Description
For now installing Uyuni on Kubernetes requires running mgradm on a cluster node... which is not what users would do in the Kubernetes world. The idea is to implement an installation based only on helm charts and probably an operator.
Goals
Install Uyuni from Rancher UI.
Resources
mgradmcode: https://github.com/uyuni-project/uyuni-tools- Uyuni operator: https://github.com/cbosdo/uyuni-operator
Looking for hackers with the skills:
This project is part of:
Hack Week 24
Activity
Comments
-

about 1 year ago by cbosdonnat | Reply
At the end of the hackweek 24, the result is very encouraging:
- The server setup can now run in a Job instead of inside the running deployment
- The server installs correctly and the deployment is ready
- Salt systems can bootstrap when using
LoadBalancerservices on k3s. - Uninstalling the custom server resource cleans everything out of the box.
- The only things the user needs is to define the secrets and SSL certificates or the issuers for cert-manager, as well as an uyuni server custom resource.
The code:
- The operator: https://github.com/cbosdo/uyuni-operator
- The Uyuni-tools changes used by the operator: PR #507
- The Uyuni setup cleanup needed to run the setup in a separate pod: PR #9508
What's next:
- Implement migration from an old RPM-based server
- Implement update / upgrade of the server
- Play with more network setups
- Test with more kubernetes distros
-

about 1 year ago by cbosdonnat | Reply
Marked the project as completed as the initial stage is complete. PRs will eventually be polished and merged
-

about 1 year ago by cbosdonnat | Reply
Demo YAML file and video are available in https://github.com/cbosdo/uyuni-operator/tree/main/docs
Similar Projects
Enable more features in mcp-server-uyuni by j_renner
Description
I would like to contribute to mcp-server-uyuni, the MCP server for Uyuni / Multi-Linux Manager) exposing additional features as tools. There is lots of relevant features to be found throughout the API, for example:
- System operations and infos
- System groups
- Maintenance windows
- Ansible
- Reporting
- ...
At the end of the week I managed to enable basic system group operations:
- List all system groups visible to the user
- Create new system groups
- List systems assigned to a group
- Add and remove systems from groups
Goals
- Set up test environment locally with the MCP server and client + a recent MLM server [DONE]
- Identify features and use cases offering a benefit with limited effort required for enablement [DONE]
- Create a PR to the repo [DONE]
Resources
Uyuni Saltboot rework by oholecek
Description
When Uyuni switched over to the containerized proxies we had to abandon salt based saltboot infrastructure we had before. Uyuni already had integration with a Cobbler provisioning server and saltboot infra was re-implemented on top of this Cobbler integration.
What was not obvious from the start was that Cobbler, having all it's features, woefully slow when dealing with saltboot size environments. We did some improvements in performance, introduced transactions, and generally tried to make this setup usable. However the underlying slowness remained.
Goals
This project is not something trying to invent new things, it is just finally implementing saltboot infrastructure directly with the Uyuni server core.
Instead of generating grub and pxelinux configurations by Cobbler for all thousands of systems and branches, we will provide a GET access point to retrieve grub or pxelinux file during the boot:
/saltboot/group/grub/$fqdn and similar for systems /saltboot/system/grub/$mac
Next we adapt our tftpd translator to query these points when asked for default or mac based config.
Lastly similar thing needs to be done on our apache server when HTTP UEFI boot is used.
Resources
Flaky Tests AI Finder for Uyuni and MLM Test Suites by oscar-barrios
Description
Our current Grafana dashboards provide a great overview of test suite health, including a panel for "Top failed tests." However, identifying which of these failures are due to legitimate bugs versus intermittent "flaky tests" is a manual, time-consuming process. These flaky tests erode trust in our test suites and slow down development.
This project aims to build a simple but powerful Python script that automates flaky test detection. The script will directly query our Prometheus instance for the historical data of each failed test, using the jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age metric. It will then format this data and send it to the Gemini API with a carefully crafted prompt, asking it to identify which tests show a flaky pattern.
