Description
This project aims to build a complete end-to-end Machine Learning pipeline running entirely on Kubernetes, using Go, and containerized ML components.
The pipeline will automate the lifecycle of a machine learning model, including:
- Data ingestion/collection
- Model training as a Kubernetes Job
- Model artifact storage in an S3-compatible registry (e.g. Minio)
- A Go-based deployment controller that automatically deploys new model versions to Kubernetes using Rancher
- A lightweight inference service that loads and serves the latest model
- Monitoring of model performance and service health through Prometheus/Grafana
The outcome is a working prototype of an MLOps workflow that demonstrates how AI workloads can be trained, versioned, deployed, and monitored using the Kubernetes ecosystem.
Goals
By the end of Hack Week, the project should:
Produce a fully functional ML pipeline running on Kubernetes with:
- Data collection job
- Training job container
- Storage and versioning of trained models
- Automated deployment of new model versions
- Model inference API service
- Basic monitoring dashboards
Showcase a Go-based deployment automation component, which scans the model registry and automatically generates & applies Kubernetes manifests for new model versions.
Enable continuous improvement by making the system modular and extensible (e.g., additional models, metrics, autoscaling, or drift detection can be added later).
Prepare a short demo explaining the end-to-end process and how new models flow through the system.
Resources
Updates
- Training pipeline and datasets
- Inference Service py
Looking for hackers with the skills:
This project is part of:
Hack Week 25
Activity
Comments
Be the first to comment!
Similar Projects
SUSE Edge Image Builder MCP by eminguez
Description
Based on my other hackweek project, SUSE Edge Image Builder's Json Schema I would like to build also a MCP to be able to generate EIB config files the AI way.
Realistically I don't think I'll be able to have something consumable at the end of this hackweek but at least I would like to start exploring MCPs, the difference between an API and MCP, etc.
Goals
- Familiarize myself with MCPs
- Unrealistic: Have an MCP that can generate an EIB config file
Resources
Result
https://github.com/e-minguez/eib-mcp
I've extensively used antigravity and its agent mode to code this. This heavily uses https://hackweek.opensuse.org/25/projects/suse-edge-image-builder-json-schema for the MCP to be built.
I've ended up learning a lot of things about "prompting", json schemas in general, some golang, MCPs and AI in general :)
Example:
Generate an Edge Image Builder configuration for an ISO image based on slmicro-6.2.iso, targeting x86_64 architecture. The output name should be 'my-edge-image' and it should install to /dev/sda. It should deploy
a 3 nodes kubernetes cluster with nodes names "node1", "node2" and "node3" as:
* hostname: node1, IP: 1.1.1.1, role: initializer
* hostname: node2, IP: 1.1.1.2, role: agent
* hostname: node3, IP: 1.1.1.3, role: agent
The kubernetes version should be k3s 1.33.4-k3s1 and it should deploy a cert-manager helm chart (the latest one available according to https://cert-manager.io/docs/installation/helm/). It should create a user
called "suse" with password "suse" and set ntp to "foo.ntp.org". The VIP address for the API should be 1.2.3.4
Generates:
``` apiVersion: "1.0" image: arch: x86_64 baseImage: slmicro-6.2.iso imageType: iso outputImageName: my-edge-image kubernetes: helm: charts: - name: cert-manager repositoryName: jetstack
Background Coding Agent by mmanno
Description
I had only bad experiences with AI one-shots. However, monitoring agent work closely and interfering often did result in productivity gains.
Now, other companies are using agents in pipelines. That makes sense to me, just like CI, we want to offload work to pipelines: Our engineering teams are consistently slowed down by "toil": low-impact, repetitive maintenance tasks. A simple linter rule change, a dependency bump, rebasing patch-sets on top of newer releases or API deprecation requires dozens of manual PRs, draining time from feature development.
So far we have been writing deterministic, script-based automation for these tasks. And it turns out to be a common trap. These scripts are brittle, complex, and become a massive maintenance burden themselves.
Can we make prompts and workflows smart enough to succeed at background coding?
Goals
We will build a platform that allows engineers to execute complex code transformations using prompts.
By automating this toil, we accelerate large-scale migrations and allow teams to focus on high-value work.
