backlog), a developer should use the AI immediately after making small, targeted changes to a component's internal logic, API, or prop structure. This strategy ensures unit tests are fixed incrementally, preventing the large backlog of broken tests that often results from major refactoring efforts.
Resource Constraint: Token Limits
A critical limiting factor impacting the viability of extensive AI usage is the limited token quota provided by SUSE for the Gemini Pro model. Due to the model's observed "try/error" strategy and the resulting high number of queries needed to complete a task, the tokens are consumed rapidly, typically becoming exhausted after only about two hours of intensive usage.
This severe constraint means that even if the performance were better, continuous, large-scale automation is not possible under the current resource allocation.
In summary, given the constraints of high latency and limited token availability, we must pivot our strategy. We should shift the focus from using the AI as a brute-force bug-fixing tool to using it as a scaffolding and incremental maintenance assistant.
- Tool:
-

-

2 months ago by joseivanlopez | Reply
I also experimented with other command-line interface tools, specifically cline. The tool performed exceptionally well, offering the key advantage of enabling concurrent execution of different AI models. This allows for testing free models available through platforms like Ollama (e.g., gpt-oss or deepseek-r1). I utilized it successfully with the cloude-soonet model. However, the severe limitations of the free usage tier ultimately prevented me from conducting any meaningful or conclusive tests.
-

2 months ago by ancorgs | Reply
I ran an extra experiment. Not about unit tests but about code refactoring. TBH, I didn't have time yet to analyze the result. But some of the unit tests are still green (not all of them). See this pull request
-

Similar Projects
Bring up Agama based tests for openSUSE Tumbleweed by szarate
Description
Agama has been around for some time already, and we have some tests for it on Tumbleweed however they are only on the development job group and are too few to be helpful in assessing the quality of a build
This project aims at enabling and creating new testsuites for the agama flavor, using the already existsing DVD and NET flavors as starting points
Goals
- Introduce tests based on the Agama flavor in the main Tumbleweed job group
- Create Tumbleweed yaml schedules for agama installer and its own jsonette profile (The one being used now are reused from leap)
- Fan out tests that have long runtimes (i.e tackle this ticket)
- Reduce redundancy in tests
Resources
Build a terminal user-interface (TUI) for Agama by IGonzalezSosa
Description
Officially, Agama offers two different user interfaces. On the one hand, we have the web-based interface, which is the one you see when you run the installation media. On the other hand, we have a command-line interface. In both cases, you can use them using a remote system, either using a browser or the agama CLI.
We would expect most of the cases to be covered by this approach. However, if you cannot use the web-based interface and, for some reason, you cannot access the system through the network, your only option is to use the CLI. This interface offers a mechanism to modify Agama's configuration using an editor (vim, by default), but perhaps you might want to have a more user-friendly way.
Goals
The main goal of this project is to built a minimal terminal user-interface for Agama. This interface will allow the user to install the system providing just a few settings (selecting a product, a storage device and a user password). Then it should report the installation progress.
Resources
- https://agama-project.github.io/
- https://ratatui.rs/
Conclusions
We have summarized our conclusions in a pull request. It includes screenshots ;-) We did not implement all the features we wanted, but we learn a lot during the process. We know that, if needed, we could write a TUI for Agama and we have an idea about how to build it. Good enough.
"what is it" file and directory analysis via MCP and local LLM, for console and KDE by rsimai
Description
Users sometimes wonder what files or directories they find on their local PC are good for. If they can't determine from the filename or metadata, there should an easy way to quickly analyze the content and at least guess the meaning. An LLM could help with that, through the use of a filesystem MCP and to-text-converters for typical file types. Ideally this is integrated into the desktop environment but works as well from a console. All data is processed locally or "on premise", no artifacts remain or leave the system.
Goals
- The user can run a command from the console, to check on a file or directory
- The filemanager contains the "analyze" feature within the context menu
- The local LLM could serve for other use cases where privacy matters
TBD
- Find or write capable one-shot and interactive MCP client
- Find or write simple+secure file access MCP server
- Create local LLM service with appropriate footprint, containerized
- Shell command with options
- KDE integration (Dolphin)
- Package
- Document
Resources
SUSE Edge Image Builder MCP by eminguez
Description
Based on my other hackweek project, SUSE Edge Image Builder's Json Schema I would like to build also a MCP to be able to generate EIB config files the AI way.
Realistically I don't think I'll be able to have something consumable at the end of this hackweek but at least I would like to start exploring MCPs, the difference between an API and MCP, etc.