The final output will be a clean JSON list of the most probable flaky tests, which can then be used to populate a new "Top Flaky Tests" panel in our existing Grafana test suite dashboard.
Goals
By the end of Hack Week, we aim to have a single, working Python script that:
- Connects to Prometheus and executes a query to fetch detailed test failure history.
- Processes the raw data into a format suitable for the Gemini API.
- Successfully calls the Gemini API with the data and a clear prompt.
- Parses the AI's response to extract a simple list of flaky tests.
- Saves the list to a JSON file that can be displayed in Grafana.
- New panel in our Dashboard listing the Flaky tests
Resources
- Jenkins Prometheus Exporter: https://github.com/uyuni-project/jenkins-exporter/
- Data Source: Our internal Prometheus server.
- Key Metric:
jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age{jobname, buildid, suite, case, status, failedsince}. - Existing Query for Reference:
count by (suite) (max_over_time(jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age{status=~"FAILED|REGRESSION", jobname="$jobname"}[$__range])). - AI Model: The Google Gemini API.
- Example about how to interact with Gemini API: https://github.com/srbarrios/FailTale/
- Visualization: Our internal Grafana Dashboard.
- Internal IaC: https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/tree/master/srv/salt/monitoring
Outcome
- Jenkins Flaky Test Detector: https://github.com/srbarrios/jenkins-flaky-tests-detector and its container
- IaC on MLM Team: https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/tree/master/srv/salt/monitoring/jenkinsflakytestsdetector?reftype=heads, https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/blob/master/srv/salt/monitoring/grafana/dashboards/flaky-tests.json?ref_type=heads, and others.
- Grafana Dashboard: https://grafana.mgr.suse.de/d/flaky-tests/flaky-tests-detection @ @ text
Move Uyuni Test Framework from Selenium to Playwright + AI by oscar-barrios
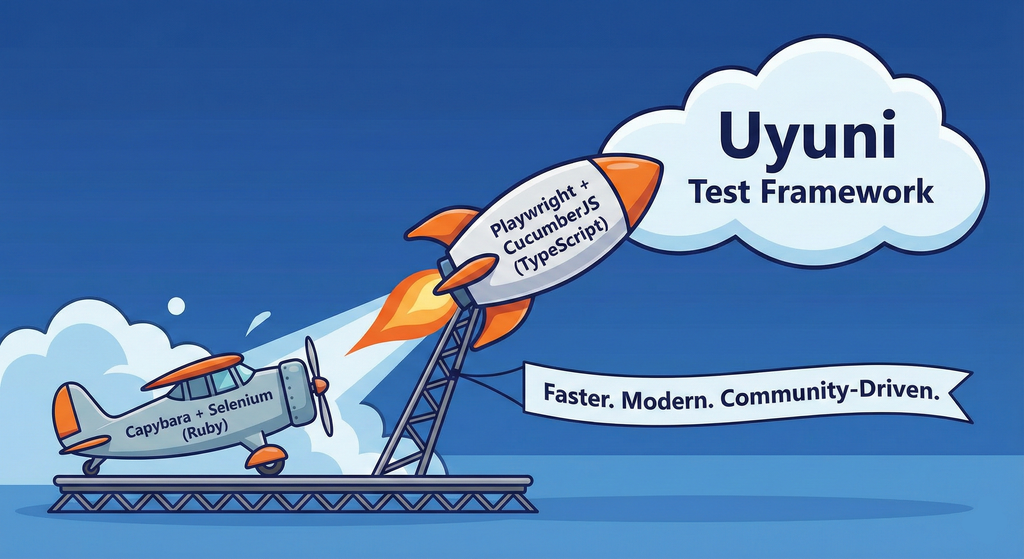
Description
This project aims to migrate the existing Uyuni Test Framework from Selenium to Playwright. The move will improve the stability, speed, and maintainability of our end-to-end tests by leveraging Playwright's modern features. We'll be rewriting the current Selenium code in Ruby to Playwright code in TypeScript, which includes updating the test framework runner, step definitions, and configurations. This is also necessary because we're moving from Cucumber Ruby to CucumberJS.