Our platform will consist of three main components:
- "Change" Definition: Engineers will define a transformation as a simple, declarative manifest:
- The target repositories.
- A wrapper to run a "coding agent", e.g., "gemini-cli".
- The task as a natural language prompt.
- The target repositories.
- "Change" Management Service: A central service that orchestrates the jobs. It will receive Change definitions and be responsible for the job lifecycle.
- Execution Runners: We could use existing sandboxed CI runners (like GitHub/GitLab runners) to execute each job or spawn a container.
MVP
- Define the Change manifest format.
- Build the core Management Service that can accept and queue a Change.
- Connect management service and runners, dynamically dispatch jobs to runners.
- Create a basic runner script that can run a hard-coded prompt against a test repo and open a PR.
Stretch Goals:
- Multi-layered approach, Workflow Agents trigger Coding Agents:
- Workflow Agent: Gather information about the task interactively from the user.
- Coding Agent: Once the interactive agent has refined the task into a clear prompt, it hands this prompt off to the "coding agent." This background agent is responsible for executing the task and producing the actual pull request.
- Workflow Agent: Gather information about the task interactively from the user.
- Use MCP:
- Workflow Agent gathers context information from Slack, Github, etc.
- Workflow Agent triggers a Coding Agent.
- Workflow Agent gathers context information from Slack, Github, etc.
- Create a "Standard Task" library with reliable prompts.
- Rebasing rancher-monitoring to a new version of kube-prom-stack
- Update charts to use new images
- Apply changes to comply with a new linter
- Bump complex Go dependencies, like k8s modules
- Backport pull requests to other branches
- Rebasing rancher-monitoring to a new version of kube-prom-stack
- Add “review agents” that review the generated PR.
See also
Backporting patches using LLM by jankara
Description
Backporting Linux kernel fixes (either for CVE issues or as part of general git-fixes workflow) is boring and mostly mechanical work (dealing with changes in context, renamed variables, new helper functions etc.). The idea of this project is to explore usage of LLM for backporting Linux kernel commits to SUSE kernels using LLM.
Goals
- Create safe environment allowing LLM to run and backport patches without exposing the whole filesystem to it (for privacy and security reasons).
- Write prompt that will guide LLM through the backporting process. Fine tune it based on experimental results.
- Explore success rate of LLMs when backporting various patches.
Resources
- Docker
- Gemini CLI
Repository
Current version of the container with some instructions for use are at: https://gitlab.suse.de/jankara/gemini-cli-backporter
Song Search with CLAP by gcolangiuli
Description
Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining (CLAP) is an open-source library that enables the training of a neural network on both Audio and Text descriptions, making it possible to search for Audio using a Text input. Several pre-trained models for song search are already available on huggingface

Goals
Evaluate how CLAP can be used for song searching and determine which types of queries yield the best results by developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in Python. Based on the results of this MVP, future steps could include:
- Music Tagging;
- Free text search;
- Integration with an LLM (for example, with MCP or the OpenAI API) for music suggestions based on your own library.
The code for this project will be entirely written using AI to better explore and demonstrate AI capabilities.
Result
In this MVP we implemented:
- Async Song Analysis with Clap model
- Free Text Search of the songs
- Similar song search based on vector representation
- Containerised version with web interface
We also documented what went well and what can be improved in the use of AI.
You can have a look at the result here:
Future implementation can be related to performance improvement and stability of the analysis.
References
- CLAP: The main model being researched;
- huggingface: Pre-trained models for CLAP;
- Free Music Archive: Creative Commons songs that can be used for testing;
MCP Server for SCC by digitaltomm
Description
Provide an MCP Server implementation for customers to access data on scc.suse.com via MCP protocol. The core benefit of this MCP interface is that it has direct (read) access to customer data in SCC, so the AI agent gets enhanced knowledge about individual customer data, like subscriptions, orders and registered systems.
