Description
In SUMA/Uyuni team we spend a lot of time reviewing test reports, analyzing each of the test cases failing, checking if the test is a flaky test, checking logs, etc.
Goals
Speed up the review by automating some parts through AI, in a way that we can consume some summary of that report that could be meaningful for the reviewer.
Resources
No idea about the resources yet, but we will make use of:
- HTML/JSON Report (text + screenshots)
- The Test Suite Status GithHub board (via API)
- The environment tested (via SSH)
- The test framework code (via files)
No Hackers yet
This project is part of:
Hack Week 24
Activity
Comments
-

-

2 months ago by oscar-barrios | Reply
I end up continuing this project on my free time, and I made some progress here: https://github.com/srbarrios/FailTale
Similar Projects
Flaky Tests AI Finder for Uyuni and MLM Test Suites by oscar-barrios
Description
Our current Grafana dashboards provide a great overview of test suite health, including a panel for "Top failed tests." However, identifying which of these failures are due to legitimate bugs versus intermittent "flaky tests" is a manual, time-consuming process. These flaky tests erode trust in our test suites and slow down development.
This project aims to build a simple but powerful Python script that automates flaky test detection. The script will directly query our Prometheus instance for the historical data of each failed test, using the jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age metric. It will then format this data and send it to the Gemini API with a carefully crafted prompt, asking it to identify which tests show a flaky pattern.
The final output will be a clean JSON list of the most probable flaky tests, which can then be used to populate a new "Top Flaky Tests" panel in our existing Grafana test suite dashboard.
Goals
By the end of Hack Week, we aim to have a single, working Python script that:
- Connects to Prometheus and executes a query to fetch detailed test failure history.
- Processes the raw data into a format suitable for the Gemini API.
- Successfully calls the Gemini API with the data and a clear prompt.
- Parses the AI's response to extract a simple list of flaky tests.
- Saves the list to a JSON file that can be displayed in Grafana.
- New panel in our Dashboard listing the Flaky tests
Resources
- Jenkins Prometheus Exporter: https://github.com/uyuni-project/jenkins-exporter/
- Data Source: Our internal Prometheus server.
- Key Metric:
jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age{jobname, buildid, suite, case, status, failedsince}. - Existing Query for Reference:
count by (suite) (max_over_time(jenkins_build_test_case_failure_age{status=~"FAILED|REGRESSION", jobname="$jobname"}[$__range])). - AI Model: The Google Gemini API.
- Example about how to interact with Gemini API: https://github.com/srbarrios/FailTale/
- Visualization: Our internal Grafana Dashboard.
- Internal IaC: https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/tree/master/srv/salt/monitoring
Outcome
- Jenkins Flaky Test Detector: https://github.com/srbarrios/jenkins-flaky-tests-detector and its container
- IaC on MLM Team: https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/tree/master/srv/salt/monitoring/jenkinsflakytestsdetector?reftype=heads, https://gitlab.suse.de/galaxy/infrastructure/-/blob/master/srv/salt/monitoring/grafana/dashboards/flaky-tests.json?ref_type=heads, and others.
- Grafana Dashboard: https://grafana.mgr.suse.de/d/flaky-tests/flaky-tests-detection @ @ text
Set Up an Ephemeral Uyuni Instance by mbussolotto
Description
To test, check, and verify the latest changes in the master branch, we want to easily set up an ephemeral environment.
Goals
- Create an ephemeral environment manually
Create an ephemeral environment automatically
Resources
https://github.com/uyuni-project/uyuni
https://www.uyuni-project.org/uyuni-docs/en/uyuni/index.html
Move Uyuni Test Framework from Selenium to Playwright + AI by oscar-barrios
Description
This project aims to migrate the existing Uyuni Test Framework from Selenium to Playwright. The move will improve the stability, speed, and maintainability of our end-to-end tests by leveraging Playwright's modern features. We'll be rewriting the current Selenium code in Ruby to Playwright code in TypeScript, which includes updating the test framework runner, step definitions, and configurations. This is also necessary because we're moving from Cucumber Ruby to CucumberJS.
