Project Description
As Generative AI is everywhere around, we want to research its possibilities, how it can help SUSE, its employees and customers. The initial idea is to build solution based on Amazon Bedrock, to integrate our asset management tools and to be able to query the data and get the answers using human-like text.
Goal for this Hackweek
Populate all available data from SUSE Asset management tools (integrate with Jira Insight, Racktables, CloudAccountMetadata, Cloudquery,...) into the foundational model (e.g. Amazon Titan). Then make the foundational model able to answer simple queries like how many VMs are running in PRG2 or who are the owners of EC2 instances of t2 family.
This is only one of the ideas for GenAI we have. Most probably we will try to cover also another scenarios. If you are interested or you have any other idea how to utilize foundational models, let us know.
Resources
- https://aws.amazon.com/bedrock/
- https://github.com/aws-samples/amazon-bedrock-workshop
- Specifically for this hackweek was created AWS Account
ITPE Gen IA Dev (047178302800)accessible via Okta - whoever is interested, please contact me (or raise JiraSD ticket to be added to CLZ: ITPE Gen IA Dev) and use region us-west-2 (don't mind the typo, heh). - we have booked AWS engineer, expert on Bedrock on 2023-11-06 (1-5pm CET, meeting link) - anyone interested can join
Keywords
AI, GenAI, GenerativeAI, AWS, Amazon Bedrock, Amazon Titan, Asset Management
Looking for hackers with the skills:
ai genai generativeai aws amazontitan assetmanagement bedrock
This project is part of:
Hack Week 23
Activity
Comments
-

-

about 2 years ago by mpiala | Reply
and recording of the workshop: Gen AI with AWS-20231106_130308-Meeting Recording.mp4
-

about 2 years ago by vadim | Reply
@mpiala now that we all have some hands on experience with bedrock I suggest that you create a few workgroup sessions for tomorrow / Thursday and invite contributors. I'd split the work into three workstreams:
- Create infrastructure / pipelines that would deploy the project in a reproducible way
- Create a crawler that would parse the source data and populate a vector database (probably a lambda that can be triggered by cloudwatch)
- Create a backend that would query the vector DB, run inference and integrate with slack
For vector DB we can use something off the shelf, like pinecone.io - later we can move it to Athena or something else.
Similar Projects
Song Search with CLAP by gcolangiuli
Description
Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining (CLAP) is an open-source library that enables the training of a neural network on both Audio and Text descriptions, making it possible to search for Audio using a Text input. Several pre-trained models for song search are already available on huggingface

Goals
Evaluate how CLAP can be used for song searching and determine which types of queries yield the best results by developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in Python. Based on the results of this MVP, future steps could include:
- Music Tagging;
- Free text search;
- Integration with an LLM (for example, with MCP or the OpenAI API) for music suggestions based on your own library.
The code for this project will be entirely written using AI to better explore and demonstrate AI capabilities.
Result
In this MVP we implemented:
- Async Song Analysis with Clap model
- Free Text Search of the songs
- Similar song search based on vector representation
- Containerised version with web interface
We also documented what went well and what can be improved in the use of AI.
You can have a look at the result here:
Future implementation can be related to performance improvement and stability of the analysis.
References
- CLAP: The main model being researched;
- huggingface: Pre-trained models for CLAP;
- Free Music Archive: Creative Commons songs that can be used for testing;
Backporting patches using LLM by jankara
Description
Backporting Linux kernel fixes (either for CVE issues or as part of general git-fixes workflow) is boring and mostly mechanical work (dealing with changes in context, renamed variables, new helper functions etc.). The idea of this project is to explore usage of LLM for backporting Linux kernel commits to SUSE kernels using LLM.
Goals
- Create safe environment allowing LLM to run and backport patches without exposing the whole filesystem to it (for privacy and security reasons).
- Write prompt that will guide LLM through the backporting process. Fine tune it based on experimental results.
- Explore success rate of LLMs when backporting various patches.