Architecture
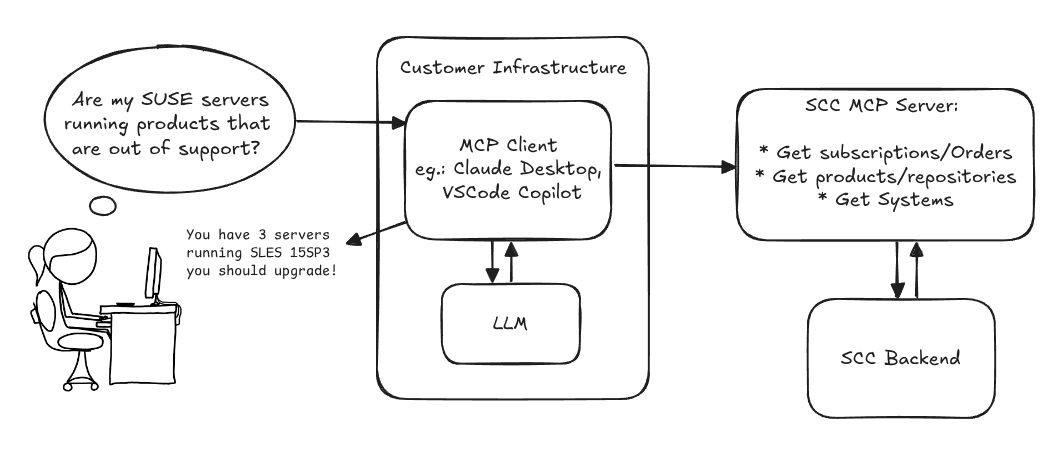
Goals
We want to demonstrate a proof of concept to connect to the SCC MCP server with any AI agent, for example gemini-cli or codex. Enabling the user to ask questions regarding their SCC inventory.
For this Hackweek, we target that users get proper responses to these example questions:
- Which of my currently active systems are running products that are out of support?
- Do I have ready to use registration codes for SLES?
- What are the latest 5 released patches for SLES 15 SP6? Output as a list with release date, patch name, affected package names and fixed CVEs.
- Which versions of kernel-default are available on SLES 15 SP6?
Technical Notes
Similar to the organization APIs, this can expose to customers data about their subscriptions, orders, systems and products. Authentication should be done by organization credentials, similar to what needs to be provided to RMT/MLM. Customers can connect to the SCC MCP server from their own MCP-compatible client and Large Language Model (LLM), so no third party is involved.
Milestones
[x] Basic MCP API setup MCP endpoints [x] Products / Repositories [x] Subscriptions / Orders [x] Systems [x] Packages [x] Document usage with Gemini CLI, Codex
Resources
Gemini CLI setup:
~/.gemini/settings.json:
Exploring Modern AI Trends and Kubernetes-Based AI Infrastructure by jluo
Description
Build a solid understanding of the current landscape of Artificial Intelligence and how modern cloud-native technologies—especially Kubernetes—support AI workloads.
Goals
Use Gemini Learning Mode to guide the exploration, surface relevant concepts, and structure the learning journey:
- Gain insight into the latest AI trends, tools, and architectural concepts.
- Understand how Kubernetes and related cloud-native technologies are used in the AI ecosystem (model training, deployment, orchestration, MLOps).
Resources
Red Hat AI Topic Articles
- https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/ai
Kubeflow Documentation
- https://www.kubeflow.org/docs/
Q4 2025 CNCF Technology Landscape Radar report:
- https://www.cncf.io/announcements/2025/11/11/cncf-and-slashdata-report-finds-leading-ai-tools-gaining-adoption-in-cloud-native-ecosystems/
- https://www.cncf.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/cncfreporttechradar_111025a.pdf
Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol
- https://developers.googleblog.com/en/a2a-a-new-era-of-agent-interoperability/
Preparing KubeVirtBMC for project transfer to the KubeVirt organization by zchang
Description
KubeVirtBMC is preparing to transfer the project to the KubeVirt organization. One requirement is to enhance the modeling design's security. The current v1alpha1 API (the VirtualMachineBMC CRD) was designed during the proof-of-concept stage. It's immature and inherently insecure due to its cross-namespace object references, exposing security concerns from an RBAC perspective.
The other long-awaited feature is the ability to mount virtual media so that virtual machines can boot from remote ISO images.