If you're still curious about the AI in the title, it was just a way to grab your attention. Thanks for your understanding.
Nah, let's be honest ![]() AI helped a lot to vibe code a good part of the Ruby methods of the Test framework, moving them to Typescript, along with the migration from Capybara to Playwright. I've been using "Cline" as plugin for WebStorm IDE, using Gemini API behind it.
AI helped a lot to vibe code a good part of the Ruby methods of the Test framework, moving them to Typescript, along with the migration from Capybara to Playwright. I've been using "Cline" as plugin for WebStorm IDE, using Gemini API behind it.
Goals
- Migrate Core tests including Onboarding of clients
- Improve test reliabillity: Measure and confirm a significant reduction of flakiness.
- Implement a robust framework: Establish a well-structured and reusable Playwright test framework using the CucumberJS
Resources
- Existing Uyuni Test Framework (Cucumber Ruby + Capybara + Selenium)
- My Template for CucumberJS + Playwright in TypeScript
- Started Hackweek Project
Set Uyuni to manage edge clusters at scale by RDiasMateus
Description
Prepare a Poc on how to use MLM to manage edge clusters. Those cluster are normally equal across each location, and we have a large number of them.
The goal is to produce a set of sets/best practices/scripts to help users manage this kind of setup.
Goals
step 1: Manual set-up
Goal: Have a running application in k3s and be able to update it using System Update Controler (SUC)
- Deploy Micro 6.2 machine
Deploy k3s - single node
- https://docs.k3s.io/quick-start
Build/find a simple web application (static page)
- Build/find a helmchart to deploy the application
Deploy the application on the k3s cluster
Install App updates through helm update
Install OS updates using MLM
step 2: Automate day 1
Goal: Trigger the application deployment and update from MLM
- Salt states For application (with static data)
- Deploy the application helmchart, if not present
- install app updates through helmchart parameters
- Link it to GIT
- Define how to link the state to the machines (based in some pillar data? Using configuration channels by importing the state? Naming convention?)
- Use git update to trigger helmchart app update
- Recurrent state applying configuration channel?
step 3: Multi-node cluster
Goal: Use SUC to update a multi-node cluster.
- Create a multi-node cluster
- Deploy application
- call the helm update/install only on control plane?
- Install App updates through helm update
- Prepare a SUC for OS update (k3s also? How?)
- https://github.com/rancher/system-upgrade-controller
- https://documentation.suse.com/cloudnative/k3s/latest/en/upgrades/automated.html
- Update/deploy the SUC?
- Update/deploy the SUC CRD with the update procedure
Technical talks at universities by agamez
Description
This project aims to empower the next generation of tech professionals by offering hands-on workshops on containerization and Kubernetes, with a strong focus on open-source technologies. By providing practical experience with these cutting-edge tools and fostering a deep understanding of open-source principles, we aim to bridge the gap between academia and industry.
For now, the scope is limited to Spanish universities, since we already have the contacts and have started some conversations.
Goals
- Technical Skill Development: equip students with the fundamental knowledge and skills to build, deploy, and manage containerized applications using open-source tools like Kubernetes.
- Open-Source Mindset: foster a passion for open-source software, encouraging students to contribute to open-source projects and collaborate with the global developer community.
- Career Readiness: prepare students for industry-relevant roles by exposing them to real-world use cases, best practices, and open-source in companies.
Resources
- Instructors: experienced open-source professionals with deep knowledge of containerization and Kubernetes.
- SUSE Expertise: leverage SUSE's expertise in open-source technologies to provide insights into industry trends and best practices.
Cluster API Provider for Harvester by rcase
Project Description
The Cluster API "infrastructure provider" for Harvester, also named CAPHV, makes it possible to use Harvester with Cluster API. This enables people and organisations to create Kubernetes clusters running on VMs created by Harvester using a declarative spec.
The project has been bootstrapped in HackWeek 23, and its code is available here.