Goals
- Familiarize myself with MCPs
- Unrealistic: Have an MCP that can generate an EIB config file
Resources
Result
https://github.com/e-minguez/eib-mcp
I've extensively used antigravity and its agent mode to code this. This heavily uses https://hackweek.opensuse.org/25/projects/suse-edge-image-builder-json-schema for the MCP to be built.
I've ended up learning a lot of things about "prompting", json schemas in general, some golang, MCPs and AI in general :)
Example:
Generate an Edge Image Builder configuration for an ISO image based on slmicro-6.2.iso, targeting x86_64 architecture. The output name should be 'my-edge-image' and it should install to /dev/sda. It should deploy
a 3 nodes kubernetes cluster with nodes names "node1", "node2" and "node3" as:
* hostname: node1, IP: 1.1.1.1, role: initializer
* hostname: node2, IP: 1.1.1.2, role: agent
* hostname: node3, IP: 1.1.1.3, role: agent
The kubernetes version should be k3s 1.33.4-k3s1 and it should deploy a cert-manager helm chart (the latest one available according to https://cert-manager.io/docs/installation/helm/). It should create a user
called "suse" with password "suse" and set ntp to "foo.ntp.org". The VIP address for the API should be 1.2.3.4
Generates:
``` apiVersion: "1.0" image: arch: x86_64 baseImage: slmicro-6.2.iso imageType: iso outputImageName: my-edge-image kubernetes: helm: charts: - name: cert-manager repositoryName: jetstack
Exploring Modern AI Trends and Kubernetes-Based AI Infrastructure by jluo
Description
Build a solid understanding of the current landscape of Artificial Intelligence and how modern cloud-native technologies—especially Kubernetes—support AI workloads.
Goals
Use Gemini Learning Mode to guide the exploration, surface relevant concepts, and structure the learning journey:
- Gain insight into the latest AI trends, tools, and architectural concepts.
- Understand how Kubernetes and related cloud-native technologies are used in the AI ecosystem (model training, deployment, orchestration, MLOps).
Resources
Red Hat AI Topic Articles
- https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/ai
Kubeflow Documentation
- https://www.kubeflow.org/docs/
Q4 2025 CNCF Technology Landscape Radar report:
- https://www.cncf.io/announcements/2025/11/11/cncf-and-slashdata-report-finds-leading-ai-tools-gaining-adoption-in-cloud-native-ecosystems/
- https://www.cncf.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/cncfreporttechradar_111025a.pdf
Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol
- https://developers.googleblog.com/en/a2a-a-new-era-of-agent-interoperability/
Is SUSE Trending? Popularity and Developer Sentiment Insight Using Native AI Capabilities by terezacerna
Description
This project aims to explore the popularity and developer sentiment around SUSE and its technologies compared to Red Hat and their technologies. Using publicly available data sources, I will analyze search trends, developer preferences, repository activity, and media presence. The final outcome will be an interactive Power BI dashboard that provides insights into how SUSE is perceived and discussed across the web and among developers.
Goals
- Assess the popularity of SUSE products and brand compared to Red Hat using Google Trends.
- Analyze developer satisfaction and usage trends from the Stack Overflow Developer Survey.
- Use the GitHub API to compare SUSE and Red Hat repositories in terms of stars, forks, contributors, and issue activity.
- Perform sentiment analysis on GitHub issue comments to measure community tone and engagement using built-in Copilot capabilities.
- Perform sentiment analysis on Reddit comments related to SUSE technologies using built-in Copilot capabilities.
- Use Gnews.io to track and compare the volume of news articles mentioning SUSE and Red Hat technologies.
- Test the integration of Copilot (AI) within Power BI for enhanced data analysis and visualization.
- Deliver a comprehensive Power BI report summarizing findings and insights.
- Test the full potential of Power BI, including its AI features and native language Q&A.
Resources
- Google Trends: Web scraping for search popularity data
- Stack Overflow Developer Survey: For technology popularity and satisfaction comparison
- GitHub API: For repository data (stars, forks, contributors, issues, comments).
- Gnews.io API: For article volume and mentions analysis.
- Reddit: SUSE related topics with comments.
Uyuni Health-check Grafana AI Troubleshooter by ygutierrez
Description
This project explores the feasibility of using the open-source Grafana LLM plugin to enhance the Uyuni Health-check tool with LLM capabilities. The idea is to integrate a chat-based "AI Troubleshooter" directly into existing dashboards, allowing users to ask natural-language questions about errors, anomalies, or performance issues.
Goals
- Investigate if and how the
grafana-llm-appplug-in can be used within the Uyuni Health-check tool. - Investigate if this plug-in can be used to query LLMs for troubleshooting scenarios.