Goals
- Deliver the v1beta1 API and its corresponding controller implementation
- Enable the Redfish virtual media mount function for KubeVirt virtual machines
Resources
- The KubeVirtBMC repo: https://github.com/starbops/kubevirtbmc
- The new v1beta1 API: https://github.com/starbops/kubevirtbmc/issues/83
- Redfish virtual media mount: https://github.com/starbops/kubevirtbmc/issues/44
Rancher/k8s Trouble-Maker by tonyhansen
Project Description
When studying for my RHCSA, I found trouble-maker, which is a program that breaks a Linux OS and requires you to fix it. I want to create something similar for Rancher/k8s that can allow for troubleshooting an unknown environment.
Goals for Hackweek 25
- Update to modern Rancher and verify that existing tests still work
- Change testing logic to populate secrets instead of requiring a secondary script
- Add new tests
Goals for Hackweek 24 (Complete)
- Create a basic framework for creating Rancher/k8s cluster lab environments as needed for the Break/Fix
- Create at least 5 modules that can be applied to the cluster and require troubleshooting
Resources
- https://github.com/celidon/rancher-troublemaker
- https://github.com/rancher/terraform-provider-rancher2
- https://github.com/rancher/tf-rancher-up
- https://github.com/rancher/quickstart
Self-Scaling LLM Infrastructure Powered by Rancher by ademicev0
Self-Scaling LLM Infrastructure Powered by Rancher

Description
The Problem
Running LLMs can get expensive and complex pretty quickly.
Today there are typically two choices:
- Use cloud APIs like OpenAI or Anthropic. Easy to start with, but costs add up at scale.
- Self-host everything - set up Kubernetes, figure out GPU scheduling, handle scaling, manage model serving... it's a lot of work.
What if there was a middle ground?
What if infrastructure scaled itself instead of making you scale it?
Can we use existing Rancher capabilities like CAPI, autoscaling, and GitOps to make this simpler instead of building everything from scratch?
Project Repository: github.com/alexander-demicev/llmserverless
What This Project Does
A key feature is hybrid deployment: requests can be routed based on complexity or privacy needs. Simple or low-sensitivity queries can use public APIs (like OpenAI), while complex or private requests are handled in-house on local infrastructure. This flexibility allows balancing cost, privacy, and performance - using cloud for routine tasks and on-premises resources for sensitive or demanding workloads.
A complete, self-scaling LLM infrastructure that:
- Scales to zero when idle (no idle costs)
- Scales up automatically when requests come in
- Adds more nodes when needed, removes them when demand drops
- Runs on any infrastructure - laptop, bare metal, or cloud
Think of it as "serverless for LLMs" - focus on building, the infrastructure handles itself.
How It Works
A combination of open source tools working together:
Flow:
- Users interact with OpenWebUI (chat interface)
- Requests go to LiteLLM Gateway
- LiteLLM routes requests to:
- Ollama (Knative) for local model inference (auto-scales pods)
- Or cloud APIs for fallback
A CLI for Harvester by mohamed.belgaied
Harvester does not officially come with a CLI tool, the user is supposed to interact with Harvester mostly through the UI. Though it is theoretically possible to use kubectl to interact with Harvester, the manipulation of Kubevirt YAML objects is absolutely not user friendly. Inspired by tools like multipass from Canonical to easily and rapidly create one of multiple VMs, I began the development of Harvester CLI. Currently, it works but Harvester CLI needs some love to be up-to-date with Harvester v1.0.2 and needs some bug fixes and improvements as well.
Project Description
Harvester CLI is a command line interface tool written in Go, designed to simplify interfacing with a Harvester cluster as a user. It is especially useful for testing purposes as you can easily and rapidly create VMs in Harvester by providing a simple command such as:
harvester vm create my-vm --count 5
to create 5 VMs named my-vm-01 to my-vm-05.
Harvester CLI is functional but needs a number of improvements: up-to-date functionality with Harvester v1.0.2 (some minor issues right now), modifying the default behaviour to create an opensuse VM instead of an ubuntu VM, solve some bugs, etc.
Github Repo for Harvester CLI: https://github.com/belgaied2/harvester-cli
Done in previous Hackweeks
- Create a Github actions pipeline to automatically integrate Harvester CLI to Homebrew repositories: DONE
- Automatically package Harvester CLI for OpenSUSE / Redhat RPMs or DEBs: DONE
Goal for this Hackweek
The goal for this Hackweek is to bring Harvester CLI up-to-speed with latest Harvester versions (v1.3.X and v1.4.X), and improve the code quality as well as implement some simple features and bug fixes.