Work done in HackWeek 2023
- Have a early working version of the provider available on Rancher Sandbox : *DONE *
- Demonstrated the created cluster can be imported using Rancher Turtles: DONE
- Stretch goal - demonstrate using the new provider with CAPRKE2: DONE and the templates are available on the repo
DONE in HackWeek 24:
- Add more Unit Tests
- Improve Status Conditions for some phases
- Add cloud provider config generation
- Testing with Harvester v1.3.2
- Template improvements
- Issues creation
DONE in 2025 (out of Hackweek)
- Support of ClusterClass
- Add to
clusterctlcommunity providers, you can add it directly withclusterctl - Testing on newer versions of Harvester v1.4.X and v1.5.X
- Support for
clusterctl generate cluster ... - Improve Status Conditions to reflect current state of Infrastructure
- Improve CI (some bugs for release creation)
Goals for HackWeek 2025
- FIRST and FOREMOST, any topic is important to you
- Add e2e testing
- Certify the provider for Rancher Turtles
- Add Machine pool labeling
- Add PCI-e passthrough capabilities.
- Other improvement suggestions are welcome!
Thanks to @isim and Dominic Giebert for their contributions!
Resources
Looking for help from anyone interested in Cluster API (CAPI) or who wants to learn more about Harvester.
This will be an infrastructure provider for Cluster API. Some background reading for the CAPI aspect:
Kubernetes-Based ML Lifecycle Automation by lmiranda
Description
This project aims to build a complete end-to-end Machine Learning pipeline running entirely on Kubernetes, using Go, and containerized ML components.
The pipeline will automate the lifecycle of a machine learning model, including:
- Data ingestion/collection
- Model training as a Kubernetes Job
- Model artifact storage in an S3-compatible registry (e.g. Minio)
- A Go-based deployment controller that automatically deploys new model versions to Kubernetes using Rancher
- A lightweight inference service that loads and serves the latest model
- Monitoring of model performance and service health through Prometheus/Grafana
The outcome is a working prototype of an MLOps workflow that demonstrates how AI workloads can be trained, versioned, deployed, and monitored using the Kubernetes ecosystem.
Goals
By the end of Hack Week, the project should:
Produce a fully functional ML pipeline running on Kubernetes with:
- Data collection job
- Training job container
- Storage and versioning of trained models
- Automated deployment of new model versions
- Model inference API service
- Basic monitoring dashboards
Showcase a Go-based deployment automation component, which scans the model registry and automatically generates & applies Kubernetes manifests for new model versions.
Enable continuous improvement by making the system modular and extensible (e.g., additional models, metrics, autoscaling, or drift detection can be added later).
Prepare a short demo explaining the end-to-end process and how new models flow through the system.
Resources
Updates
- Training pipeline and datasets
- Inference Service py
Preparing KubeVirtBMC for project transfer to the KubeVirt organization by zchang
Description
KubeVirtBMC is preparing to transfer the project to the KubeVirt organization. One requirement is to enhance the modeling design's security. The current v1alpha1 API (the VirtualMachineBMC CRD) was designed during the proof-of-concept stage. It's immature and inherently insecure due to its cross-namespace object references, exposing security concerns from an RBAC perspective.
The other long-awaited feature is the ability to mount virtual media so that virtual machines can boot from remote ISO images.
Goals
- Deliver the v1beta1 API and its corresponding controller implementation
- Enable the Redfish virtual media mount function for KubeVirt virtual machines
Resources
- The KubeVirtBMC repo: https://github.com/starbops/kubevirtbmc
- The new v1beta1 API: https://github.com/starbops/kubevirtbmc/issues/83
- Redfish virtual media mount: https://github.com/starbops/kubevirtbmc/issues/44
A CLI for Harvester by mohamed.belgaied
Harvester does not officially come with a CLI tool, the user is supposed to interact with Harvester mostly through the UI. Though it is theoretically possible to use kubectl to interact with Harvester, the manipulation of Kubevirt YAML objects is absolutely not user friendly. Inspired by tools like multipass from Canonical to easily and rapidly create one of multiple VMs, I began the development of Harvester CLI. Currently, it works but Harvester CLI needs some love to be up-to-date with Harvester v1.0.2 and needs some bug fixes and improvements as well.