If you're still curious about the AI in the title, it was just a way to grab your attention. Thanks for your understanding.
Nah, let's be honest ![]() AI helped a lot to vibe code a good part of the Ruby methods of the Test framework, moving them to Typescript, along with the migration from Capybara to Playwright. I've been using "Cline" as plugin for WebStorm IDE, using Gemini API behind it.
AI helped a lot to vibe code a good part of the Ruby methods of the Test framework, moving them to Typescript, along with the migration from Capybara to Playwright. I've been using "Cline" as plugin for WebStorm IDE, using Gemini API behind it.
Goals
- Migrate Core tests including Onboarding of clients
- Improve test reliabillity: Measure and confirm a significant reduction of flakiness.
- Implement a robust framework: Establish a well-structured and reusable Playwright test framework using the CucumberJS
Resources
- Existing Uyuni Test Framework (Cucumber Ruby + Capybara + Selenium)
- My Template for CucumberJS + Playwright in TypeScript
- Started Hackweek Project
Enable more features in mcp-server-uyuni by j_renner
Description
I would like to contribute to mcp-server-uyuni, the MCP server for Uyuni / Multi-Linux Manager) exposing additional features as tools. There is lots of relevant features to be found throughout the API, for example:
- System operations and infos
- System groups
- Maintenance windows
- Ansible
- Reporting
- ...
At the end of the week I managed to enable basic system group operations:
- List all system groups visible to the user
- Create new system groups
- List systems assigned to a group
- Add and remove systems from groups
Goals
- Set up test environment locally with the MCP server and client + a recent MLM server [DONE]
- Identify features and use cases offering a benefit with limited effort required for enablement [DONE]
- Create a PR to the repo [DONE]
Resources
Uyuni Health-check Grafana AI Troubleshooter by ygutierrez
Description
This project explores the feasibility of using the open-source Grafana LLM plugin to enhance the Uyuni Health-check tool with LLM capabilities. The idea is to integrate a chat-based "AI Troubleshooter" directly into existing dashboards, allowing users to ask natural-language questions about errors, anomalies, or performance issues.
Goals
- Investigate if and how the
grafana-llm-appplug-in can be used within the Uyuni Health-check tool. - Investigate if this plug-in can be used to query LLMs for troubleshooting scenarios.
- Evaluate support for local LLMs and external APIs through the plugin.
- Evaluate if and how the Uyuni MCP server could be integrated as another source of information.
Resources
Try out Neovim Plugins supporting AI Providers by enavarro_suse
Description
Experiment with several Neovim plugins that integrate AI model providers such as Gemini and Ollama.
Goals
Evaluate how these plugins enhance the development workflow, how they differ in capabilities, and how smoothly they integrate into Neovim for day-to-day coding tasks.
Resources
- Neovim 0.11.5
- AI-enabled Neovim plugins:
- avante.nvim: https://github.com/yetone/avante.nvim
- Gp.nvim: https://github.com/Robitx/gp.nvim
- parrot.nvim: https://github.com/frankroeder/parrot.nvim
- gemini.nvim: https://dotfyle.com/plugins/kiddos/gemini.nvim
- ...
- Accounts or API keys for AI model providers.
- Local model serving setup (e.g., Ollama)
- Test projects or codebases for practical evaluation:
- OBS: https://build.opensuse.org/
- OBS blog and landing page: https://openbuildservice.org/
- ...
Bugzilla goes AI - Phase 1 by nwalter
Description
This project, Bugzilla goes AI, aims to boost developer productivity by creating an autonomous AI bug agent during Hackweek. The primary goal is to reduce the time employees spend triaging bugs by integrating Ollama to summarize issues, recommend next steps, and push focused daily reports to a Web Interface.
Goals
To reduce employee time spent on Bugzilla by implementing an AI tool that triages and summarizes bug reports, providing actionable recommendations to the team via Web Interface.
Project Charter
Description
Project Achievements during Hackweek
In this file you can read about what we achieved during Hackweek.
