Description
Our current Grafana dashboards provide a great overview of test suite health, including a panel for "Top failed tests." However, identifying which of these failures are due to legitimate bugs versus intermittent "flaky tests" is a manual, time-consuming process. These flaky tests erode trust in our test suites and slow down development.
This project aims to build a simple but powerful Python script that automates flaky test detection. The script will directly query our Prometheus instance for the historical data of each failed test, using the jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age metric. It will then format this data and send it to the Gemini API with a carefully crafted prompt, asking it to identify which tests show a flaky pattern.
The final output will be a clean JSON list of the most probable flaky tests, which can then be used to populate a new "Top Flaky Tests" panel in our existing Grafana test suite dashboard.
Goals
By the end of Hack Week, we aim to have a single, working Python script that:
- Connects to Prometheus and executes a query to fetch detailed test failure history.
- Processes the raw data into a format suitable for the Gemini API.
- Successfully calls the Gemini API with the data and a clear prompt.
- Parses the AI's response to extract a simple list of flaky tests.
- Saves the list to a JSON file that can be displayed in Grafana.
- New panel in our Dashboard listing the Flaky tests
Resources
- Jenkins Prometheus Exporter: https://github.com/uyuni-project/jenkins-exporter/
- Data Source: Our internal Prometheus server.
- Key Metric:
jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age{jobname, buildid, suite, case, status, failedsince}. - Existing Query for Reference:
count by (suite) (max_over_time(jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age{status=~"FAILED|REGRESSION", jobname="$jobname"}[$__range])). - AI Model: The Google Gemini API.
- Example about how to interact with Gemini API: https://github.com/srbarrios/FailTale/
- Visualization: Our internal Grafana Dashboard.
- Internal IaC: https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/tree/master/srv/salt/monitoring
Outcome
- Jenkins Flaky Test Detector: https://github.com/srbarrios/jenkins-flaky-tests-detector and its container
- IaC on MLM Team: https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/tree/master/srv/salt/monitoring/jenkinsflakytestsdetector?reftype=heads, https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/blob/master/srv/salt/monitoring/grafana/dashboards/flaky-tests.json?ref_type=heads, and others.
- Grafana Dashboard: https://grafana.mgr.suse.de/d/flaky-tests/flaky-tests-detection @ @ text
Looking for hackers with the skills:
This project is part of:
Hack Week 25
Activity
Comments
-

about 2 months ago by oscar-barrios | Reply
The code of the flaky detector is here: https://github.com/srbarrios/jenkins-flaky-tests-detector
I also published a Docker container to use it here: https://github.com/srbarrios/jenkins-flaky-tests-detector/pkgs/container/jenkins-flaky-tests-detector
The plan now is to write a Salt state in our MLM internal infra, so it runs this container, it expose the results in a web server running on the container, and then I parse it on Grafana.
-

about 2 months ago by oscar-barrios | Reply
I created the new Grafana dashboard for Uyuni here: https://grafana.mgr.suse.de/d/flaky-tests/flaky-tests-detection?orgId=1&from=now-6h&to=now&timezone=browser&refresh=1m
Next step now is to build it in a way that I can get the flaky tests for all the Jenkins job test results that we monitoring in MLM.
-

about 2 months ago by oscar-barrios | Reply
Now we can select any of the running test suites, and get a list of the most probable flaky tests :)
-

about 2 months ago by oscar-barrios | Reply
I will consider this hackweek done for now, to move to my second hackweek project. The outcome it has been good, I must admit that I also vibe coded some parts using Gemini 3. Also, the script analyzing the prometheus series is not relying only on a LLM call, but it also do a first triage based on a simple algorithm, saving resources to ask AI only for ambiguos and complex test failures.
Similar Projects
Set Uyuni to manage edge clusters at scale by RDiasMateus
Description
Prepare a Poc on how to use MLM to manage edge clusters. Those cluster are normally equal across each location, and we have a large number of them.
The goal is to produce a set of sets/best practices/scripts to help users manage this kind of setup.
Goals
step 1: Manual set-up
Goal: Have a running application in k3s and be able to update it using System Update Controler (SUC)
- Deploy Micro 6.2 machine
Deploy k3s - single node
- https://docs.k3s.io/quick-start
Build/find a simple web application (static page)
- Build/find a helmchart to deploy the application
Deploy the application on the k3s cluster
Install App updates through helm update
Install OS updates using MLM
step 2: Automate day 1
Goal: Trigger the application deployment and update from MLM
- Salt states For application (with static data)
- Deploy the application helmchart, if not present
- install app updates through helmchart parameters
- Link it to GIT
- Define how to link the state to the machines (based in some pillar data? Using configuration channels by importing the state? Naming convention?)
