The idea is to play around with a minecraft-like block exploration game, written from scratch in C using SDL2 and OpenGL 3.0. Minimal dependencies, probably won't be a game as such before the end of the week, but the goal is to have a world generated and to be able to walk around in it. Why? Mainly to refresh my 3D knowledge, catch up with what's happened since I last played with that stuff, and to have fun. :)
The project is now finished, at least as far as I got during this week. There is still a lot remaining to have a proper game.
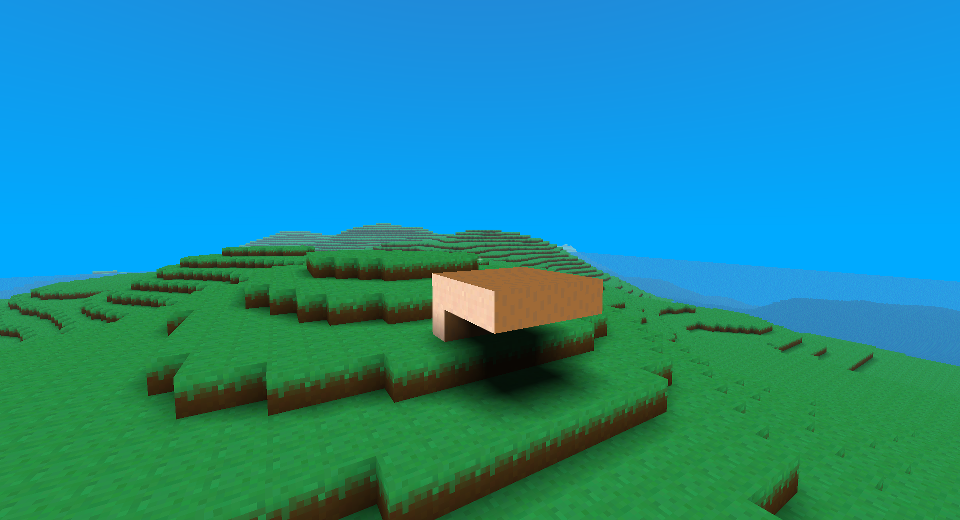
I managed to get a basic block world running with infinitely generating terrain, loading as the player moves around. There is some basic lighting which is visible in one of the screenshots above.
During the process I encountered a lot of interesting problems, mainly reacquainting myself with 3D math and ANSI C (and GDB). The first screenshot above is the result of an interesting bug when adding the functionality to grab screenshots directly in the game. I thought it had a certain aesthetic appeal.
This project is part of:
Hack Week 11
Activity
Comments
Similar Projects
Port some classic game to Linux by MDoucha
Let's pick some old classic game, reverse engineer the data formats and game rules and write an open source engine for it from scratch. Some games from 1990s are simple enough that we could have a playable prototype by the end of the week.
Write which games you'd like to hack on in the comments. Don't forget to check e.g. on Open Source Game Clones, Github and SourceForge whether the game is ported already.
Hack Week 25 - Master of Orion II: Battle at Antares
Work on Master of Orion II continued with Tech Review and Colony list screens.
Hack Week 24 - Master of Orion II: Battle at Antares & Chaos Overlords
Work on Master of Orion II continues but we can hack more than one game. Chaos Overlords is a dystopian, lighthearted, cyberpunk turn-based strategy game originally released in 1996 for Windows 95 and Mac OS. The player takes on the role of a Chaos Overlord, attempting to control a city. Gameplay involves hiring mercenary gangs and deploying them on an 8-by-8 grid of city sectors to generate income, occupy sectors and take over the city.
How to ~~install & play~~ observe the decompilation progress:
- Clone the Git repository
- A playable reimplementation does not exist yet, but when it does, it will be linked in the repository mentioned above.
Further work needed:
- Analyze the remaining unknown data structures, most of which are related to the AI.
- Decompile the AI completely. The strong AI is part of the appeal of the game. It cannot be left out.
- Reimplement the game.
Hack Week 20, 21, 22 & 23 - Master of Orion II: Battle at Antares
Master of Orion II is one of the greatest turn-based 4X games of the 1990s. Explore the galaxy, colonize planets, research new technologies, fight space monsters and alien empires and in the end, become the ruler of the galaxy one way or another.
How to install & play:
- Clone the Git repository
- Run
./bootstrap; ./configure; make && make install - Copy all *.LBX files from the original Master of Orion II to the installation data directory (
/usr/local/share/openorion2by default) - Run
openorion2
Further work needed:
- Analyze the rest of the original savegame format and a few remaining data files.
- Implement most of the game. The open source engine currently supports only loading saved games from the original version and viewing the galaxy map, fleet management and list of known planets.
Hack Week 19 - Signus: The Artifact Wars
Signus is a Czech turn-based strategy game similar to Panzer General or Battle Isle series. Originally published in 1998 and open-sourced by the original developers in 2003.
How to install & play:
- Clone the Git repository
- Run
./bootstrap; ./configure; make && make installin bothsignusandsignus-datadirectories. - Run
signus
Further work needed:
Sim racing track database by avicenzi
Description
Do you wonder which tracks are available in each sim racing game? Wonder no more.
