Project Description
Uyuni recently made the switch from Javascript to Typescript. Alas, the team has a very mixed bag of experience with the technology and we could use a way to get everyone up to speed quickly.
One great way to learn new things is through games. There are numerous examples of learning-oriented games in the tech space already: Grid Garden, Flexbox Froggy etc. There don't seem to be any games aimed at learning Typescript, but we could make one!
Goal for this Hackweek
During Hackweek, the aim is to:
- ideate a set of game mechanics that can be used to teach Typescript in an engaging way
- develop a working prototype that demonstrates gameplay, ideally a few levels or comparable
The target audience will probably be people with some prior programming knowledge, but the smaller the resulting constraint, the better.
If the resulting prototype is good, the project can be followed up on after the Hackweek with proper polish, additional levels etc.
Resources
Examples of learning-oriented games: https://codepip.com/games/
Typescript docs: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/
Looking for hackers with the skills:
This project is part of:
Hack Week 20
Activity
Comments
-

almost 5 years ago by Etheryte | Reply
The result of the Hackweek is a working prototype that integrates Typescript validation with an editor and gameplay logic. Only had time to build one simple level, but it demonstrates all modules correctly working and how the gameplay works. See https://etheryte.github.io/the-typescript-game/ for a demo.
Similar Projects
Move Uyuni Test Framework from Selenium to Playwright + AI by oscar-barrios
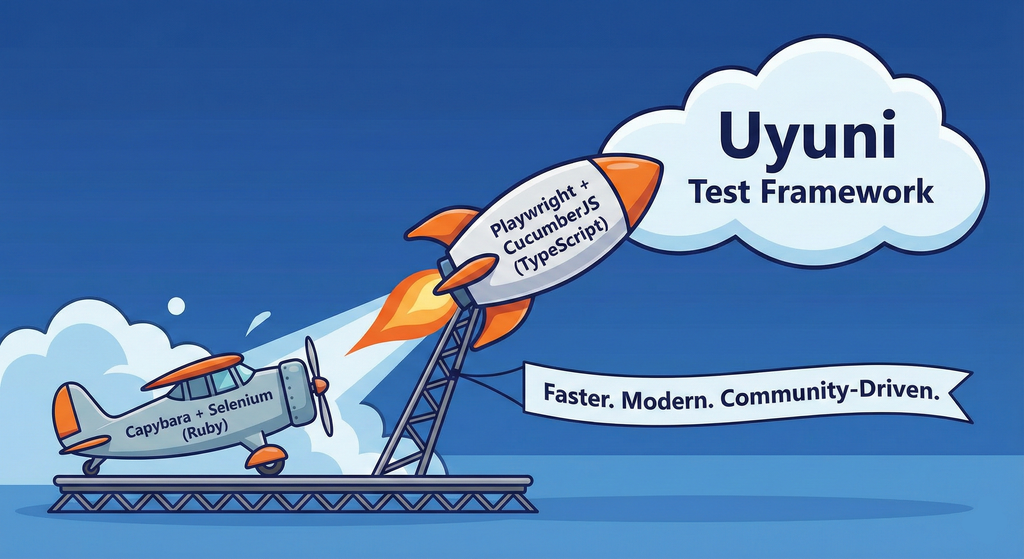
Description
This project aims to migrate the existing Uyuni Test Framework from Selenium to Playwright. The move will improve the stability, speed, and maintainability of our end-to-end tests by leveraging Playwright's modern features. We'll be rewriting the current Selenium code in Ruby to Playwright code in TypeScript, which includes updating the test framework runner, step definitions, and configurations. This is also necessary because we're moving from Cucumber Ruby to CucumberJS.
If you're still curious about the AI in the title, it was just a way to grab your attention. Thanks for your understanding.
Nah, let's be honest ![]() AI helped a lot to vibe code a good part of the Ruby methods of the Test framework, moving them to Typescript, along with the migration from Capybara to Playwright. I've been using "Cline" as plugin for WebStorm IDE, using Gemini API behind it.
AI helped a lot to vibe code a good part of the Ruby methods of the Test framework, moving them to Typescript, along with the migration from Capybara to Playwright. I've been using "Cline" as plugin for WebStorm IDE, using Gemini API behind it.
Goals
- Migrate Core tests including Onboarding of clients
- Improve test reliabillity: Measure and confirm a significant reduction of flakiness.