- Use git update to trigger helmchart app update
- Recurrent state applying configuration channel?
step 3: Multi-node cluster
Goal: Use SUC to update a multi-node cluster.
- Create a multi-node cluster
- Deploy application
- call the helm update/install only on control plane?
- Install App updates through helm update
- Prepare a SUC for OS update (k3s also? How?)
- https://github.com/rancher/system-upgrade-controller
- https://documentation.suse.com/cloudnative/k3s/latest/en/upgrades/automated.html
- Update/deploy the SUC?
- Update/deploy the SUC CRD with the update procedure
Testing and adding GNU/Linux distributions on Uyuni by juliogonzalezgil
Join the Gitter channel! https://gitter.im/uyuni-project/hackweek
Uyuni is a configuration and infrastructure management tool that saves you time and headaches when you have to manage and update tens, hundreds or even thousands of machines. It also manages configuration, can run audits, build image containers, monitor and much more!
Currently there are a few distributions that are completely untested on Uyuni or SUSE Manager (AFAIK) or just not tested since a long time, and could be interesting knowing how hard would be working with them and, if possible, fix whatever is broken.
For newcomers, the easiest distributions are those based on DEB or RPM packages. Distributions with other package formats are doable, but will require adapting the Python and Java code to be able to sync and analyze such packages (and if salt does not support those packages, it will need changes as well). So if you want a distribution with other packages, make sure you are comfortable handling such changes.
No developer experience? No worries! We had non-developers contributors in the past, and we are ready to help as long as you are willing to learn. If you don't want to code at all, you can also help us preparing the documentation after someone else has the initial code ready, or you could also help with testing :-)
The idea is testing Salt (including bootstrapping with bootstrap script) and Salt-ssh clients
To consider that a distribution has basic support, we should cover at least (points 3-6 are to be tested for both salt minions and salt ssh minions):
- Reposync (this will require using spacewalk-common-channels and adding channels to the .ini file)
- Onboarding (salt minion from UI, salt minion from bootstrap scritp, and salt-ssh minion) (this will probably require adding OS to the bootstrap repository creator)
- Package management (install, remove, update...)
- Patching
- Applying any basic salt state (including a formula)
- Salt remote commands
- Bonus point: Java part for product identification, and monitoring enablement
- Bonus point: sumaform enablement (https://github.com/uyuni-project/sumaform)
- Bonus point: Documentation (https://github.com/uyuni-project/uyuni-docs)
- Bonus point: testsuite enablement (https://github.com/uyuni-project/uyuni/tree/master/testsuite)
If something is breaking: we can try to fix it, but the main idea is research how supported it is right now. Beyond that it's up to each project member how much to hack :-)
- If you don't have knowledge about some of the steps: ask the team
- If you still don't know what to do: switch to another distribution and keep testing.
This card is for EVERYONE, not just developers. Seriously! We had people from other teams helping that were not developers, and added support for Debian and new SUSE Linux Enterprise and openSUSE Leap versions :-)
In progress/done for Hack Week 25
Guide
We started writin a Guide: Adding a new client GNU Linux distribution to Uyuni at https://github.com/uyuni-project/uyuni/wiki/Guide:-Adding-a-new-client-GNU-Linux-distribution-to-Uyuni, to make things easier for everyone, specially those not too familiar wht Uyuni or not technical.
openSUSE Leap 16.0
The distribution will all love!
https://en.opensuse.org/openSUSE:Roadmap#DRAFTScheduleforLeap16.0
Curent Status We started last year, it's complete now for Hack Week 25! :-D
[W]Reposync (this will require using spacewalk-common-channels and adding channels to the .ini file) NOTE: Done, client tools for SLMicro6 are using as those for SLE16.0/openSUSE Leap 16.0 are not available yet[W]Onboarding (salt minion from UI, salt minion from bootstrap scritp, and salt-ssh minion) (this will probably require adding OS to the bootstrap repository creator)[W]Package management (install, remove, update...). Works, even reboot requirement detection
Enhance setup wizard for Uyuni by PSuarezHernandez
Description
This project wants to enhance the intial setup on Uyuni after its installation, so it's easier for a user to start using with it.
Uyuni currently uses "uyuni-tools" (mgradm) as the installation entrypoint, to trigger the installation of Uyuni in the given host, but does not really perform an initial setup, for instance:
- user creation
- adding products / channels
- generating bootstrap repos
- create activation keys
- ...