AI-Powered Unit Test Automation for Agama by joseivanlopez
The Agama project is a multi-language Linux installer that leverages the distinct strengths of several key technologies:
- Rust: Used for the back-end services and the core HTTP API, providing performance and safety.
- TypeScript (React/PatternFly): Powers the modern web user interface (UI), ensuring a consistent and responsive user experience.
- Ruby: Integrates existing, robust YaST libraries (e.g.,
yast-storage-ng) to reuse established functionality.
The Problem: Testing Overhead
Developing and maintaining code across these three languages requires a significant, tedious effort in writing, reviewing, and updating unit tests for each component. This high cost of testing is a drain on developer resources and can slow down the project's evolution.
The Solution: AI-Driven Automation
This project aims to eliminate the manual overhead of unit testing by exploring and integrating AI-driven code generation tools. We will investigate how AI can:
- Automatically generate new unit tests as code is developed.
- Intelligently correct and update existing unit tests when the application code changes.
By automating this crucial but monotonous task, we can free developers to focus on feature implementation and significantly improve the speed and maintainability of the Agama codebase.
Goals
- Proof of Concept: Successfully integrate and demonstrate an authorized AI tool (e.g.,
gemini-cli) to automatically generate unit tests. - Workflow Integration: Define and document a new unit test automation workflow that seamlessly integrates the selected AI tool into the existing Agama development pipeline.
- Knowledge Sharing: Establish a set of best practices for using AI in code generation, sharing the learned expertise with the broader team.
Contribution & Resources
We are seeking contributors interested in AI-powered development and improving developer efficiency. Whether you have previous experience with code generation tools or are eager to learn, your participation is highly valuable.
If you want to dive deep into AI for software quality, please reach out and join the effort!
- Authorized AI Tools: Tools supported by SUSE (e.g.,
gemini-cli) - Focus Areas: Rust, TypeScript, and Ruby components within the Agama project.
Interesting Links
Exploring Modern AI Trends and Kubernetes-Based AI Infrastructure by jluo
Description
Build a solid understanding of the current landscape of Artificial Intelligence and how modern cloud-native technologies—especially Kubernetes—support AI workloads.
Goals
Use Gemini Learning Mode to guide the exploration, surface relevant concepts, and structure the learning journey:
- Gain insight into the latest AI trends, tools, and architectural concepts.
- Understand how Kubernetes and related cloud-native technologies are used in the AI ecosystem (model training, deployment, orchestration, MLOps).
Resources
Red Hat AI Topic Articles
- https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/ai
Kubeflow Documentation
- https://www.kubeflow.org/docs/
Q4 2025 CNCF Technology Landscape Radar report:
- https://www.cncf.io/announcements/2025/11/11/cncf-and-slashdata-report-finds-leading-ai-tools-gaining-adoption-in-cloud-native-ecosystems/
- https://www.cncf.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/cncfreporttechradar_111025a.pdf
Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol
- https://developers.googleblog.com/en/a2a-a-new-era-of-agent-interoperability/
MCP Server for SCC by digitaltomm
Description
Provide an MCP Server implementation for customers to access data on scc.suse.com via MCP protocol. The core benefit of this MCP interface is that it has direct (read) access to customer data in SCC, so the AI agent gets enhanced knowledge about individual customer data, like subscriptions, orders and registered systems.