- Evaluate support for local LLMs and external APIs through the plugin.
- Evaluate if and how the Uyuni MCP server could be integrated as another source of information.
Resources
Looking at Rust if it could be an interesting programming language by jsmeix
Get some basic understanding of Rust security related features from a general point of view.
This Hack Week project is not to learn Rust to become a Rust programmer. This might happen later but it is not the goal of this Hack Week project.
The goal of this Hack Week project is to evaluate if Rust could be an interesting programming language.
An interesting programming language must make it easier to write code that is correct and stays correct when over time others maintain and enhance it than the opposite.
Mail client with mailing list workflow support in Rust by acervesato
Description
To create a mail user interface using Rust programming language, supporting mailing list patches workflow. I know, aerc is already there, but I would like to create something simpler, without integrated protocols. Just a plain user interface that is using some crates to read and create emails which are fetched and sent via external tools.
I already know Rust, but not the async support, which is needed in this case in order to handle events inside the mail folder and to send notifications.
Goals
- simple user interface in the style of
aerc, with some vim keybindings for motions and search - automatic run of external tools (like
mbsync) for checking emails - automatic run commands for notifications
- apply patch set from ML
- tree-sitter support with styles
Resources
- ratatui: user interface (https://ratatui.rs/)
- notify: folder watcher (https://docs.rs/notify/latest/notify/)
- mail-parser: parser for emails (https://crates.io/crates/mail-parser)
- mail-builder: create emails in proper format (https://docs.rs/mail-builder/latest/mail_builder/)
- gitpatch: ML support (https://crates.io/crates/gitpatch)
- tree-sitter-rust: support for mail format (https://crates.io/crates/tree-sitter)
OpenPlatform Self-Service Portal by tmuntan1
Description
In SUSE IT, we developed an internal developer platform for our engineers using SUSE technologies such as RKE2, SUSE Virtualization, and Rancher. While it works well for our existing users, the onboarding process could be better.
To improve our customer experience, I would like to build a self-service portal to make it easy for people to accomplish common actions. To get started, I would have the portal create Jira SD tickets for our customers to have better information in our tickets, but eventually I want to add automation to reduce our workload.
Goals
- Build a frontend website (Angular) that helps customers create Jira SD tickets.
- Build a backend (Rust with Axum) for the backend, which would do all the hard work for the frontend.
Resources (SUSE VPN only)
- development site: https://ui-dev.openplatform.suse.com/login?returnUrl=%2Fopenplatform%2Fforms
- https://gitlab.suse.de/itpe/core/open-platform/op-portal/backend
- https://gitlab.suse.de/itpe/core/open-platform/op-portal/frontend
Arcticwolf - A rust based user space NFS server by vcheng
Description
Rust has similar performance to C. Also, have a better async IO module and high integration with io_uring. This project aims to develop a user-space NFS server based on Rust.
Goals
- Get an understanding of how cargo works
- Get an understanding of how XDR was generated with xdrgen
- Create the RUST-based NFS server that supports basic operations like mount/readdir/read/write
Result (2025 Hackweek)
- In progress PR: https://github.com/Vicente-Cheng/arcticwolf/pull/1
Resources
https://github.com/Vicente-Cheng/arcticwolf
RMT.rs: High-Performance Registration Path for RMT using Rust by gbasso
Description
The SUSE Repository Mirroring Tool (RMT) is a critical component for managing software updates and subscriptions, especially for our Public Cloud Team (PCT). In a cloud environment, hundreds or even thousands of new SUSE instances (VPS/EC2) can be provisioned simultaneously. Each new instance attempts to register against an RMT server, creating a "thundering herd" scenario.
We have observed that the current RMT server, written in Ruby, faces performance issues under this high-concurrency registration load. This can lead to request overhead, slow registration times, and outright registration failures, delaying the readiness of new cloud instances.
This Hackweek project aims to explore a solution by re-implementing the performance-critical registration path in Rust. The goal is to leverage Rust's high performance, memory safety, and first-class concurrency handling to create an alternative registration endpoint that is fast, reliable, and can gracefully manage massive, simultaneous request spikes.
The new Rust module will be integrated into the existing RMT Ruby application, allowing us to directly compare the performance of both implementations.
Goals
The primary objective is to build and benchmark a high-performance Rust-based alternative for the RMT server registration endpoint.
Key goals for the week:
- Analyze & Identify: Dive into the
SUSE/rmtRuby codebase to identify and map out the exact critical path for server registration (e.g., controllers, services, database interactions). - Develop in Rust: Implement a functionally equivalent version of this registration logic in Rust.