Goals
- Provide initial setup wizard as part of mgradm uyuni installation
Resources
Uyuni Saltboot rework by oholecek
Description
When Uyuni switched over to the containerized proxies we had to abandon salt based saltboot infrastructure we had before. Uyuni already had integration with a Cobbler provisioning server and saltboot infra was re-implemented on top of this Cobbler integration.
What was not obvious from the start was that Cobbler, having all it's features, woefully slow when dealing with saltboot size environments. We did some improvements in performance, introduced transactions, and generally tried to make this setup usable. However the underlying slowness remained.
Goals
This project is not something trying to invent new things, it is just finally implementing saltboot infrastructure directly with the Uyuni server core.
Instead of generating grub and pxelinux configurations by Cobbler for all thousands of systems and branches, we will provide a GET access point to retrieve grub or pxelinux file during the boot:
/saltboot/group/grub/$fqdn and similar for systems /saltboot/system/grub/$mac
Next we adapt our tftpd translator to query these points when asked for default or mac based config.
Lastly similar thing needs to be done on our apache server when HTTP UEFI boot is used.
Resources
Enable more features in mcp-server-uyuni by j_renner
Description
I would like to contribute to mcp-server-uyuni, the MCP server for Uyuni / Multi-Linux Manager) exposing additional features as tools. There is lots of relevant features to be found throughout the API, for example:
- System operations and infos
- System groups
- Maintenance windows
- Ansible
- Reporting
- ...
At the end of the week I managed to enable basic system group operations:
- List all system groups visible to the user
- Create new system groups
- List systems assigned to a group
- Add and remove systems from groups
Goals
- Set up test environment locally with the MCP server and client + a recent MLM server [DONE]
- Identify features and use cases offering a benefit with limited effort required for enablement [DONE]
- Create a PR to the repo [DONE]
Resources
Uyuni Health-check Grafana AI Troubleshooter by ygutierrez
Description
This project explores the feasibility of using the open-source Grafana LLM plugin to enhance the Uyuni Health-check tool with LLM capabilities. The idea is to integrate a chat-based "AI Troubleshooter" directly into existing dashboards, allowing users to ask natural-language questions about errors, anomalies, or performance issues.
Goals
- Investigate if and how the
grafana-llm-appplug-in can be used within the Uyuni Health-check tool. - Investigate if this plug-in can be used to query LLMs for troubleshooting scenarios.
- Evaluate support for local LLMs and external APIs through the plugin.
- Evaluate if and how the Uyuni MCP server could be integrated as another source of information.
Resources
SUSE Observability MCP server by drutigliano
Description
The idea is to implement the SUSE Observability Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server as a specialized, middle-tier API designed to translate the complex, high-cardinality observability data from StackState (topology, metrics, and events) into highly structured, contextually rich, and LLM-ready snippets.
This MCP Server abstract the StackState APIs. Its primary function is to serve as a Tool/Function Calling target for AI agents. When an AI receives an alert or a user query (e.g., "What caused the outage?"), the AI calls an MCP Server endpoint. The server then fetches the relevant operational facts, summarizes them, normalizes technical identifiers (like URNs and raw metric names) into natural language concepts, and returns a concise JSON or YAML payload. This payload is then injected directly into the LLM's prompt, ensuring the final diagnosis or action is grounded in real-time, accurate SUSE Observability data, effectively minimizing hallucinations.
Goals
- Grounding AI Responses: Ensure that all AI diagnoses, root cause analyses, and action recommendations are strictly based on verifiable, real-time data retrieved from the SUSE Observability StackState platform.
- Simplifying Data Access: Abstract the complexity of StackState's native APIs (e.g., Time Travel, 4T Data Model) into simple, semantic functions that can be easily invoked by LLM tool-calling mechanisms.
- Data Normalization: Convert complex, technical identifiers (like component URNs, raw metric names, and proprietary health states) into standardized, natural language terms that an LLM can easily reason over.
- Enabling Automated Remediation: Define clear, action-oriented MCP endpoints (e.g., execute_runbook) that allow the AI agent to initiate automated operational workflows (e.g., restarts, scaling) after a diagnosis, closing the loop on observability.
Hackweek STEP
- Create a functional MCP endpoint exposing one (or more) tool(s) to answer queries like "What is the health of service X?") by fetching, normalizing, and returning live StackState data in an LLM-ready format.