Architecture
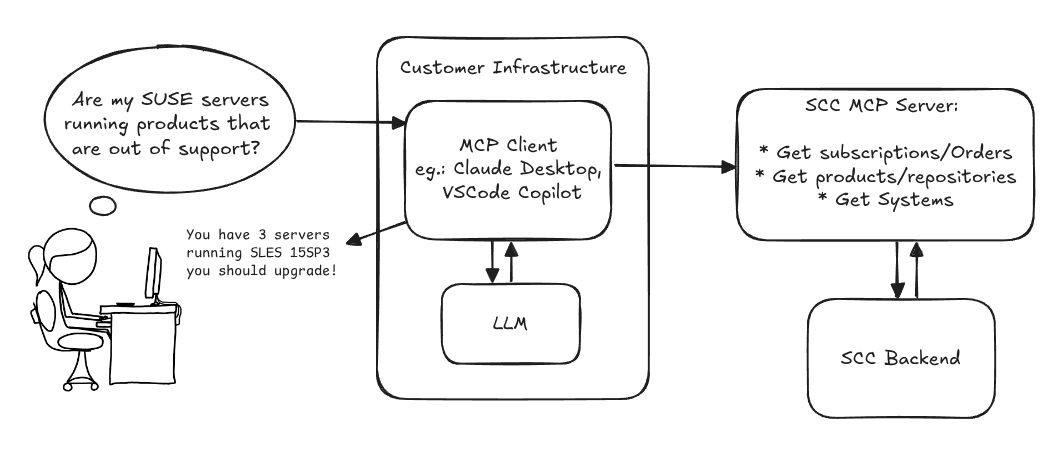
Goals
We want to demonstrate a proof of concept to connect to the SCC MCP server with any AI agent, for example gemini-cli or codex. Enabling the user to ask questions regarding their SCC inventory.
For this Hackweek, we target that users get proper responses to these example questions:
- Which of my currently active systems are running products that are out of support?
- Do I have ready to use registration codes for SLES?
- What are the latest 5 released patches for SLES 15 SP6? Output as a list with release date, patch name, affected package names and fixed CVEs.
- Which versions of kernel-default are available on SLES 15 SP6?
Technical Notes
Similar to the organization APIs, this can expose to customers data about their subscriptions, orders, systems and products. Authentication should be done by organization credentials, similar to what needs to be provided to RMT/MLM. Customers can connect to the SCC MCP server from their own MCP-compatible client and Large Language Model (LLM), so no third party is involved.
Milestones
[x] Basic MCP API setup MCP endpoints [x] Products / Repositories [x] Subscriptions / Orders [x] Systems [x] Packages [x] Document usage with Gemini CLI, Codex
Resources
Gemini CLI setup:
~/.gemini/settings.json:
openQA tests needles elaboration using AI image recognition by mdati
Description
In the openQA test framework, to identify the status of a target SUT image, a screenshots of GUI or CLI-terminal images,
the needles framework scans the many pictures in its repository, having associated a given set of tags (strings), selecting specific smaller parts of each available image. For the needles management actually we need to keep stored many screenshots, variants of GUI and CLI-terminal images, eachone accompanied by a dedicated set of data references (json).
A smarter framework, using image recognition based on AI or other image elaborations tools, nowadays widely available, could improve the matching process and hopefully reduce time and errors, during the images verification and detection process.
Goals
Main scope of this idea is to match a "graphical" image of the console or GUI status of a running openQA test, an image of a shell console or application-GUI screenshot, using less time and resources and with less errors in data preparation and use, than the actual openQA needles framework; that is:
- having a given SUT (system under test) GUI or CLI-terminal screenshot, with a local distribution of pixels or text commands related to a running test status,
- we want to identify a desired target, e.g. a screen image status or data/commands context,
- based on AI/ML-pretrained archives containing object or other proper elaboration tools,
- possibly able to identify also object not present in the archive, i.e. by means of AI/ML mechanisms.
- the matching result should be then adapted to continue working in the openQA test, likewise and in place of the same result that would have been produced by the original openQA needles framework.
- We expect an improvement of the matching-time(less time), reliability of the expected result(less error) and simplification of archive maintenance in adding/removing objects(smaller DB and less actions).
Hackweek POC:
Main steps
- Phase 1 - Plan
- study the available tools
- prepare a plan for the process to build
- Phase 2 - Implement
- write and build a draft application
- Phase 3 - Data
- prepare the data archive from a subset of needles
- initialize/pre-train the base archive
- select a screenshot from the subset, removing/changing some part
- Phase 4 - Test
- run the POC application
- expect the image type is identified in a good %.
Resources
First step of this project is quite identification of useful resources for the scope; some possibilities are:
- SUSE AI and other ML tools (i.e. Tensorflow)
- Tools able to manage images
- RPA test tools (like i.e. Robot framework)
- other.