Resources
- Docker
- Gemini CLI
Repository
Current version of the container with some instructions for use are at: https://gitlab.suse.de/jankara/gemini-cli-backporter
Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition by mackenzie.techdocs

Description
Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition is an AI-powered documentation navigator that makes finding information across SUSE, Rancher, K3s, and RKE2 documentation effortless. Built as a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, it enables semantic search, intelligent Q&A, and documentation summarization using 100% open-source AI models (no API keys required!). The project also allows you to bring your own keys from Anthropic and Open AI for parallel processing.
Goals
- [ X ] Build functional MCP server with documentation tools
- [ X ] Implement semantic search with vector embeddings
- [ X ] Create user-friendly web interface
- [ X ] Optimize indexing performance (parallel processing)
- [ X ] Add SUSE branding and polish UX
- [ X ] Stretch Goal: Add more documentation sources
- [ X ] Stretch Goal: Implement document change detection for auto-updates
Coming Soon!
- Community Feedback: Test with real users and gather improvement suggestions
Resources
- Repository: Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition GitHub
- UI Demo: Live UI Demo of Docs Navigator MCP: SUSE Edition
MCP Server for SCC by digitaltomm
Description
Provide an MCP Server implementation for customers to access data on scc.suse.com via MCP protocol. The core benefit of this MCP interface is that it has direct (read) access to customer data in SCC, so the AI agent gets enhanced knowledge about individual customer data, like subscriptions, orders and registered systems.
Architecture
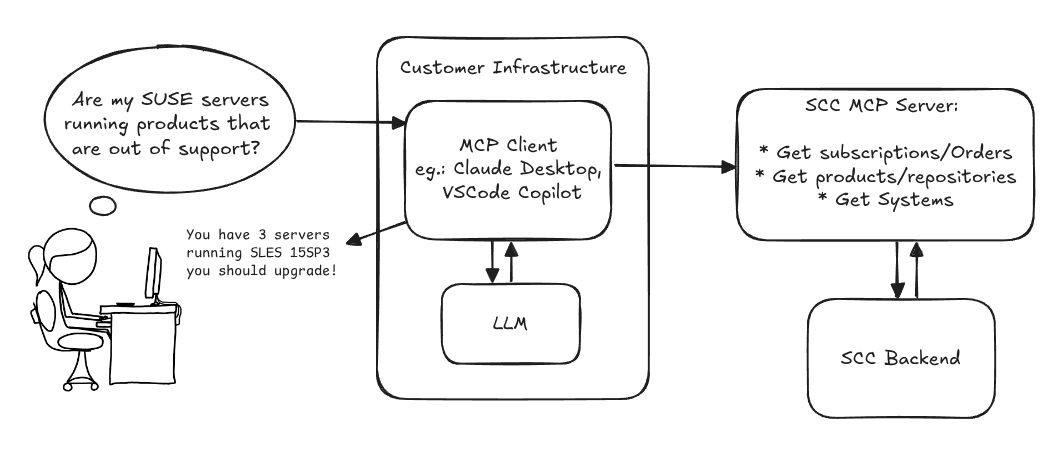
Goals
We want to demonstrate a proof of concept to connect to the SCC MCP server with any AI agent, for example gemini-cli or codex. Enabling the user to ask questions regarding their SCC inventory.
For this Hackweek, we target that users get proper responses to these example questions:
- Which of my currently active systems are running products that are out of support?
- Do I have ready to use registration codes for SLES?
- What are the latest 5 released patches for SLES 15 SP6? Output as a list with release date, patch name, affected package names and fixed CVEs.
- Which versions of kernel-default are available on SLES 15 SP6?
Technical Notes
Similar to the organization APIs, this can expose to customers data about their subscriptions, orders, systems and products. Authentication should be done by organization credentials, similar to what needs to be provided to RMT/MLM. Customers can connect to the SCC MCP server from their own MCP-compatible client and Large Language Model (LLM), so no third party is involved.