Some nice additions might be: * Improve handling of namespaced objects * Add features, such as network management or Load Balancer creation ? * Add more unit tests and, why not, e2e tests * Improve CI * Improve the overall code quality * Test the program and create issues for it
Issue list is here: https://github.com/belgaied2/harvester-cli/issues
Resources
The project is written in Go, and using client-go the Kubernetes Go Client libraries to communicate with the Harvester API (which is Kubernetes in fact).
Welcome contributions are:
- Testing it and creating issues
- Documentation
- Go code improvement
What you might learn
Harvester CLI might be interesting to you if you want to learn more about:
- GitHub Actions
- Harvester as a SUSE Product
- Go programming language
- Kubernetes API
- Kubevirt API objects (Manipulating VMs and VM Configuration in Kubernetes using Kubevirt)
Exploring Modern AI Trends and Kubernetes-Based AI Infrastructure by jluo
Description
Build a solid understanding of the current landscape of Artificial Intelligence and how modern cloud-native technologies—especially Kubernetes—support AI workloads.
Goals
Use Gemini Learning Mode to guide the exploration, surface relevant concepts, and structure the learning journey:
- Gain insight into the latest AI trends, tools, and architectural concepts.
- Understand how Kubernetes and related cloud-native technologies are used in the AI ecosystem (model training, deployment, orchestration, MLOps).
Resources
Red Hat AI Topic Articles
- https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/ai
Kubeflow Documentation
- https://www.kubeflow.org/docs/
Q4 2025 CNCF Technology Landscape Radar report:
- https://www.cncf.io/announcements/2025/11/11/cncf-and-slashdata-report-finds-leading-ai-tools-gaining-adoption-in-cloud-native-ecosystems/
- https://www.cncf.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/cncfreporttechradar_111025a.pdf
Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol
- https://developers.googleblog.com/en/a2a-a-new-era-of-agent-interoperability/
Advent of Code: The Diaries by amanzini
Description
It was the Night Before Compile Time ...
Hackweek 25 (December 1-5) perfectly coincides with the first five days of Advent of Code 2025. This project will leverage this overlap to participate in the event in real-time.
To add a layer of challenge and exploration (in the true spirit of Hackweek), the puzzles will be solved using a non-mainstream, modern language like Ruby, D, Crystal, Gleam or Zig.
The primary project intent is not just simply to solve the puzzles, but to exercise result sharing and documentation. I'd create a public-facing repository documenting the process. This involves treating each day's puzzle as a mini-project: solving it, then documenting the solution with detailed write-ups, analysis of the language's performance and ergonomics, and visualizations.
|
\ ' /
-- (*) --
>*<
>0<@<
>>>@<<*
>@>*<0<<<
>*>>@<<<@<<
>@>>0<<<*<<@<
>*>>0<<@<<<@<<<
>@>>*<<@<>*<<0<*<
\*/ >0>>*<<@<>0><<*<@<<
___\\U//___ >*>>@><0<<*>>@><*<0<<
|\\ | | \\| >@>>0<*<0>>@<<0<<<*<@<<
| \\| | _(UU)_ >((*))_>0><*<0><@<<<0<*<
|\ \| || / //||.*.*.*.|>>@<<*<<@>><0<<<
|\\_|_|&&_// ||*.*.*.*|_\\db//_
""""|'.'.'.|~~|.*.*.*| ____|_
|'.'.'.| ^^^^^^|____|>>>>>>|
~~~~~~~~ '""""`------'
------------------------------------------------
This ASCII pic can be found at
https://asciiart.website/art/1831
Goals
Code, Docs, and Memes: An AoC Story
Have fun!
Involve more people, play together
Solve Days 1-5: Successfully solve both parts of the Advent of Code 2025 puzzles for Days 1-5 using the chosen non-mainstream language.
Daily Documentation & Language Review: Publish a detailed write-up for each day. This documentation will include the solution analysis, the chosen algorithm, and specific commentary on the language's ergonomics, performance, and standard library for the given task.