Project references
- Repository: openqa-needles-AI-driven
Testing and adding GNU/Linux distributions on Uyuni by juliogonzalezgil
Join the Gitter channel! https://gitter.im/uyuni-project/hackweek
Uyuni is a configuration and infrastructure management tool that saves you time and headaches when you have to manage and update tens, hundreds or even thousands of machines. It also manages configuration, can run audits, build image containers, monitor and much more!
Currently there are a few distributions that are completely untested on Uyuni or SUSE Manager (AFAIK) or just not tested since a long time, and could be interesting knowing how hard would be working with them and, if possible, fix whatever is broken.
For newcomers, the easiest distributions are those based on DEB or RPM packages. Distributions with other package formats are doable, but will require adapting the Python and Java code to be able to sync and analyze such packages (and if salt does not support those packages, it will need changes as well). So if you want a distribution with other packages, make sure you are comfortable handling such changes.
No developer experience? No worries! We had non-developers contributors in the past, and we are ready to help as long as you are willing to learn. If you don't want to code at all, you can also help us preparing the documentation after someone else has the initial code ready, or you could also help with testing :-)
The idea is testing Salt (including bootstrapping with bootstrap script) and Salt-ssh clients
To consider that a distribution has basic support, we should cover at least (points 3-6 are to be tested for both salt minions and salt ssh minions):
- Reposync (this will require using spacewalk-common-channels and adding channels to the .ini file)
- Onboarding (salt minion from UI, salt minion from bootstrap scritp, and salt-ssh minion) (this will probably require adding OS to the bootstrap repository creator)
- Package management (install, remove, update...)
- Patching
- Applying any basic salt state (including a formula)
- Salt remote commands
- Bonus point: Java part for product identification, and monitoring enablement
- Bonus point: sumaform enablement (https://github.com/uyuni-project/sumaform)
- Bonus point: Documentation (https://github.com/uyuni-project/uyuni-docs)
- Bonus point: testsuite enablement (https://github.com/uyuni-project/uyuni/tree/master/testsuite)
If something is breaking: we can try to fix it, but the main idea is research how supported it is right now. Beyond that it's up to each project member how much to hack :-)
- If you don't have knowledge about some of the steps: ask the team
- If you still don't know what to do: switch to another distribution and keep testing.
This card is for EVERYONE, not just developers. Seriously! We had people from other teams helping that were not developers, and added support for Debian and new SUSE Linux Enterprise and openSUSE Leap versions :-)
In progress/done for Hack Week 25
Guide
We started writin a Guide: Adding a new client GNU Linux distribution to Uyuni at https://github.com/uyuni-project/uyuni/wiki/Guide:-Adding-a-new-client-GNU-Linux-distribution-to-Uyuni, to make things easier for everyone, specially those not too familiar wht Uyuni or not technical.
openSUSE Leap 16.0
The distribution will all love!
https://en.opensuse.org/openSUSE:Roadmap#DRAFTScheduleforLeap16.0
Curent Status We started last year, it's complete now for Hack Week 25! :-D
[W]Reposync (this will require using spacewalk-common-channels and adding channels to the .ini file) NOTE: Done, client tools for SLMicro6 are using as those for SLE16.0/openSUSE Leap 16.0 are not available yet[W]Onboarding (salt minion from UI, salt minion from bootstrap scritp, and salt-ssh minion) (this will probably require adding OS to the bootstrap repository creator)[W]Package management (install, remove, update...). Works, even reboot requirement detection
Multimachine on-prem test with opentofu, ansible and Robot Framework by apappas
Description
A long time ago I explored using the Robot Framework for testing. A big deficiency over our openQA setup is that bringing up and configuring the connection to a test machine is out of scope.
Nowadays we have a way¹ to deploy SUTs outside openqa, but we only use if for cloud tests in conjuction with openqa. Using knowledge gained from that project I am going to try to create a test scenario that replicates an openqa test but this time including the deployment and setup of the SUT.
Goals
Create a simple multimachine test scenario with the support server and SUT all created by the robot framework.
Resources
- https://github.com/SUSE/qe-sap-deployment
- terraform-libvirt-provider