Milestones
[x] Basic MCP API setup MCP endpoints [x] Products / Repositories [x] Subscriptions / Orders [x] Systems [x] Packages [x] Document usage with Gemini CLI, Codex
Resources
Gemini CLI setup:
~/.gemini/settings.json:
Extended private brain - RAG my own scripts and data into offline LLM AI by tjyrinki_suse
Description
For purely studying purposes, I'd like to find out if I could teach an LLM some of my own accumulated knowledge, to use it as a sort of extended brain.
I might use qwen3-coder or something similar as a starting point.
Everything would be done 100% offline without network available to the container, since I prefer to see when network is needed, and make it so it's never needed (other than initial downloads).
Goals
- Learn something about RAG, LLM, AI.
- Find out if everything works offline as intended.
- As an end result have a new way to access my own existing know-how, but so that I can query the wisdom in them.
- Be flexible to pivot in any direction, as long as there are new things learned.
Resources
To be found on the fly.
Timeline
Day 1 (of 4)
- Tried out a RAG demo, expanded on feeding it my own data
- Experimented with qwen3-coder to add a persistent chat functionality, and keeping vectors in a pickle file
- Optimizations to keep everything within context window
- Learn and add a bit of PyTest
Day 2
- More experimenting and more data
- Study ChromaDB
- Add a Web UI that works from another computer even though the container sees network is down
Day 3
- The above RAG is working well enough for demonstration purposes.
- Pivot to trying out OpenCode, configuring local Ollama qwen3-coder there, to analyze the RAG demo.
- Figured out how to configure Ollama template to be usable under OpenCode. OpenCode locally is super slow to just running qwen3-coder alone.
Day 4 (final day)
- Battle with OpenCode that was both slow and kept on piling up broken things.
- Call it success as after all the agentic AI was working locally.
- Clean up the mess left behind a bit.
Blog Post
Summarized the findings at blog post.
GenAI-Powered Systemic Bug Evaluation and Management Assistant by rtsvetkov
Motivation
What is the decision critical question which one can ask on a bug? How this question affects the decision on a bug and why?
Let's make GenAI look on the bug from the systemic point and evaluate what we don't know. Which piece of information is missing to take a decision?
Description
To build a tool that takes a raw bug report (including error messages and context) and uses a large language model (LLM) to generate a series of structured, Socratic-style or Systemic questions designed to guide a the integration and development toward the root cause, rather than just providing a direct, potentially incorrect fix.
Goals
Set up a Python environment
Set the environment and get a Gemini API key. 2. Collect 5-10 realistic bug reports (from open-source projects, personal projects, or public forums like Stack Overflow—include the error message and the initial context).
Build the Dialogue Loop
- Write a basic Python script using the Gemini API.
- Implement a simple conversational loop: User Input (Bug) -> AI Output (Question) -> User Input (Answer to AI's question) -> AI Output (Next Question). Code Implementation
Socratic/Systemic Strategy Implementation
- Refine the logic to ensure the questions follow a Socratic and Systemic path (e.g., from symptom-> context -> assumptions -> -> critical parts -> ).
- Implement Function Calling (an advanced feature of the Gemini API) to suggest specific actions to the user, like "Run a ping test" or "Check the database logs."
- Implement Bugzillla call to collect the
- Implement Questioning Framework as LLVM pre-conditioning
- Define set of instructions
- Assemble the Tool
Resources
What are Systemic Questions?
Systemic questions explore the relationships, patterns, and interactions within a system rather than focusing on isolated elements.
In IT, they help uncover hidden dependencies, feedback loops, assumptions, and side-effects during debugging or architecture analysis.
Gitlab Project
gitlab.suse.de/sle-prjmgr/BugDecisionCritical_Question
SUSE Observability MCP server by drutigliano
Description
The idea is to implement the SUSE Observability Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server as a specialized, middle-tier API designed to translate the complex, high-cardinality observability data from StackState (topology, metrics, and events) into highly structured, contextually rich, and LLM-ready snippets.