- Integrate: Explore and implement a method for Ruby/Rust integration to "hot-wire" the new Rust module into the RMT application. This may involve using FFI, or libraries like
rb-sysormagnus. - Benchmark: Create a benchmarking script (e.g., using
k6,ab, or a custom tool) that simulates the high-concurrency registration load from thousands of clients. - Compare & Present: Conduct a comparative performance analysis (requests per second, latency, success/error rates, CPU/memory usage) between the original Ruby path and the new Rust path. The deliverable will be this data and a summary of the findings.
Resources
- RMT Source Code (Ruby):
https://github.com/SUSE/rmt
- RMT Documentation:
https://documentation.suse.com/sles/15-SP7/html/SLES-all/book-rmt.html
- Tooling & Stacks:
- RMT/Ruby development environment (for running the base RMT)
- Rust development environment (
rustup,cargo)
- Potential Integration Libraries:
- rb-sys:
https://github.com/oxidize-rb/rb-sys - Magnus:
https://github.com/matsadler/magnus
- rb-sys:
- Benchmarking Tools:
k6(https://k6.io/)ab(ApacheBench)
Move Uyuni Test Framework from Selenium to Playwright + AI by oscar-barrios
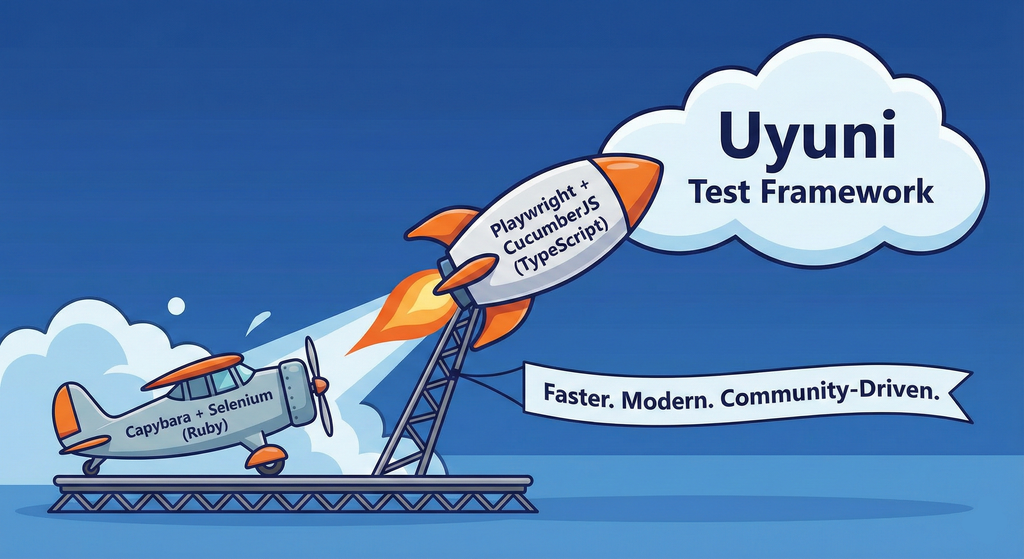
Description
This project aims to migrate the existing Uyuni Test Framework from Selenium to Playwright. The move will improve the stability, speed, and maintainability of our end-to-end tests by leveraging Playwright's modern features. We'll be rewriting the current Selenium code in Ruby to Playwright code in TypeScript, which includes updating the test framework runner, step definitions, and configurations. This is also necessary because we're moving from Cucumber Ruby to CucumberJS.
If you're still curious about the AI in the title, it was just a way to grab your attention. Thanks for your understanding.
Nah, let's be honest ![]() AI helped a lot to vibe code a good part of the Ruby methods of the Test framework, moving them to Typescript, along with the migration from Capybara to Playwright. I've been using "Cline" as plugin for WebStorm IDE, using Gemini API behind it.
AI helped a lot to vibe code a good part of the Ruby methods of the Test framework, moving them to Typescript, along with the migration from Capybara to Playwright. I've been using "Cline" as plugin for WebStorm IDE, using Gemini API behind it.
Goals
- Migrate Core tests including Onboarding of clients
- Improve test reliabillity: Measure and confirm a significant reduction of flakiness.
- Implement a robust framework: Establish a well-structured and reusable Playwright test framework using the CucumberJS
Resources
- Existing Uyuni Test Framework (Cucumber Ruby + Capybara + Selenium)
- My Template for CucumberJS + Playwright in TypeScript
- Started Hackweek Project