- Implement a robust framework: Establish a well-structured and reusable Playwright test framework using the CucumberJS
Resources
- Existing Uyuni Test Framework (Cucumber Ruby + Capybara + Selenium)
- My Template for CucumberJS + Playwright in TypeScript
- Started Hackweek Project
AI-Powered Unit Test Automation for Agama by joseivanlopez
The Agama project is a multi-language Linux installer that leverages the distinct strengths of several key technologies:
- Rust: Used for the back-end services and the core HTTP API, providing performance and safety.
- TypeScript (React/PatternFly): Powers the modern web user interface (UI), ensuring a consistent and responsive user experience.
- Ruby: Integrates existing, robust YaST libraries (e.g.,
yast-storage-ng) to reuse established functionality.
The Problem: Testing Overhead
Developing and maintaining code across these three languages requires a significant, tedious effort in writing, reviewing, and updating unit tests for each component. This high cost of testing is a drain on developer resources and can slow down the project's evolution.
The Solution: AI-Driven Automation
This project aims to eliminate the manual overhead of unit testing by exploring and integrating AI-driven code generation tools. We will investigate how AI can:
- Automatically generate new unit tests as code is developed.
- Intelligently correct and update existing unit tests when the application code changes.
By automating this crucial but monotonous task, we can free developers to focus on feature implementation and significantly improve the speed and maintainability of the Agama codebase.
Goals
- Proof of Concept: Successfully integrate and demonstrate an authorized AI tool (e.g.,
gemini-cli) to automatically generate unit tests. - Workflow Integration: Define and document a new unit test automation workflow that seamlessly integrates the selected AI tool into the existing Agama development pipeline.
- Knowledge Sharing: Establish a set of best practices for using AI in code generation, sharing the learned expertise with the broader team.
Contribution & Resources
We are seeking contributors interested in AI-powered development and improving developer efficiency. Whether you have previous experience with code generation tools or are eager to learn, your participation is highly valuable.
If you want to dive deep into AI for software quality, please reach out and join the effort!
- Authorized AI Tools: Tools supported by SUSE (e.g.,
gemini-cli) - Focus Areas: Rust, TypeScript, and Ruby components within the Agama project.
Interesting Links
Kudos aka openSUSE Recognition Platform by lkocman
Description
Relevant blog post at news-o-o
I started the Kudos application shortly after Leap 16.0 to create a simple, friendly way to recognize people for their work and contributions to openSUSE. There’s so much more to our community than just submitting requests in OBS or gitea we have translations (not only in Weblate), wiki edits, forum and social media moderation, infrastructure maintenance, booth participation, talks, manual testing, openQA test suites, and more!
Goals
Kudos under github.com/openSUSE/kudos with build previews aka netlify
Have a kudos.opensuse.org instance running in production
Build an easy-to-contribute recognition platform for the openSUSE community a place where everyone can send and receive appreciation for their work, across all areas of contribution.
In the future, we could even explore reward options such as vouchers for t-shirts or other community swag, small tokens of appreciation to make recognition more tangible.
Resources
(Do not create new badge requests during hackweek, unless you'll make the badge during hackweek)
- Source code: openSUSE/kudos
- Badges: openSUSE/kudos-badges
- Issue tracker: kudos/issues
Uyuni read-only replica by cbosdonnat
Description
For now, there is no possible HA setup for Uyuni. The idea is to explore setting up a read-only shadow instance of an Uyuni and make it as useful as possible.
Possible things to look at:
- live sync of the database, probably using the WAL. Some of the tables may have to be skipped or some features disabled on the RO instance (taskomatic, PXT sessions…)
- Can we use a load balancer that routes read-only queries to either instance and the other to the RW one? For example, packages or PXE data can be served by both, the API GET requests too. The rest would be RW.
Goals
- Prepare a document explaining how to do it.
- PR with the needed code changes to support it
Uyuni Health-check Grafana AI Troubleshooter by ygutierrez
Description
This project explores the feasibility of using the open-source Grafana LLM plugin to enhance the Uyuni Health-check tool with LLM capabilities. The idea is to integrate a chat-based "AI Troubleshooter" directly into existing dashboards, allowing users to ask natural-language questions about errors, anomalies, or performance issues.
Goals
- Investigate if and how the
grafana-llm-appplug-in can be used within the Uyuni Health-check tool. - Investigate if this plug-in can be used to query LLMs for troubleshooting scenarios.
- Evaluate support for local LLMs and external APIs through the plugin.
- Evaluate if and how the Uyuni MCP server could be integrated as another source of information.