Project Description
Harvester CLI is a command line interface tool written in Go, designed to simplify interfacing with a Harvester cluster as a user. It is especially useful for testing purposes as you can easily and rapidly create VMs in Harvester by providing a simple command such as:
harvester vm create my-vm --count 5
to create 5 VMs named my-vm-01 to my-vm-05.
Harvester CLI is functional but needs a number of improvements: up-to-date functionality with Harvester v1.0.2 (some minor issues right now), modifying the default behaviour to create an opensuse VM instead of an ubuntu VM, solve some bugs, etc.
Github Repo for Harvester CLI: https://github.com/belgaied2/harvester-cli
Done in previous Hackweeks
- Create a Github actions pipeline to automatically integrate Harvester CLI to Homebrew repositories: DONE
- Automatically package Harvester CLI for OpenSUSE / Redhat RPMs or DEBs: DONE
Goal for this Hackweek
The goal for this Hackweek is to bring Harvester CLI up-to-speed with latest Harvester versions (v1.3.X and v1.4.X), and improve the code quality as well as implement some simple features and bug fixes.
Some nice additions might be: * Improve handling of namespaced objects * Add features, such as network management or Load Balancer creation ? * Add more unit tests and, why not, e2e tests * Improve CI * Improve the overall code quality * Test the program and create issues for it
Issue list is here: https://github.com/belgaied2/harvester-cli/issues
Resources
The project is written in Go, and using client-go the Kubernetes Go Client libraries to communicate with the Harvester API (which is Kubernetes in fact).
Welcome contributions are:
- Testing it and creating issues
- Documentation
- Go code improvement
What you might learn
Harvester CLI might be interesting to you if you want to learn more about:
- GitHub Actions
- Harvester as a SUSE Product
- Go programming language
- Kubernetes API
- Kubevirt API objects (Manipulating VMs and VM Configuration in Kubernetes using Kubevirt)
Q2Boot - A handy QEMU VM launcher by amanzini
Description
Q2Boot (Qemu Quick Boot) is a command-line tool that wraps QEMU to provide a streamlined experience for launching virtual machines. It automatically configures common settings like KVM acceleration, virtio drivers, and networking while allowing customization through both configuration files and command-line options.
The project originally was a personal utility in D, now recently rewritten in idiomatic Go. It lives at repository https://github.com/ilmanzo/q2boot
Goals
Improve the project, testing with different scenarios , address issues and propose new features. It will benefit of some basic integration testing by providing small sample disk images.
Updates
- Dec 1, 2025 : refactor command line options, added structured logging. Released v0.0.2
- Dec 2, 2025 : added external monitor via telnet option
- Dec 4, 2025 : released v0.0.3 with architecture auto-detection
- Dec 5, 2025 : filing new issues and general polishment. Designing E2E testing
Resources
Play with the userfaultfd(2) system call and download on demand using HTTP Range Requests with Golang by rbranco
Description
The userfaultfd(2) is a cool system call to handle page faults in user-space. This should allow me to list the contents of an ISO or similar archive without downloading the whole thing. The userfaultfd(2) part can also be done in theory with the PROT_NONE mprotect + SIGSEGV trick, for complete Unix portability, though reportedly being slower.
Goals
- Create my own library for userfaultfd(2) in Golang.
- Create my own library for HTTP Range Requests.
- Complete portability with Unix.
- Benchmarks.
- Contribute some tests to LTP.
Resources
- https://docs.kernel.org/admin-guide/mm/userfaultfd.html
- https://www.cons.org/cracauer/cracauer-userfaultfd.html
A CLI for Harvester by mohamed.belgaied
Harvester does not officially come with a CLI tool, the user is supposed to interact with Harvester mostly through the UI. Though it is theoretically possible to use kubectl to interact with Harvester, the manipulation of Kubevirt YAML objects is absolutely not user friendly. Inspired by tools like multipass from Canonical to easily and rapidly create one of multiple VMs, I began the development of Harvester CLI. Currently, it works but Harvester CLI needs some love to be up-to-date with Harvester v1.0.2 and needs some bug fixes and improvements as well.