Scope
- Implement read-only MCP server that can:
- Connect to a live SUSE Observability instance and authenticate (with API token)
- Use tools to fetch data for a specific component URN (e.g., current health state, metrics, possibly topology neighbors, ...).
- Normalize response fields (e.g., URN to "Service Name," health state DEVIATING to "Unhealthy", raw metrics).
- Return the data as a structured JSON payload compliant with the MCP specification.
Deliverables
- MCP Server v0.1 A running Golang MCP server with at least one tool.
- A README.md and a test script (e.g., curl commands or a simple notebook) showing how an AI agent would call the endpoint and the resulting JSON payload.
Outcome A functional and testable API endpoint that proves the core concept: translating complex StackState data into a simple, LLM-ready format. This provides the foundation for developing AI-driven diagnostics and automated remediation.
Resources
- https://www.honeycomb.io/blog/its-the-end-of-observability-as-we-know-it-and-i-feel-fine
- https://www.datadoghq.com/blog/datadog-remote-mcp-server
- https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/2025-06-18/index
- https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/develop/build-server
Basic implementation
- https://github.com/drutigliano19/suse-observability-mcp-server
Results
Successfully developed and delivered a fully functional SUSE Observability MCP Server that bridges language models with SUSE Observability's operational data. This project demonstrates how AI agents can perform intelligent troubleshooting and root cause analysis using structured access to real-time infrastructure data.
Example execution
Song Search with CLAP by gcolangiuli
Description
Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining (CLAP) is an open-source library that enables the training of a neural network on both Audio and Text descriptions, making it possible to search for Audio using a Text input. Several pre-trained models for song search are already available on huggingface

Goals
Evaluate how CLAP can be used for song searching and determine which types of queries yield the best results by developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in Python. Based on the results of this MVP, future steps could include:
- Music Tagging;
- Free text search;
- Integration with an LLM (for example, with MCP or the OpenAI API) for music suggestions based on your own library.
The code for this project will be entirely written using AI to better explore and demonstrate AI capabilities.
Result
In this MVP we implemented:
- Async Song Analysis with Clap model
- Free Text Search of the songs
- Similar song search based on vector representation
- Containerised version with web interface
We also documented what went well and what can be improved in the use of AI.
You can have a look at the result here:
Future implementation can be related to performance improvement and stability of the analysis.
References
- CLAP: The main model being researched;
- huggingface: Pre-trained models for CLAP;
- Free Music Archive: Creative Commons songs that can be used for testing;
Enable more features in mcp-server-uyuni by j_renner
Description
I would like to contribute to mcp-server-uyuni, the MCP server for Uyuni / Multi-Linux Manager) exposing additional features as tools. There is lots of relevant features to be found throughout the API, for example:
- System operations and infos
- System groups
- Maintenance windows
- Ansible
- Reporting
- ...
At the end of the week I managed to enable basic system group operations:
- List all system groups visible to the user
- Create new system groups
- List systems assigned to a group
- Add and remove systems from groups
Goals
- Set up test environment locally with the MCP server and client + a recent MLM server [DONE]
- Identify features and use cases offering a benefit with limited effort required for enablement [DONE]
- Create a PR to the repo [DONE]
Resources
The Agentic Rancher Experiment: Do Androids Dream of Electric Cattle? by moio
Rancher is a beast of a codebase. Let's investigate if the new 2025 generation of GitHub Autonomous Coding Agents and Copilot Workspaces can actually tame it. 
The Plan
Create a sandbox GitHub Organization, clone in key Rancher repositories, and let the AI loose to see if it can handle real-world enterprise OSS maintenance - or if it just hallucinates new breeds of Kubernetes resources!
Specifically, throw "Agentic Coders" some typical tasks in a complex, long-lived open-source project, such as:
❥ The Grunt Work: generate missing GoDocs, unit tests, and refactorings. Rebase PRs.
❥ The Complex Stuff: fix actual (historical) bugs and feature requests to see if they can traverse the complexity without (too much) human hand-holding.
❥ Hunting Down Gaps: find areas lacking in docs, areas of improvement in code, dependency bumps, and so on.
If time allows, also experiment with Model Context Protocol (MCP) to give agents context on our specific build pipelines and CI/CD logs.
Why?
We know AI can write "Hello World." and also moderately complex programs from a green field. But can it rebase a 3-month-old PR with conflicts in rancher/rancher? I want to find the breaking point of current AI agents to determine if and how they can help us to reduce our technical debt, work faster and better. At the same time, find out about pitfalls and shortcomings.