This MCP Server abstract the StackState APIs. Its primary function is to serve as a Tool/Function Calling target for AI agents. When an AI receives an alert or a user query (e.g., "What caused the outage?"), the AI calls an MCP Server endpoint. The server then fetches the relevant operational facts, summarizes them, normalizes technical identifiers (like URNs and raw metric names) into natural language concepts, and returns a concise JSON or YAML payload. This payload is then injected directly into the LLM's prompt, ensuring the final diagnosis or action is grounded in real-time, accurate SUSE Observability data, effectively minimizing hallucinations.
Goals
- Grounding AI Responses: Ensure that all AI diagnoses, root cause analyses, and action recommendations are strictly based on verifiable, real-time data retrieved from the SUSE Observability StackState platform.
- Simplifying Data Access: Abstract the complexity of StackState's native APIs (e.g., Time Travel, 4T Data Model) into simple, semantic functions that can be easily invoked by LLM tool-calling mechanisms.
- Data Normalization: Convert complex, technical identifiers (like component URNs, raw metric names, and proprietary health states) into standardized, natural language terms that an LLM can easily reason over.
- Enabling Automated Remediation: Define clear, action-oriented MCP endpoints (e.g., execute_runbook) that allow the AI agent to initiate automated operational workflows (e.g., restarts, scaling) after a diagnosis, closing the loop on observability.
Hackweek STEP
- Create a functional MCP endpoint exposing one (or more) tool(s) to answer queries like "What is the health of service X?") by fetching, normalizing, and returning live StackState data in an LLM-ready format.
Scope
- Implement read-only MCP server that can:
- Connect to a live SUSE Observability instance and authenticate (with API token)
- Use tools to fetch data for a specific component URN (e.g., current health state, metrics, possibly topology neighbors, ...).
- Normalize response fields (e.g., URN to "Service Name," health state DEVIATING to "Unhealthy", raw metrics).
- Return the data as a structured JSON payload compliant with the MCP specification.
Deliverables
- MCP Server v0.1 A running Golang MCP server with at least one tool.
- A README.md and a test script (e.g., curl commands or a simple notebook) showing how an AI agent would call the endpoint and the resulting JSON payload.
Outcome A functional and testable API endpoint that proves the core concept: translating complex StackState data into a simple, LLM-ready format. This provides the foundation for developing AI-driven diagnostics and automated remediation.
Resources
- https://www.honeycomb.io/blog/its-the-end-of-observability-as-we-know-it-and-i-feel-fine
- https://www.datadoghq.com/blog/datadog-remote-mcp-server
- https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/2025-06-18/index
- https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/develop/build-server
Basic implementation
- https://github.com/drutigliano19/suse-observability-mcp-server
Results
Successfully developed and delivered a fully functional SUSE Observability MCP Server that bridges language models with SUSE Observability's operational data. This project demonstrates how AI agents can perform intelligent troubleshooting and root cause analysis using structured access to real-time infrastructure data.
Example execution
Create a Cloud-Native policy engine with notifying capabilities to optimize resource usage by gbazzotti
Description
The goal of this project is to begin the initial phase of development of an all-in-one Cloud-Native Policy Engine that notifies resource owners when their resources infringe predetermined policies. This was inspired by a current issue in the CES-SRE Team where other solutions seemed to not exactly correspond to the needs of the specific workloads running on the Public Cloud Team space.
The initial architecture can be checked out on the Repository listed under Resources.
Among the features that will differ this project from other monitoring/notification systems:
- Pre-defined sensible policies written at the software-level, avoiding a learning curve by requiring users to write their own policies
- All-in-one functionality: logging, mailing and all other actions are not required to install any additional plugins/packages
- Easy account management, being able to parse all required configuration by a single JSON file
- Eliminate integrations by not requiring metrics to go through a data-agreggator
Goals
- Create a minimal working prototype following the workflow specified on the documentation
- Provide instructions on installation/usage
- Work on email notifying capabilities
Resources