Goals
Create a simple website that includes details about sim racing games.
The website should be static and built with Alpine.JS and TailwindCSS. Data should be consumed from JSON, easily done with Alpine.JS.
The main goal is to gather track information, because tracks vary by game. Older games might have older layouts, and newer games might have up-to-date layouts. Some games include historical layouts, some are laser scanned. Many tracks are available as DLCs.
Initially include official tracks from:
- ACC
- iRacing
- PC2
- LMU
- Raceroom
- Rennsport
These games have a short list of tracks and DLCs.
Resources
The hardest part is collecting information about tracks in each game. Active games usually have information on their website or even on Steam. Older games might be on Fandom or a Wiki. Real track information can be extracted from Wikipedia or the track website.
pudc - A PID 1 process that barks to the internet by mssola
Description
As a fun exercise in order to dig deeper into the Linux kernel, its interfaces, the RISC-V architecture, and all the dragons in between; I'm building a blog site cooked like this:
- The backend is written in a mixture of C and RISC-V assembly.
- The backend is actually PID1 (for real, not within a container).
- We poll and parse incoming HTTP requests ourselves.
- The frontend is a mere HTML page with htmx.
The project is meant to be Linux-specific, so I'm going to use io_uring, pidfs, namespaces, and Linux-specific features in order to drive all of this.
I'm open for suggestions and so on, but this is meant to be a solo project, as this is more of a learning exercise for me than anything else.
Goals
- Have a better understanding of different Linux features from user space down to the kernel internals.
- Most importantly: have fun.
Resources
Port OTPClient to GTK >= 4.18 by pstivanin
Project Description
OTPClient is currently using GTK3 and cannot easily be ported to GTK4. Since GTK4 came out, there have been quite some big changes. Also, there are now some new deprecation that will take effect with GTK5 (and are active starting from 4.10 as warnings), so I need to think ahead and port OTPClient without using any of those deprecated features.
Goal for this Hackweek
- fix the last 3 opened issues (https://github.com/paolostivanin/OTPClient/issues/402, https://github.com/paolostivanin/OTPClient/issues/404, https://github.com/paolostivanin/OTPClient/issues/406) and release a new version
- continue the rewrite from where we left last year
- if possible, finally close this 6 years old issue: https://github.com/paolostivanin/OTPClient/issues/123
Add a machine-readable output to dmidecode by jdelvare
Description
There have been repeated requests for a machine-friendly dmidecode output over the last decade. During Hack Week 19, 5 years ago, I prepared the code to support alternative output formats, but didn't have the time to go further. Last year, Jiri Hnidek from Red Hat Linux posted a proof-of-concept implementation to add JSON output support. This is a fairly large pull request which needs to be carefully reviewed and tested.
Goals
Review Jiri's work and provide constructive feedback. Merge the code if acceptable. Evaluate the costs and benefits of using a library such as json-c.
x64id: An x86/x64 instruction disassembler by m.crivellari
Description
This is an old side project. An x86/x64 machine code decoder. It is useful to get instructions' length and identify each of its fields.
Example:
C7 85 68 FF FF FF 00 00 00 00
This is the instruction:
MOV DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.38],0
What follows are some of the information collected by the disassembler, based on the specific instruction:
RAW bytes (hex): C7 85 68 FF FF FF 00 00 00 00
Instr. length: 10
Print instruction fields:
Located Prefixes 0:
OP: 0xC7
mod_reg_rm: 0x85
disp (4): 0xFFFFFF68
Iimm: 0x0
Lacks the mnemonic representation: from the previous machine code is not able to produce the "MOV..." instruction, for example.
Goals
The goal is almost easy: partially implement the mnemonic representation. I have already started during the weekend, likely tomorrow I will push the branch!
Resources
- The project: https://github.com/DispatchCode/x64-Instruction-Decoder/
- This is useful to avoid gdb and objdump in local: https://defuse.ca/online-x86-assembler.htm
- Another interesting resource is https://godbolt.org/
Progress
- An initial implementation can be found at: https://github.com/DispatchCode/x64-Instruction-Decoder/tree/mnemonic-support It is described under the "Mnemonic translation" in the README file!
Let's consider this example:
[...other bytes...] 43 89 44 B5 00 01 00 [...other bytes...]
Smart lighting with Pico 2 by jmodak
Description
I am trying to create a smart-lighting project with a Raspberry Pi Pico that reacts to a movie's visuals and audio that involves combining two distinct functions: ambient screen lighting(visual response) and sound-reactive lighting(audio response)
Goals
- Visuals: Capturing the screen's colour requires an external device to analyse screen content and send colour data to the MCU via serial communication.
- Audio: A sound sensor module connected directly to the Pico that can detect sound volume.
- Pico 2W: The MCU receives data fro, both inputs and controls an LED strip.
Resources
- Raspberry Pi Pico 2 W
- RGB LED strip
- Sound detecting sensor
- Power supply
- breadboard and wires