The CONCLUSION!!!
A ![]() State of the Union
State of the Union ![]() document was compiled to summarize lessons learned this week. For more gory details, just read on the diary below!
document was compiled to summarize lessons learned this week. For more gory details, just read on the diary below! ![]()
"what is it" file and directory analysis via MCP and local LLM, for console and KDE by rsimai
Description
Users sometimes wonder what files or directories they find on their local PC are good for. If they can't determine from the filename or metadata, there should an easy way to quickly analyze the content and at least guess the meaning. An LLM could help with that, through the use of a filesystem MCP and to-text-converters for typical file types. Ideally this is integrated into the desktop environment but works as well from a console. All data is processed locally or "on premise", no artifacts remain or leave the system.
Goals
- The user can run a command from the console, to check on a file or directory
- The filemanager contains the "analyze" feature within the context menu
- The local LLM could serve for other use cases where privacy matters
TBD
- Find or write capable one-shot and interactive MCP client
- Find or write simple+secure file access MCP server
- Create local LLM service with appropriate footprint, containerized
- Shell command with options
- KDE integration (Dolphin)
- Package
- Document
Resources
Move Uyuni Test Framework from Selenium to Playwright + AI by oscar-barrios
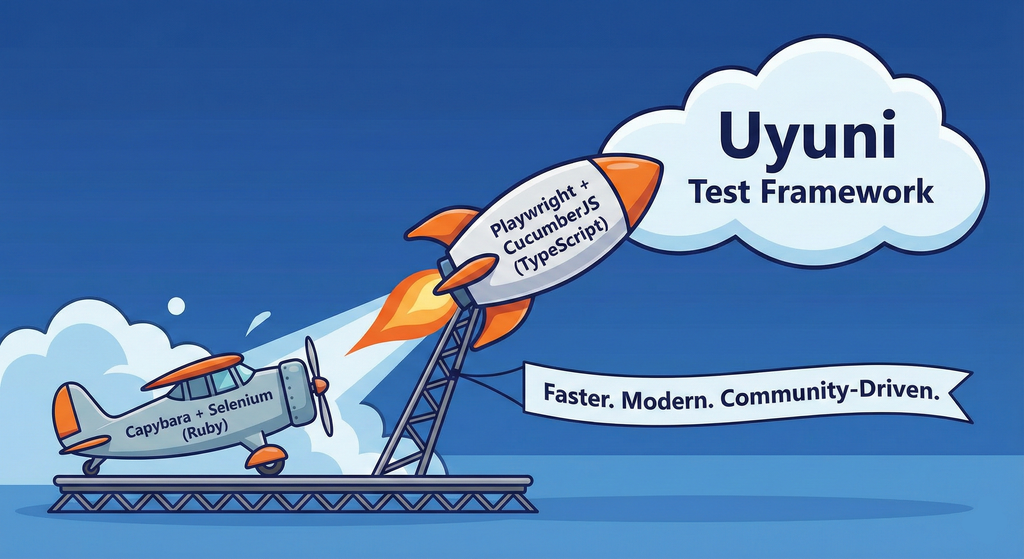
Description
This project aims to migrate the existing Uyuni Test Framework from Selenium to Playwright. The move will improve the stability, speed, and maintainability of our end-to-end tests by leveraging Playwright's modern features. We'll be rewriting the current Selenium code in Ruby to Playwright code in TypeScript, which includes updating the test framework runner, step definitions, and configurations. This is also necessary because we're moving from Cucumber Ruby to CucumberJS.
If you're still curious about the AI in the title, it was just a way to grab your attention. Thanks for your understanding.
Nah, let's be honest ![]() AI helped a lot to vibe code a good part of the Ruby methods of the Test framework, moving them to Typescript, along with the migration from Capybara to Playwright. I've been using "Cline" as plugin for WebStorm IDE, using Gemini API behind it.
AI helped a lot to vibe code a good part of the Ruby methods of the Test framework, moving them to Typescript, along with the migration from Capybara to Playwright. I've been using "Cline" as plugin for WebStorm IDE, using Gemini API behind it.
Goals
- Migrate Core tests including Onboarding of clients
- Improve test reliabillity: Measure and confirm a significant reduction of flakiness.
- Implement a robust framework: Establish a well-structured and reusable Playwright test framework using the CucumberJS
Resources
- Existing Uyuni Test Framework (Cucumber Ruby + Capybara + Selenium)
- My Template for CucumberJS + Playwright in TypeScript
- Started Hackweek Project