Project Description
Harvester CLI is a command line interface tool written in Go, designed to simplify interfacing with a Harvester cluster as a user. It is especially useful for testing purposes as you can easily and rapidly create VMs in Harvester by providing a simple command such as:
harvester vm create my-vm --count 5
to create 5 VMs named my-vm-01 to my-vm-05.
Harvester CLI is functional but needs a number of improvements: up-to-date functionality with Harvester v1.0.2 (some minor issues right now), modifying the default behaviour to create an opensuse VM instead of an ubuntu VM, solve some bugs, etc.
Github Repo for Harvester CLI: https://github.com/belgaied2/harvester-cli
Done in previous Hackweeks
- Create a Github actions pipeline to automatically integrate Harvester CLI to Homebrew repositories: DONE
- Automatically package Harvester CLI for OpenSUSE / Redhat RPMs or DEBs: DONE
Goal for this Hackweek
The goal for this Hackweek is to bring Harvester CLI up-to-speed with latest Harvester versions (v1.3.X and v1.4.X), and improve the code quality as well as implement some simple features and bug fixes.
Some nice additions might be: * Improve handling of namespaced objects * Add features, such as network management or Load Balancer creation ? * Add more unit tests and, why not, e2e tests * Improve CI * Improve the overall code quality * Test the program and create issues for it
Issue list is here: https://github.com/belgaied2/harvester-cli/issues
Resources
The project is written in Go, and using client-go the Kubernetes Go Client libraries to communicate with the Harvester API (which is Kubernetes in fact).
Welcome contributions are:
- Testing it and creating issues
- Documentation
- Go code improvement
What you might learn
Harvester CLI might be interesting to you if you want to learn more about:
- GitHub Actions
- Harvester as a SUSE Product
- Go programming language
- Kubernetes API
- Kubevirt API objects (Manipulating VMs and VM Configuration in Kubernetes using Kubevirt)
go-git: unlocking SHA256-based repository cloning ahead of git v3 by pgomes
Description
The go-git library implements the git internals in pure Go, so that any Go application can handle not only Git repositories, but also lower-level primitives (e.g. packfiles, idxfiles, etc) without needing to shell out to the git binary.
The focus for this Hackweek is to fast track key improvements for the project ahead of the upstream release of Git V3, which may take place at some point next year.
Goals
- Add support for cloning SHA256 repositories.
- Decrease memory churn for very large repositories (e.g. Linux Kernel repository).
- Cut the first alpha version for
go-git/v6.
Stretch goals
- Review and update the official documentation.
- Optimise use of go-git in Fleet.
- Create RFC/example for go-git plugins to improve extensibility.
- Investigate performance bottlenecks for Blame and Status.
Resources
- https://github.com/go-git/go-git/
- https://go-git.github.io/docs/
terraform-provider-feilong by e_bischoff
Project Description
People need to test operating systems and applications on s390 platform. While this is straightforward with KVM, this is very difficult with z/VM.
IBM Cloud Infrastructure Center (ICIC) harnesses the Feilong API, but you can use Feilong without installing ICIC(see this schema).
What about writing a terraform Feilong provider, just like we have the terraform libvirt provider? That would allow to transparently call Feilong from your main.tf files to deploy and destroy resources on your z/VM system.
Goal for Hackweek 23
I would like to be able to easily deploy and provision VMs automatically on a z/VM system, in a way that people might enjoy even outside of SUSE.
My technical preference is to write a terraform provider plugin, as it is the approach that involves the least software components for our deployments, while remaining clean, and compatible with our existing development infrastructure.
Goals for Hackweek 24
Feilong provider works and is used internally by SUSE Manager team. Let's push it forward!
Let's add support for fiberchannel disks and multipath.
Goals for Hackweek 25
Modernization, maturity, and maintenance: support for SLES 16 and openTofu, new API calls, fixes...
Resources
Outcome