Resources
Enable more features in mcp-server-uyuni by j_renner
Description
I would like to contribute to mcp-server-uyuni, the MCP server for Uyuni / Multi-Linux Manager) exposing additional features as tools. There is lots of relevant features to be found throughout the API, for example:
- System operations and infos
- System groups
- Maintenance windows
- Ansible
- Reporting
- ...
At the end of the week I managed to enable basic system group operations:
- List all system groups visible to the user
- Create new system groups
- List systems assigned to a group
- Add and remove systems from groups
Goals
- Set up test environment locally with the MCP server and client + a recent MLM server [DONE]
- Identify features and use cases offering a benefit with limited effort required for enablement [DONE]
- Create a PR to the repo [DONE]
Resources
mgr-ansible-ssh - Intelligent, Lightweight CLI for Distributed Remote Execution by deve5h
Description
By the end of Hack Week, the target will be to deliver a minimal functional version 1 (MVP) of a custom command-line tool named mgr-ansible-ssh (a unified wrapper for BOTH ad-hoc shell & playbooks) that allows operators to:
- Execute arbitrary shell commands on thousand of remote machines simultaneously using Ansible Runner with artifacts saved locally.
- Pass runtime options such as inventory file, remote command string/ playbook execution, parallel forks, limits, dry-run mode, or no-std-ansible-output.
- Leverage existing SSH trust relationships without additional setup.
- Provide a clean, intuitive CLI interface with --help for ease of use. It should provide consistent UX & CI-friendly interface.
- Establish a foundation that can later be extended with advanced features such as logging, grouping, interactive shell mode, safe-command checks, and parallel execution tuning.
The MVP should enable day-to-day operations to efficiently target thousands of machines with a single, consistent interface.
Goals
Primary Goals (MVP):
Build a functional CLI tool (mgr-ansible-ssh) capable of executing shell commands on multiple remote hosts using Ansible Runner. Test the tool across a large distributed environment (1000+ machines) to validate its performance and reliability.
Looking forward to significantly reducing the zypper deployment time across all 351 RMT VM servers in our MLM cluster by eliminating the dependency on the taskomatic service, bringing execution down to a fraction of the current duration. The tool should also support multiple runtime flags, such as:
mgr-ansible-ssh: Remote command execution wrapper using Ansible Runner
Usage: mgr-ansible-ssh [--help] [--version] [--inventory INVENTORY]
[--run RUN] [--playbook PLAYBOOK] [--limit LIMIT]
[--forks FORKS] [--dry-run] [--no-ansible-output]
Required Arguments
--inventory, -i Path to Ansible inventory file to use
Any One of the Arguments Is Required
--run, -r Execute the specified shell command on target hosts
--playbook, -p Execute the specified Ansible playbook on target hosts
Optional Arguments
--help, -h Show the help message and exit
--version, -v Show the version and exit
--limit, -l Limit execution to specific hosts or groups
--forks, -f Number of parallel Ansible forks
--dry-run Run in Ansible check mode (requires -p or --playbook)
--no-ansible-output Suppress Ansible stdout output
Secondary/Stretched Goals (if time permits):
- Add pretty output formatting (success/failure summary per host).
- Implement basic logging of executed commands and results.
- Introduce safety checks for risky commands (shutdown, rm -rf, etc.).
- Package the tool so it can be installed with pip or stored internally.
Resources
Collaboration is welcome from anyone interested in CLI tooling, automation, or distributed systems. Skills that would be particularly valuable include:
- Python especially around CLI dev (argparse, click, rich)
Uyuni Saltboot rework by oholecek
Description
When Uyuni switched over to the containerized proxies we had to abandon salt based saltboot infrastructure we had before. Uyuni already had integration with a Cobbler provisioning server and saltboot infra was re-implemented on top of this Cobbler integration.
What was not obvious from the start was that Cobbler, having all it's features, woefully slow when dealing with saltboot size environments. We did some improvements in performance, introduced transactions, and generally tried to make this setup usable. However the underlying slowness remained.
Goals
This project is not something trying to invent new things, it is just finally implementing saltboot infrastructure directly with the Uyuni server core.
Instead of generating grub and pxelinux configurations by Cobbler for all thousands of systems and branches, we will provide a GET access point to retrieve grub or pxelinux file during the boot:
/saltboot/group/grub/$fqdn and similar for systems /saltboot/system/grub/$mac
Next we adapt our tftpd translator to query these points when asked for default or mac based config.
Lastly similar thing needs to be done on our apache server when HTTP UEFI boot is used.
Resources